
How do you solve \[\tan x = 0\] \[?\]
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:We need to know the trigonometric table values and the basic definition \[\tan \theta \] .
To solve the given problem we need to find the values of \[\theta \] . Also, we need to know the process of calculating the value of \[\tan \theta \] the scientific calculator. We need to know the degree value \[\pi \] . Also, we need to know the relation between \[\sin \theta ,\cos \theta ,\] and \[\tan\theta \] .
Complete step by step solution:
The given question is shown below,
\[\tan x = 0\]
We need to find the value \[\theta \] from the above equation. Before that, we need to know the basic definition of \[\tan \theta \] .
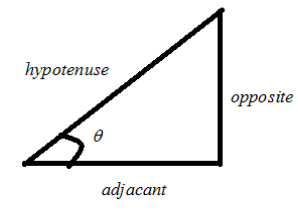
The above figure represents a triangle marked with the opposite side, adjacent side, and hypotenuse side according to the position of \[\theta \] .
The above figure is used to represent the definition of \[\sin \theta ,\cos \theta ,\] and \[\tan \theta \] . Let’s see the definitions of \[\sin \theta ,\cos\theta ,\] and \[\tan \theta \] ,
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\]
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{adjacant}}{{hypotenuse}}\]
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacant}}\]
From the above three equations, we can define the \[\tan \theta \] as follows,
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}\] \[ \to \left( A \right)\]
We need to find the value of \[\tan x = 0\] . So, we get
\[x = \arctan \left( 0 \right)\]
We know that,
\[\sin \left( 0 \right) = 0\]
\[0 = \arcsin \left( 0 \right)\]
\[
\sin \left( \pi \right) = 0 \\
\pi = \arcsin \left( 0 \right) \\\]
From the equation, \[\left( A \right)\] we get when the value of \[\sin \theta \] is \[0\] , then
automatically the value of \[\tan \theta \] is \[0\] \[(i.e\tan x = 0)\] . So, we get
\[
\tan \left( 0 \right) = 0 \\
0 = \arctan \left( 0 \right) \\
\tan \left( \pi \right) = 0 \\
\pi = \arctan \left( 0 \right) \\
\]
So when \[\theta \] the value is \[0,\pi ,2\pi ,3\pi ,......\] the value of \[\tan \theta \] becomes \[0\] .
So, the final answer is,
If \[\tan x = 0\] , then the value of \[x = 0,\pi ,2\pi ,3\pi ,....\]
Note: In this type of question we would find the value of \[x\] from the given equation. In this problem, we use trigonometric table values for finding the value of \[x\] . Also, we can use a scientific calculator to find the value \[x\] . On finding the \[x\] value in the scientific calculator we can use radian mode or degree mode. If we want to find \[x\] value in decimal we can use radian mode otherwise we can use degree mode.

To solve the given problem we need to find the values of \[\theta \] . Also, we need to know the process of calculating the value of \[\tan \theta \] the scientific calculator. We need to know the degree value \[\pi \] . Also, we need to know the relation between \[\sin \theta ,\cos \theta ,\] and \[\tan\theta \] .
Complete step by step solution:
The given question is shown below,
\[\tan x = 0\]
We need to find the value \[\theta \] from the above equation. Before that, we need to know the basic definition of \[\tan \theta \] .
The above figure represents a triangle marked with the opposite side, adjacent side, and hypotenuse side according to the position of \[\theta \] .
The above figure is used to represent the definition of \[\sin \theta ,\cos \theta ,\] and \[\tan \theta \] . Let’s see the definitions of \[\sin \theta ,\cos\theta ,\] and \[\tan \theta \] ,
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\]
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{adjacant}}{{hypotenuse}}\]
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacant}}\]
From the above three equations, we can define the \[\tan \theta \] as follows,
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}\] \[ \to \left( A \right)\]
We need to find the value of \[\tan x = 0\] . So, we get
\[x = \arctan \left( 0 \right)\]
We know that,
\[\sin \left( 0 \right) = 0\]
\[0 = \arcsin \left( 0 \right)\]
\[
\sin \left( \pi \right) = 0 \\
\pi = \arcsin \left( 0 \right) \\\]
From the equation, \[\left( A \right)\] we get when the value of \[\sin \theta \] is \[0\] , then
automatically the value of \[\tan \theta \] is \[0\] \[(i.e\tan x = 0)\] . So, we get
\[
\tan \left( 0 \right) = 0 \\
0 = \arctan \left( 0 \right) \\
\tan \left( \pi \right) = 0 \\
\pi = \arctan \left( 0 \right) \\
\]
So when \[\theta \] the value is \[0,\pi ,2\pi ,3\pi ,......\] the value of \[\tan \theta \] becomes \[0\] .
So, the final answer is,
If \[\tan x = 0\] , then the value of \[x = 0,\pi ,2\pi ,3\pi ,....\]
Note: In this type of question we would find the value of \[x\] from the given equation. In this problem, we use trigonometric table values for finding the value of \[x\] . Also, we can use a scientific calculator to find the value \[x\] . On finding the \[x\] value in the scientific calculator we can use radian mode or degree mode. If we want to find \[x\] value in decimal we can use radian mode otherwise we can use degree mode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




