
How do you graph the line \[y = - 3x + 3\]?
Answer
556.8k+ views
Hint: Here, we are given a linear equation in two variables. We will substitute different values of \[x\] in the given equation to find corresponding values of \[y\]. This will give us the coordinate points and using these points we will draw the graph of the given equation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We are given an equation of a line-
\[y = - 3x + 3\]……………………………………………………………………………………………..\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, we will find the coordinates for the given equation of a line.
Now, by substituting \[x = 0\] in equation\[\left( 1 \right)\] , we get
\[y = - 3\left( 0 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 3\]
Substituting \[x = 1\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] , we get
\[y = - 3\left( 1 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 0\]
The co-ordinates \[\left( {0,3} \right)\] and \[\left( {1,0} \right)\] are the \[x\]-intercept and \[y\] -intercept respectively.
Now, by substituting \[x = 2\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] , we get
\[y = - 3\left( 2 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 3\]
Substituting \[x = 3\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[y = - 3\left( 3 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 6\]
Now, by substituting \[x = 4\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[y = - 3\left( 4 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 9\]
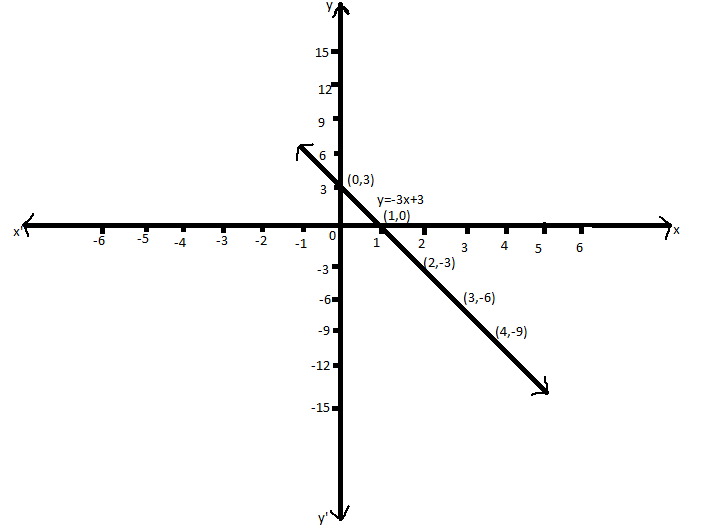
So, the coordinates of the equation of line are \[\left( {0,3} \right)\],\[\left( {1,0} \right)\] ,\[\left( {2, - 3} \right)\] ,\[\left( {3, - 6} \right)\] and \[\left( {4, - 9} \right)\]
Therefore, the coordinates of the equation of line are \[\left( {0,3} \right)\],\[\left( {1,0} \right)\] ,\[\left( {2, - 3} \right)\] ,\[\left( {3, - 6} \right)\] and \[\left( {4, - 9} \right)\].
Now, we plot the graph for the co-ordinates, we get
Note:
We will solve the linear equation in two variables by the method of substitution to find the solution set at different points. Thus the solution set becomes the coordinates of the point in the graph for the linear equation. Linear equation in two variables is an equation with the highest power of 1 in two variables. Thus the graph of a linear equation is always a straight line. The given equation of the line is in the slope-intercept form\[y = mx + c\] where \[m\] is the slope and \[c\] is the \[y\]-intercept. A point crossing the x-axis is called x-intercept and A point crossing the y-axis is called the y-intercept.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We are given an equation of a line-
\[y = - 3x + 3\]……………………………………………………………………………………………..\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, we will find the coordinates for the given equation of a line.
Now, by substituting \[x = 0\] in equation\[\left( 1 \right)\] , we get
\[y = - 3\left( 0 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 3\]
Substituting \[x = 1\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] , we get
\[y = - 3\left( 1 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 0\]
The co-ordinates \[\left( {0,3} \right)\] and \[\left( {1,0} \right)\] are the \[x\]-intercept and \[y\] -intercept respectively.
Now, by substituting \[x = 2\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] , we get
\[y = - 3\left( 2 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 3\]
Substituting \[x = 3\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[y = - 3\left( 3 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 6\]
Now, by substituting \[x = 4\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[y = - 3\left( 4 \right) + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 9\]
So, the coordinates of the equation of line are \[\left( {0,3} \right)\],\[\left( {1,0} \right)\] ,\[\left( {2, - 3} \right)\] ,\[\left( {3, - 6} \right)\] and \[\left( {4, - 9} \right)\]
Therefore, the coordinates of the equation of line are \[\left( {0,3} \right)\],\[\left( {1,0} \right)\] ,\[\left( {2, - 3} \right)\] ,\[\left( {3, - 6} \right)\] and \[\left( {4, - 9} \right)\].
Now, we plot the graph for the co-ordinates, we get

Note:
We will solve the linear equation in two variables by the method of substitution to find the solution set at different points. Thus the solution set becomes the coordinates of the point in the graph for the linear equation. Linear equation in two variables is an equation with the highest power of 1 in two variables. Thus the graph of a linear equation is always a straight line. The given equation of the line is in the slope-intercept form\[y = mx + c\] where \[m\] is the slope and \[c\] is the \[y\]-intercept. A point crossing the x-axis is called x-intercept and A point crossing the y-axis is called the y-intercept.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




