
How do you solve $2\cos 2x + 1 = 0$?
Answer
537k+ views
Hint: We have to find all possible values of $x$ satisfying a given equation. For this first, subtract 1 from both sides of the equation. Then, divide each term by 2 and simplify. Next, take the inverse cosine of both sides of the equation to extract $x$ from inside the cosine. Also, the cosine function is negative in the second and third quadrants. To find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from $2\pi $ to find the solution in the third quadrant. Since, the period of the $\cos \left( {2x} \right)$ function is $\pi $ so values will repeat every $\pi $ radians in both directions. Then, we will get all solutions of the given equation.
Formula used:
$\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$\cos \left( {\pi - x} \right) = - \cos x$
$\cos \left( {\pi + x} \right) = - \cos x$
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation: $2\cos 2x + 1 = 0$
We have to find all possible values of $x$ satisfying given equation.
Subtract 1 from both sides of the equation.
$2\cos 2x = - 1$
Divide each term by 2 and simplify.
$\cos 2x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
Take the inverse cosine of both sides of the equation to extract $x$ from inside the cosine.
$2x = \arccos \left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
The exact value of $\arccos \left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$.
$2x = 2\pi - \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Divide each term by 2 and simplify.
$x = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
The cosine function is negative in the second and third quadrants. To find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from $\pi $ to find the solution in the third quadrant.
$x = \pi - \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Since, the period of the $\cos \left( {2x} \right)$ function is $\pi $ so values will repeat every $\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$
Final solution: Hence, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$ are solutions of the given equation.
Note: In above question, we can find the solutions of given equation by plotting the equation, $2\cos 2x + 1 = 0$ on graph paper and determine all its solutions.
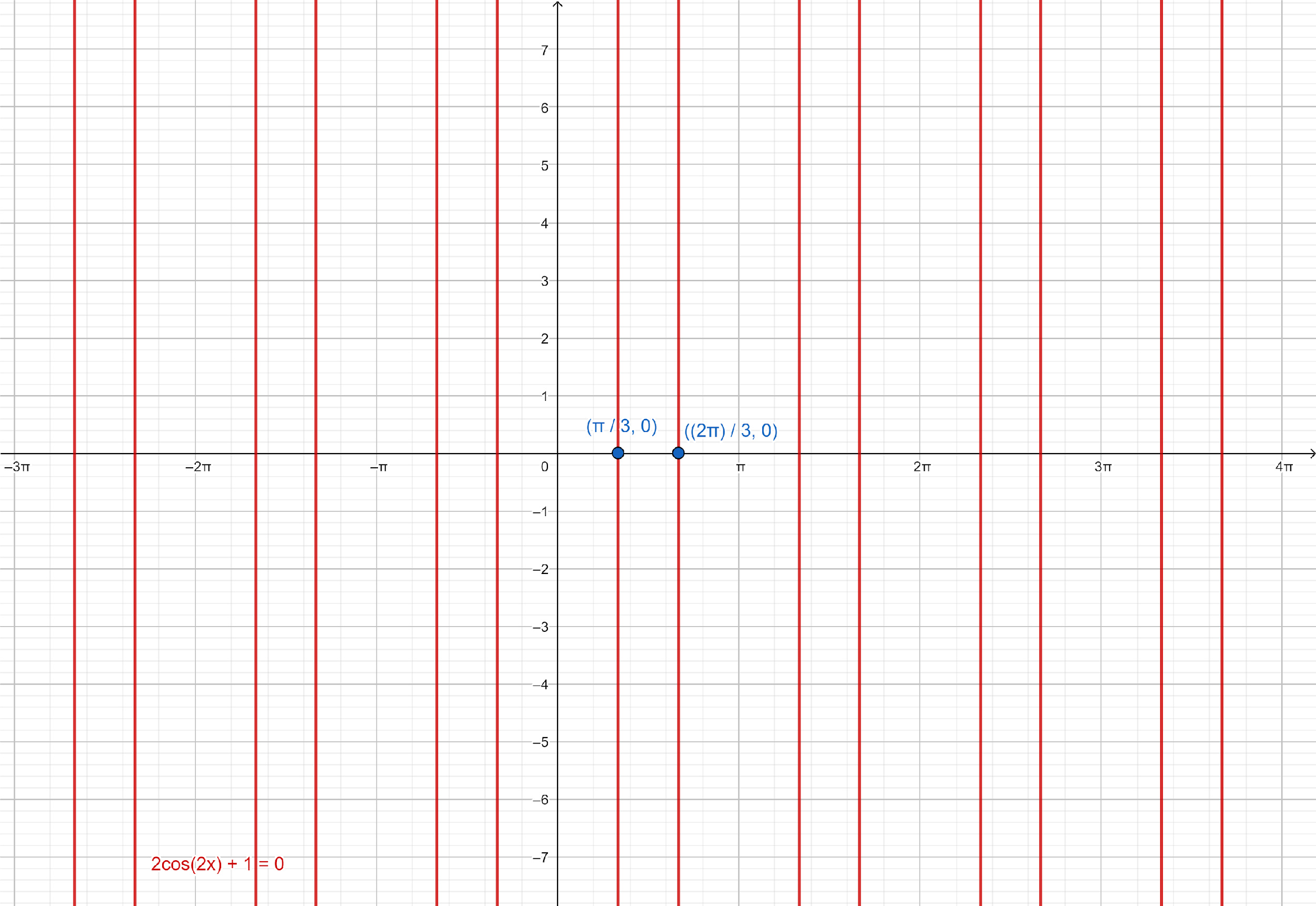
From the graph paper, we can see that $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$ are solutions of given equation, and solution repeat every $\pi $ radians in both directions.
So, these will be the solutions of the given equation.
Final solution: Hence, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$ are solutions of the given equation.
We can also find the value of $x$ using trigonometric properties.
First, we will find the values of $x$ satisfying $\cos 2x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$…(i)
So, using the property $\cos \left( {\pi - x} \right) = - \cos x$ and $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ in equation (i).
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = - \cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = \cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Now, using the property $\cos \left( {\pi + x} \right) = - \cos x$ and $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ in equation (i).
