
How do you name halides?
Answer
540.3k+ views
Hint :To answer this question firstly let us understand what we mean by halides. Halides are defined as the binary compounds in which one part is an element or group of elements and the other parts is the halogen atom. There are two types of halides possible. Halides can be organic halides as well as inorganic halides.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To answer this question let us firstly see the naming of inorganic halides.
Inorganic halides are binary compounds which have one atom as halogen while another atom is basically any other element. The naming of such halides is very simple. Follow some basic rules.
Rule 1: For naming such halides we write the name of an element other than halogen in the compound as it is as a prefix and in the suffix, we add the name of the halogen atom. While writing the name of the halogen we need to convert (-ine to -ide). For example, chlorine is converted to chloride.
Few examples are as follows:
$ HCl $ is named as hydrogen chloride.
$ NaCl $ is named as sodium chloride.
Rule 2: If there are many halogen atoms present in the compound then we need to mention the oxidation state of the non-halogen element is brackets.
For example, $ FeCl $ is Iron (I) chloride whereas $ FeC{l_2} $ is Iron (II) chloride.
For organic compounds:
In organic chemistry, we have a class of halogen derivatives which are known as haloalkanes or alkyl halides. The naming of these organic compounds is based on the rules of the IUPAC. Let us see the rules for the nomenclature of alkyl halides.
Rule 1: Select the longest continuous chain containing the carbon attached to the halogen group and name it as the parent chain. If a double or triple bond is present, parent chain must contain it.
Rule 2: Number the carbon atom of the parent chain, beginning from the end nearer to the first substituent regardless of whether it is alkyl or halo group.
Rule 3: If two or more substituents are present then they are named in the alphabetical order along with their appropriate positions.
Rule 4: If two different substituents are present at the same position, from the two ends, then numbering of the chain is done in such a way that substituent which comes first in the alphabetical order gets a lower number.
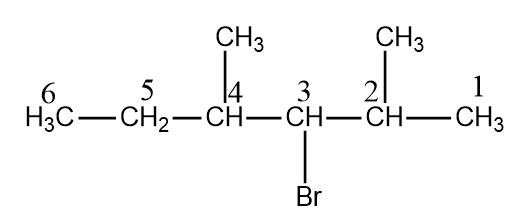
In this the parent chain is hexane as it is the largest chain. For numbering we will follow rule-2. Therefore, by rule-2 numbering starts from Right side of the chain. Apart from this there are other substituents methyl at (2 and 4) carbon atoms. Bromine at carbon – 3. Therefore, the name of the compound will be ( $ 3 $ -bromo- $ 2,4 $ dimethyl hexane).
Note :
It may be noted that in the above nomenclature since there were two methyl groups present therefore, we used the term ‘’di’’. Similarly, in IUPAC nomenclature ‘’tri’’ denotes three substituents. Also please note that while writing the name we have followed the alphabetical order.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To answer this question let us firstly see the naming of inorganic halides.
Inorganic halides are binary compounds which have one atom as halogen while another atom is basically any other element. The naming of such halides is very simple. Follow some basic rules.
Rule 1: For naming such halides we write the name of an element other than halogen in the compound as it is as a prefix and in the suffix, we add the name of the halogen atom. While writing the name of the halogen we need to convert (-ine to -ide). For example, chlorine is converted to chloride.
Few examples are as follows:
$ HCl $ is named as hydrogen chloride.
$ NaCl $ is named as sodium chloride.
Rule 2: If there are many halogen atoms present in the compound then we need to mention the oxidation state of the non-halogen element is brackets.
For example, $ FeCl $ is Iron (I) chloride whereas $ FeC{l_2} $ is Iron (II) chloride.
For organic compounds:
In organic chemistry, we have a class of halogen derivatives which are known as haloalkanes or alkyl halides. The naming of these organic compounds is based on the rules of the IUPAC. Let us see the rules for the nomenclature of alkyl halides.
Rule 1: Select the longest continuous chain containing the carbon attached to the halogen group and name it as the parent chain. If a double or triple bond is present, parent chain must contain it.
Rule 2: Number the carbon atom of the parent chain, beginning from the end nearer to the first substituent regardless of whether it is alkyl or halo group.
Rule 3: If two or more substituents are present then they are named in the alphabetical order along with their appropriate positions.
Rule 4: If two different substituents are present at the same position, from the two ends, then numbering of the chain is done in such a way that substituent which comes first in the alphabetical order gets a lower number.

In this the parent chain is hexane as it is the largest chain. For numbering we will follow rule-2. Therefore, by rule-2 numbering starts from Right side of the chain. Apart from this there are other substituents methyl at (2 and 4) carbon atoms. Bromine at carbon – 3. Therefore, the name of the compound will be ( $ 3 $ -bromo- $ 2,4 $ dimethyl hexane).
Note :
It may be noted that in the above nomenclature since there were two methyl groups present therefore, we used the term ‘’di’’. Similarly, in IUPAC nomenclature ‘’tri’’ denotes three substituents. Also please note that while writing the name we have followed the alphabetical order.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




