
How do you solve \[y={{x}^{2}}+3\]?
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: For solving this problem let us consider the given problem as equation (1). Now we have to compare the given equation with the parent equation and then we have to find three points as we know one of the vertices (0, 0) and we have to find another two points by substituting x values then we have to plot a graph.
Complete step-by-step solution:
For the given problem we are given to solve\[y={{x}^{2}}+3\].
To solve the given equation let us consider the given equation as equation (1).
\[y={{x}^{2}}+3........\left( 1 \right)\]
Let us consider the parent graph\[y={{x}^{2}}\]. Which has vertex at origin and this is of general shape ‘U’ and the bottom of the curved path is vertex which is origin.
Now let us consider the parent graph as reference, for that let us consider it as equation (2).
Let us consider the parent graph as equation (2).
\[y={{x}^{2}}..........\left( 2 \right)\]
By comparing equation (1) with equation (2), we can say that it was changed by a constant ‘3’.
Therefore, if we add 3 we are effectively 'lifting' the whole thing up by 3. So now the vertex is still on the y-axis but at the point \[\left( 0,3 \right)\] instead of \[\left( 0,0 \right)\].
Let us add two more points to get the graph.
Substitute x=3 in equation (1).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y={{3}^{2}}+3 \\
& \Rightarrow y=12 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the ordered pair is \[\left( 3,12 \right)\].
Substitute x=-3 in equation (1).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=-{{3}^{2}}+3 \\
& \Rightarrow y=12 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the ordered pair is \[\left( -3,12 \right)\].
Hence let us plot with help of vertex and two points.
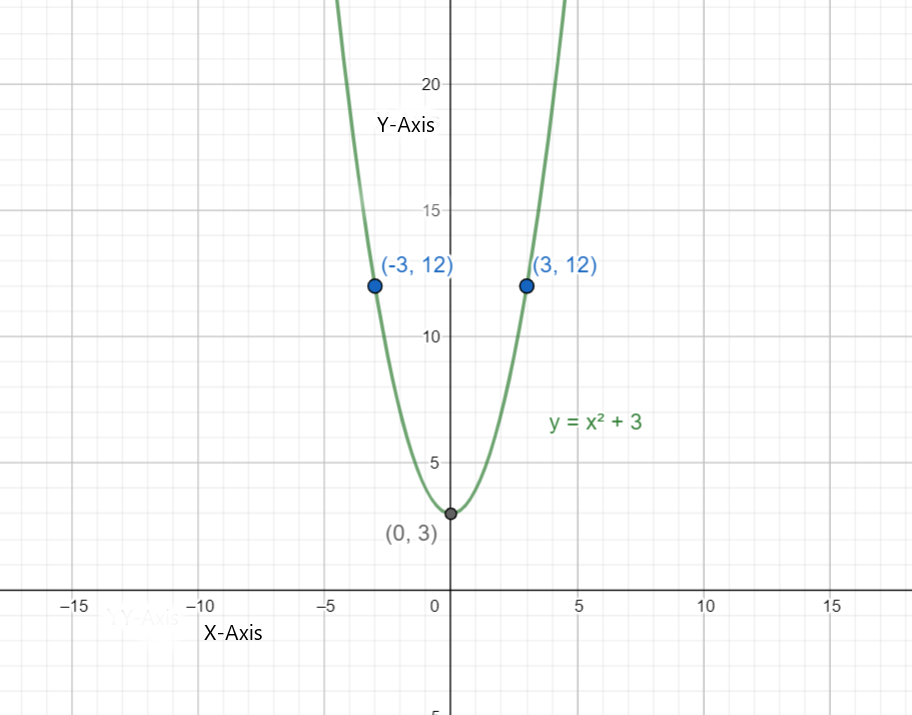
Note: We have to note a point that if the equation is like \[y={{x}^{2}}\] then the graph is like ‘U’ shaped graph and if equation is like \[x={{y}^{2}}\] then the graph is like reversed ‘U’. If we add any positive constant to the equation \[y={{x}^{2}}\] then the graph will be 'lifting' the whole thing up by the constant.
Complete step-by-step solution:
For the given problem we are given to solve\[y={{x}^{2}}+3\].
To solve the given equation let us consider the given equation as equation (1).
\[y={{x}^{2}}+3........\left( 1 \right)\]
Let us consider the parent graph\[y={{x}^{2}}\]. Which has vertex at origin and this is of general shape ‘U’ and the bottom of the curved path is vertex which is origin.
Now let us consider the parent graph as reference, for that let us consider it as equation (2).
Let us consider the parent graph as equation (2).
\[y={{x}^{2}}..........\left( 2 \right)\]
By comparing equation (1) with equation (2), we can say that it was changed by a constant ‘3’.
Therefore, if we add 3 we are effectively 'lifting' the whole thing up by 3. So now the vertex is still on the y-axis but at the point \[\left( 0,3 \right)\] instead of \[\left( 0,0 \right)\].
Let us add two more points to get the graph.
Substitute x=3 in equation (1).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y={{3}^{2}}+3 \\
& \Rightarrow y=12 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the ordered pair is \[\left( 3,12 \right)\].
Substitute x=-3 in equation (1).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=-{{3}^{2}}+3 \\
& \Rightarrow y=12 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the ordered pair is \[\left( -3,12 \right)\].
Hence let us plot with help of vertex and two points.

Note: We have to note a point that if the equation is like \[y={{x}^{2}}\] then the graph is like ‘U’ shaped graph and if equation is like \[x={{y}^{2}}\] then the graph is like reversed ‘U’. If we add any positive constant to the equation \[y={{x}^{2}}\] then the graph will be 'lifting' the whole thing up by the constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




