
How is cosine calculated?
Answer
547.2k+ views
Hint: Cosine is the angle which is defined as the ratio of the side which is adjacent to the angle $ \theta $ to the hypotenuse (which is the longest side) in the right angled triangle.
Complete answer:
Consider a right-angled triangle ABC, right-angled at B. Then the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle is the longest side, that is, the side AC. The adjacent side, called the base of the right angles triangle, is between the angle in question and the right angle, that is, the side BC is the base. The side opposite to the hypotenuse AC, which is opposite to the angle in question and perpendicular to the base is called the perpendicular, that is AB.
Now, in any right angled triangle, for angle C
\[\sin C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
$
\cos C = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}} \\
\tan C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}} \;
$
So in shorthand notation, it can be written as
$
\sin = \dfrac{o}{h} \\
\cos = \dfrac{a}{h} \\
\tan = \dfrac{o}{a} \;
$
Where,
o represents the side opposite to the angle in question.
a represents the adjacent side which is between the angle in question and the right angle.
h represents the hypotenuse or the longest side of the triangle.
It can be remembered as : soh cah toa
For Example- Find the value of $ \cos C $ in the figure given below. Given $ AB = 3,BC = 4,AC = 5 $
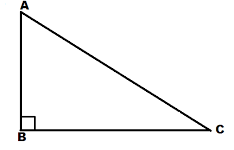
Here,
AC is the hypotenuse of the given right angled triangle and is equal to 5 units.
BC is the adjacent side or the base of the given right angled triangle and is equal to 4 units.
AB is the perpendicular of the given right angled triangle and is equal to 3 units.
Hence,
$ $ $ \cos C = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}} $
$ \Rightarrow \cos C = \dfrac{4}{5} $
Note: Trigonometric ratios in trigonometry are derived from the three sides if a right angled triangle basically the hypotenuse, the base (adjacent side) and the perpendicular (opposite side) which are widely used as trigonometric identities and trigonometric formulas in all sciences related to geometry, mathematics and many others.
Complete answer:
Consider a right-angled triangle ABC, right-angled at B. Then the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle is the longest side, that is, the side AC. The adjacent side, called the base of the right angles triangle, is between the angle in question and the right angle, that is, the side BC is the base. The side opposite to the hypotenuse AC, which is opposite to the angle in question and perpendicular to the base is called the perpendicular, that is AB.
Now, in any right angled triangle, for angle C
\[\sin C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
$
\cos C = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}} \\
\tan C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}} \;
$
So in shorthand notation, it can be written as
$
\sin = \dfrac{o}{h} \\
\cos = \dfrac{a}{h} \\
\tan = \dfrac{o}{a} \;
$
Where,
o represents the side opposite to the angle in question.
a represents the adjacent side which is between the angle in question and the right angle.
h represents the hypotenuse or the longest side of the triangle.
It can be remembered as : soh cah toa
For Example- Find the value of $ \cos C $ in the figure given below. Given $ AB = 3,BC = 4,AC = 5 $

Here,
AC is the hypotenuse of the given right angled triangle and is equal to 5 units.
BC is the adjacent side or the base of the given right angled triangle and is equal to 4 units.
AB is the perpendicular of the given right angled triangle and is equal to 3 units.
Hence,
$ $ $ \cos C = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}} $
$ \Rightarrow \cos C = \dfrac{4}{5} $
Note: Trigonometric ratios in trigonometry are derived from the three sides if a right angled triangle basically the hypotenuse, the base (adjacent side) and the perpendicular (opposite side) which are widely used as trigonometric identities and trigonometric formulas in all sciences related to geometry, mathematics and many others.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




