
How do you graph \[y = \sin \left( { - x} \right)\]?
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: Here, we will find the graph for the given trigonometric equation. We will draw the graph of the given trigonometric function by taking numerical division on \[y\]-axis and radian division on the \[x\] axis. Then by substituting different angles in the place of x we will get the required points. Then by using the points we will draw the required curve. A graph is a representation and relation of two points in a line.
Formula Used:
The difference between the square of numbers is given by the formula \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\].
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a function \[y = \sin \left( { - x} \right)\].
We know that if the given function is \[f\left( x \right)\] then upon changing the variable as negative i.e., \[x = - x\] we get \[f\left( x \right) = f\left( { - x} \right)\] .
If \[f\left( { - x} \right) = - f\left( x \right)\] , then the graph is the mirror image of \[f\left( x \right)\] with respect to \[x\] and the function is an odd function.
Thus, the combined graph of both the functions is symmetrical about \[x\]-axis.
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y = \sin \left( { - x} \right) = - \sin x\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y + \sin x = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y = \sin x = \sin x\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y - \sin x = 0\]
Thus, the combined graph of the given function is given by
\[ \Rightarrow \] Combined Graph of \[\left( {y + \sin x} \right)\left( {y - \sin x} \right) = 0\]
The difference between the square of numbers is given by the formula \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Combined Graph of \[{y^2} - {\sin ^2}x = 0\]
Now, we will draw the graph of \[y = \sin x\].
We know that the Graph of\[\sin x\] is a periodic function with \[2\pi \]. So, we will draw the graph in the interval \[\left[ {0,2\pi } \right]\].
We will follow the following steps to draw the graph of \[y = \sin x\] such that
i. Draw a \[y\]-axis with the points as \[0,1,2,3,.....\]
ii. Now, we will draw an \[x\]-axis horizontal from the origin. The points are in radians such that \[\dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi ,\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2},2\pi ,........\]
The sine curve will cut the \[x\]-axis at \[\pi ,2\pi ,3\pi ,....\] since \[\sin n\pi = 0\].
We know that \[\sin x\] is an even function, so that the function \[y = - \sin x\] is a mirror image of the graph of \[y = \sin x\]. Therefore, the graph of \[y = - \sin x\] is as follows:
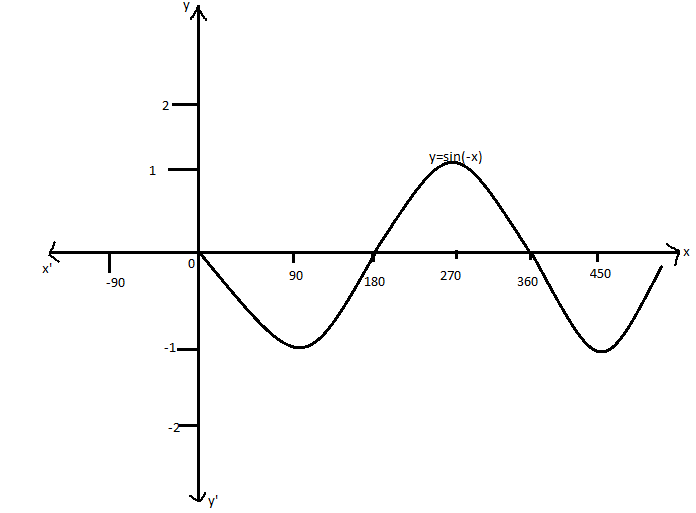
Then the combined graph is symmetrical about the \[x\] axis.
Note:
We know that we have many trigonometric identities that are related to all the other trigonometric equations. We should note in particular that sine and tangent are odd functions since both the functions are symmetric about the origin. Cosine is an even function since the function is symmetric about the y-axis. So, we take the arguments in the negative sign for odd functions and a positive sign for even function. The graph of an odd function is always the mirror image of the function.
Formula Used:
The difference between the square of numbers is given by the formula \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\].
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a function \[y = \sin \left( { - x} \right)\].
We know that if the given function is \[f\left( x \right)\] then upon changing the variable as negative i.e., \[x = - x\] we get \[f\left( x \right) = f\left( { - x} \right)\] .
If \[f\left( { - x} \right) = - f\left( x \right)\] , then the graph is the mirror image of \[f\left( x \right)\] with respect to \[x\] and the function is an odd function.
Thus, the combined graph of both the functions is symmetrical about \[x\]-axis.
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y = \sin \left( { - x} \right) = - \sin x\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y + \sin x = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y = \sin x = \sin x\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Graph of \[y - \sin x = 0\]
Thus, the combined graph of the given function is given by
\[ \Rightarrow \] Combined Graph of \[\left( {y + \sin x} \right)\left( {y - \sin x} \right) = 0\]
The difference between the square of numbers is given by the formula \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Combined Graph of \[{y^2} - {\sin ^2}x = 0\]
Now, we will draw the graph of \[y = \sin x\].
We know that the Graph of\[\sin x\] is a periodic function with \[2\pi \]. So, we will draw the graph in the interval \[\left[ {0,2\pi } \right]\].
We will follow the following steps to draw the graph of \[y = \sin x\] such that
i. Draw a \[y\]-axis with the points as \[0,1,2,3,.....\]
ii. Now, we will draw an \[x\]-axis horizontal from the origin. The points are in radians such that \[\dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi ,\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2},2\pi ,........\]
The sine curve will cut the \[x\]-axis at \[\pi ,2\pi ,3\pi ,....\] since \[\sin n\pi = 0\].
We know that \[\sin x\] is an even function, so that the function \[y = - \sin x\] is a mirror image of the graph of \[y = \sin x\]. Therefore, the graph of \[y = - \sin x\] is as follows:

Then the combined graph is symmetrical about the \[x\] axis.
Note:
We know that we have many trigonometric identities that are related to all the other trigonometric equations. We should note in particular that sine and tangent are odd functions since both the functions are symmetric about the origin. Cosine is an even function since the function is symmetric about the y-axis. So, we take the arguments in the negative sign for odd functions and a positive sign for even function. The graph of an odd function is always the mirror image of the function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




