
How do you graph $y = \csc x + 3$?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: Here, we are given the cosecant function. We know that cosecant is the periodic function. We will first use the general form equation of the cosecant function to find certain values such as the period, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.
Formula used:
$y = A\csc \left( {Bx - C} \right) + D$,where, $A$ is the vertical stretch factor, $B$ is used to find the period $P = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| B \right|}}$, $ - \dfrac{C}{B}$is the phase shift and $D$ is the vertical shift.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first use the general equation of the cosecant function and compare it with the given one to find the period, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.
The general form of cosecant equation is: $y = A\csc \left( {Bx - C} \right) + D$.
If we compare it with the given function, we get $A = 1$ and $B = 1$, $C = 0$ and $D = 3$.
We know that cosecant function has no amplitude.
Thus, we can say that
The period of the function $y = \csc x + 3$ is $P = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| B \right|}} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{1} = 2\pi $ .
Phase shift of the function $y = \csc x + 3$ is $ - \dfrac{C}{B} = - \dfrac{0}{1} = 0$.
Vertical shift of the function $y = \csc x + 3$ is $D = 3$.
By using this information, the graph of the given function $y = \csc x + 3$ can be obtained as:
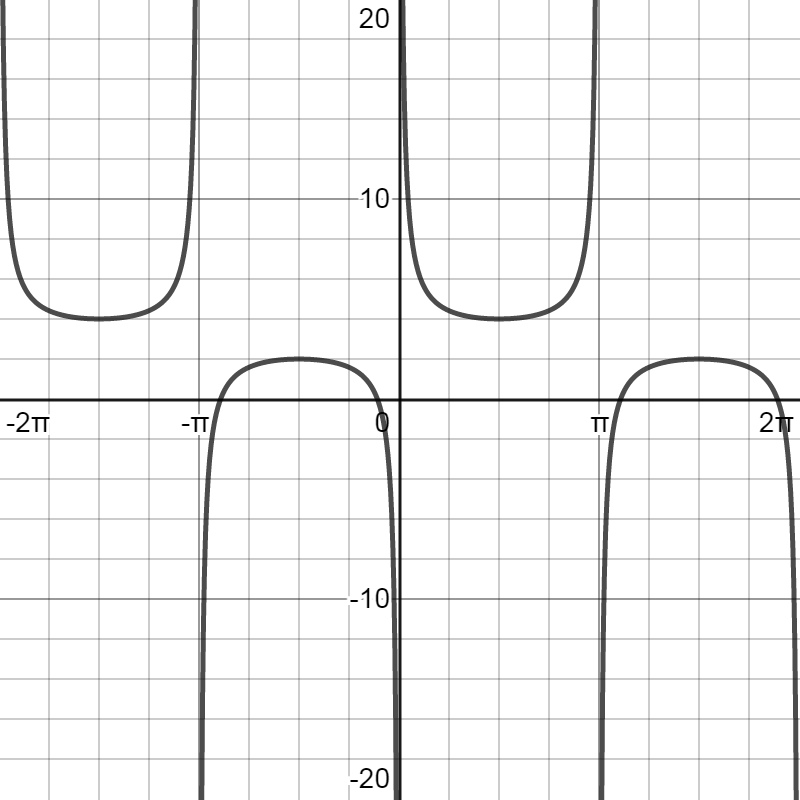
Note: The important thing to note here is that the shape of the given function $y = \csc x + 3$ is the same as that of the simple cosecant function $y = \csc x$. However, here the number 3 is added to the basic function $\csc x$. This will result in the vertical shift of the graph to 3 units. We have also seen here that the cosecant function is a periodic function that repeats its values in regular intervals or periods.
Formula used:
$y = A\csc \left( {Bx - C} \right) + D$,where, $A$ is the vertical stretch factor, $B$ is used to find the period $P = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| B \right|}}$, $ - \dfrac{C}{B}$is the phase shift and $D$ is the vertical shift.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first use the general equation of the cosecant function and compare it with the given one to find the period, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.
The general form of cosecant equation is: $y = A\csc \left( {Bx - C} \right) + D$.
If we compare it with the given function, we get $A = 1$ and $B = 1$, $C = 0$ and $D = 3$.
We know that cosecant function has no amplitude.
Thus, we can say that
The period of the function $y = \csc x + 3$ is $P = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| B \right|}} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{1} = 2\pi $ .
Phase shift of the function $y = \csc x + 3$ is $ - \dfrac{C}{B} = - \dfrac{0}{1} = 0$.
Vertical shift of the function $y = \csc x + 3$ is $D = 3$.
By using this information, the graph of the given function $y = \csc x + 3$ can be obtained as:

Note: The important thing to note here is that the shape of the given function $y = \csc x + 3$ is the same as that of the simple cosecant function $y = \csc x$. However, here the number 3 is added to the basic function $\csc x$. This will result in the vertical shift of the graph to 3 units. We have also seen here that the cosecant function is a periodic function that repeats its values in regular intervals or periods.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




