
How do you graph $y = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}$?
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: First, find the x-intercepts of the curve by putting $y = 0$. After that, find the y-intercept by putting $x = 0$. Then take a minimum of 5 points and plot the points. After plotting the points, join the points with a smooth freehand curve and identify the curve that we have obtained.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the graph of a function is the locus of points $\left( {x,y} \right)$ such that $y = f\left( x \right)$ where x, y are real numbers. We are given the following quadratic polynomial function,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}$
So, let us put $y = 0$ and find the x-intercept. We have,
$ \Rightarrow 0 = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}$
Take the square root on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow x - 5 = 0$
Add 5 on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow x - 5 + 5 = 0 + 5$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow x = 5$
It means the curve cuts the x-axis at $\left( {5,0} \right)$.
Let us put $x = 0$ and find the y-intercept. We have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {0 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( { - 5} \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 25$
It means the curve cuts the y-axis at $\left( {0,25} \right)$.
We know that all quadratic functions of the type $y = a{x^2} + bc + c$ have minimum values but not maximum.
Since the square is always non-negative, we have ${\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} \ge 0$, then we have
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} \ge 0$
So, the minimum value of $y = 0$ and the minimum value occurs when ${\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} = 0$ or $x = 5$.
We already have two points for the curve $\left( {5,0} \right)$ and $\left( {0,25} \right)$. We find y for three more points.
At $x = 9$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {9 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( 4 \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 16$
At $x = 3$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {3 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( { - 2} \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 4$
At $x = 7$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {7 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( 2 \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 4$
So, we draw the table for x and y.
We plot the above points and join them to have the graph as
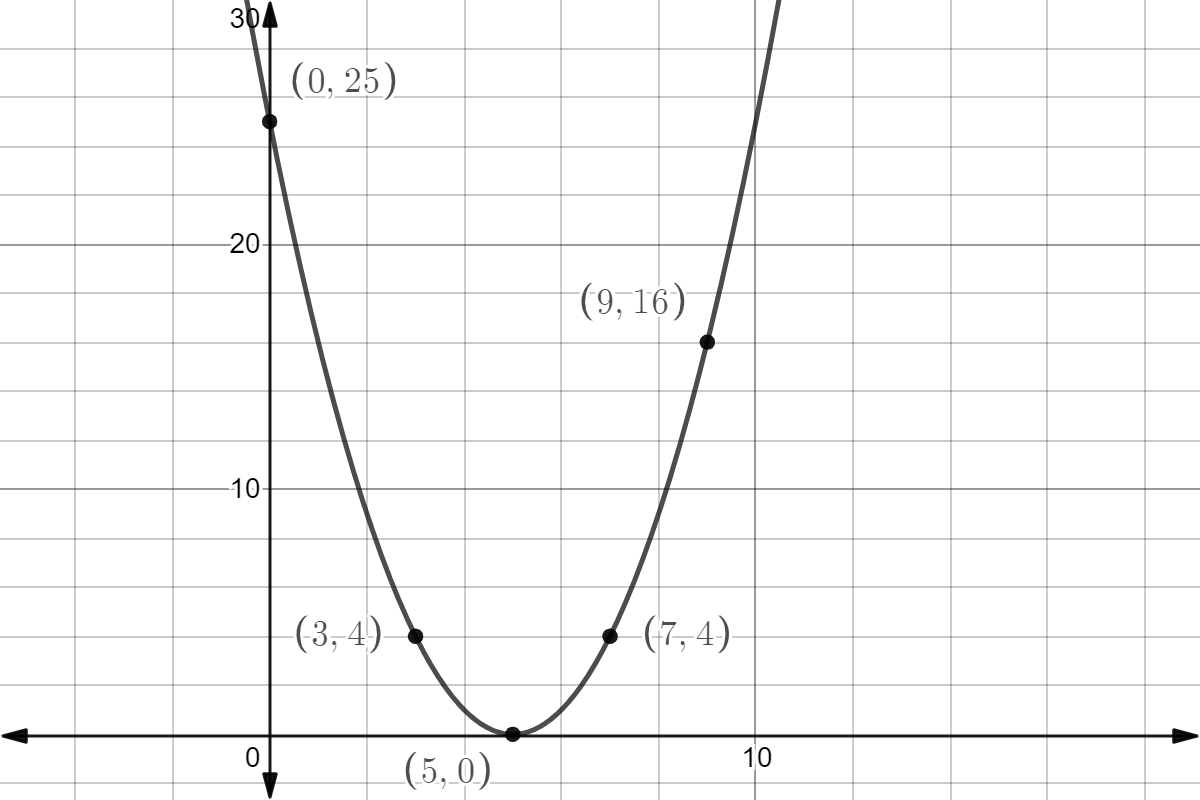
Note:
We note that the obtained graph is the graph of the upward parabola whose general equation is given by $y = a{x^2} + bx + c$ with the condition $a > 0$ whose vertex here is $\left( {5,0} \right)$ . We can directly find the minimum value of $y = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}$ by finding $x = - \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$. If $a < 0$ the equation $y = a{x^2} + bx + c$ represents a downward parabola. We also note that the obtained curve is symmetric about the line $x = 5$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the graph of a function is the locus of points $\left( {x,y} \right)$ such that $y = f\left( x \right)$ where x, y are real numbers. We are given the following quadratic polynomial function,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}$
So, let us put $y = 0$ and find the x-intercept. We have,
$ \Rightarrow 0 = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}$
Take the square root on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow x - 5 = 0$
Add 5 on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow x - 5 + 5 = 0 + 5$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow x = 5$
It means the curve cuts the x-axis at $\left( {5,0} \right)$.
Let us put $x = 0$ and find the y-intercept. We have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {0 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( { - 5} \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 25$
It means the curve cuts the y-axis at $\left( {0,25} \right)$.
We know that all quadratic functions of the type $y = a{x^2} + bc + c$ have minimum values but not maximum.
Since the square is always non-negative, we have ${\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} \ge 0$, then we have
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} \ge 0$
So, the minimum value of $y = 0$ and the minimum value occurs when ${\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} = 0$ or $x = 5$.
We already have two points for the curve $\left( {5,0} \right)$ and $\left( {0,25} \right)$. We find y for three more points.
At $x = 9$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {9 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( 4 \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 16$
At $x = 3$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {3 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( { - 2} \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 4$
At $x = 7$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {7 - 5} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( 2 \right)^2}$
Square the term on the right side,
$ \Rightarrow y = 4$
So, we draw the table for x and y.
| x | 0 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| y | 25 | 0 | 16 | 4 | 4 |
We plot the above points and join them to have the graph as

Note:
We note that the obtained graph is the graph of the upward parabola whose general equation is given by $y = a{x^2} + bx + c$ with the condition $a > 0$ whose vertex here is $\left( {5,0} \right)$ . We can directly find the minimum value of $y = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}$ by finding $x = - \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$. If $a < 0$ the equation $y = a{x^2} + bx + c$ represents a downward parabola. We also note that the obtained curve is symmetric about the line $x = 5$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