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = - \cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = \cos \left( {\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Since, the period of the $\cos \left( {2x} \right)$ function is $\pi $ so values will repeat every $\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$
Final solution: Hence, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$ are solutions of the given equation.
Formula used:
$\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$\cos \left( {\pi - x} \right) = - \cos x$
$\cos \left( {\pi + x} \right) = - \cos x$
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation: $2\cos 2x + 1 = 0$
We have to find all possible values of $x$ satisfying given equation.
Subtract 1 from both sides of the equation.
$2\cos 2x = - 1$
Divide each term by 2 and simplify.
$\cos 2x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
Take the inverse cosine of both sides of the equation to extract $x$ from inside the cosine.
$2x = \arccos \left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
The exact value of $\arccos \left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$.
$2x = 2\pi - \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Divide each term by 2 and simplify.
$x = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
The cosine function is negative in the second and third quadrants. To find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from $\pi $ to find the solution in the third quadrant.
$x = \pi - \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Since, the period of the $\cos \left( {2x} \right)$ function is $\pi $ so values will repeat every $\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$
Final solution: Hence, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$ are solutions of the given equation.
Note: In above question, we can find the solutions of given equation by plotting the equation, $2\cos 2x + 1 = 0$ on graph paper and determine all its solutions.

From the graph paper, we can see that $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$ are solutions of given equation, and solution repeat every $\pi $ radians in both directions.
So, these will be the solutions of the given equation.
Final solution: Hence, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$ are solutions of the given equation.
We can also find the value of $x$ using trigonometric properties.
First, we will find the values of $x$ satisfying $\cos 2x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$…(i)
So, using the property $\cos \left( {\pi - x} \right) = - \cos x$ and $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ in equation (i).
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = - \cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = \cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Now, using the property $\cos \left( {\pi + x} \right) = - \cos x$ and $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ in equation (i).
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = - \cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2x = \cos \left( {\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Since, the period of the $\cos \left( {2x} \right)$ function is $\pi $ so values will repeat every $\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$
Final solution: Hence, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{3} + n\pi ,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} + n\pi $, for any integer $n$ are solutions of the given equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




