
How do you simplify $\sin (ta{n^{ - 1}}x)$?
Answer
557.1k+ views
Hint:
Here basically we need to know that inverse of the trigonometric function can also be represented in the form by using the prefix $arc$ Here we need to proceed by letting the value inside the bracket which is ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x$ to be any variable say $a$ and then we will get $\tan a = x$ and now we can easily find the value of $\sin a$ which is required by using Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given to simplify the term which is given as $\sin (ta{n^{ - 1}}x)$
So let us consider the term inside the bracket which is ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x$ to be any variable say $a$
So we get ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So we will get $\tan a = x$
We can also write it as $\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$
Now we need to find the value of $\sin (ta{n^{ - 1}}x)$ which can be written as $\cos a$ according to the variable which we have let ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So let us consider the triangle $ABC$ in which we can let the angle $a$ as $\angle A$ and it is right angles at \[B\]
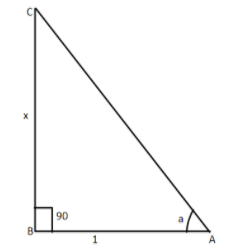
Now we are given:
$\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$$ - - - - (1)$
So we know that $\tan a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}}$$ - - - - - (2)$
So by comparing the equation (1) and (2) we will get:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
Now we know that by Pythagoras theorem we can say that in the right angles triangle:
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Now we can put in it:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
We will get:
$
A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} \\
A{C^2} = {1^2} + {x^2} \\
AC = \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \\
$
Now we know that in the right angles triangle:
$\sin a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
Now we can substitute the values of $AB,AC$ in the above equation of $\cos a$
$\sin a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
$\sin a = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Now we can substitute the value of $a$ and get:
$\sin (ta{n^{ - 1}}x)$$ = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
So we can write $\sin \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin (\operatorname{arc} (tanx))$$ = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Hence in this way by the use of Pythagoras theorem we can easily solve for such types of problems where we need to find the trigonometric function of the inverse function.
Note:
In such types of problems the student must keep in mind the basic trigonometric formula and the properties and also the use of Pythagoras theorem. We must know that $\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$ because:
$\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - {{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$
Here basically we need to know that inverse of the trigonometric function can also be represented in the form by using the prefix $arc$ Here we need to proceed by letting the value inside the bracket which is ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x$ to be any variable say $a$ and then we will get $\tan a = x$ and now we can easily find the value of $\sin a$ which is required by using Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given to simplify the term which is given as $\sin (ta{n^{ - 1}}x)$
So let us consider the term inside the bracket which is ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x$ to be any variable say $a$
So we get ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So we will get $\tan a = x$
We can also write it as $\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$
Now we need to find the value of $\sin (ta{n^{ - 1}}x)$ which can be written as $\cos a$ according to the variable which we have let ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So let us consider the triangle $ABC$ in which we can let the angle $a$ as $\angle A$ and it is right angles at \[B\]

Now we are given:
$\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$$ - - - - (1)$
So we know that $\tan a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}}$$ - - - - - (2)$
So by comparing the equation (1) and (2) we will get:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
Now we know that by Pythagoras theorem we can say that in the right angles triangle:
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Now we can put in it:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
We will get:
$
A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} \\
A{C^2} = {1^2} + {x^2} \\
AC = \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \\
$
Now we know that in the right angles triangle:
$\sin a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
Now we can substitute the values of $AB,AC$ in the above equation of $\cos a$
$\sin a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
$\sin a = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Now we can substitute the value of $a$ and get:
$\sin (ta{n^{ - 1}}x)$$ = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
So we can write $\sin \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin (\operatorname{arc} (tanx))$$ = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Hence in this way by the use of Pythagoras theorem we can easily solve for such types of problems where we need to find the trigonometric function of the inverse function.
Note:
In such types of problems the student must keep in mind the basic trigonometric formula and the properties and also the use of Pythagoras theorem. We must know that $\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$ because:
$\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - {{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




