
How do you graph $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$
Answer
546.9k+ views
Hint: We equate the given equation of elliptic curve with the general equation of \[\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]. We find the number of x intercepts and the value of the y intercept. We also find the coordinates of the focus and the vertices to place the curve in the graph.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given equation $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$ is an elliptic curve.
We convert the equation into a square form and get
$\begin{align}
& 16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 4x+4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-9 \right)}^{2}}=216={{\left( 6\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-9 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( 6\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}}=1 \\
\end{align}$
We equate $\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-9 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( 6\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}}=1$ with the general equation of parabola \[\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]. We can also see that ${{b}^{2}}>{{a}^{2}}$. The formula changes if ${{b}^{2}}<{{a}^{2}}$.
For the general equation $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$ is the centre. The vertices are $\left( \alpha ,\beta \pm a \right)$. The coordinates of the foci are $\left( \alpha ,\beta \pm be \right)$. Here \[e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}}\] is the eccentricity.
This gives the centre as $\left( -1,9 \right)$. The vertices are $\left( -1,9\pm \dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)$.
Here $e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{1}{16}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{15}}{4}$ is the eccentricity value.
The coordinates of the foci are $\left( -1,9\pm 9 \sqrt{\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)$.
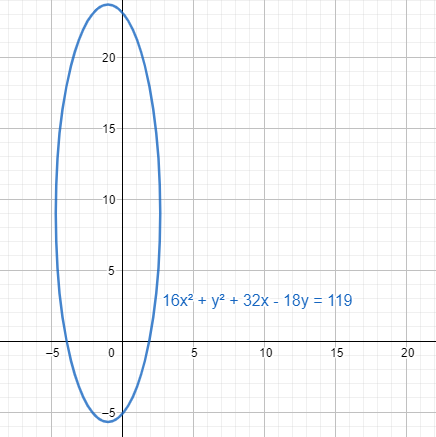
We first find the Y-axis intercepts. In that case for the Y-axis, we have to take the coordinate values of x as 0. Putting the value of $x=0$ in the equation $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}-18y-119=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{18\pm \sqrt{{{18}^{2}}-4\times \left( -119 \right)\times 1}}{2\times 1}=\dfrac{18\pm \sqrt{800}}{2}=9\pm 10\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
So, the intercept point for Y-axis is $\left( 0,9\pm 10\sqrt{2} \right)$.
We find the X-axis intercepts. In that case for X-axis, we have to take the coordinate values of y as 0. Putting the value of $y=0$ in the equation $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$, we get
\[\begin{align}
& 16{{x}^{2}}+32x-119=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-32\pm \sqrt{{{32}^{2}}-4\times \left( -119 \right)\times 16}}{2\times 16}=\dfrac{-32\pm \sqrt{8640}}{32}=\dfrac{-4\pm 3\sqrt{15}}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
The intercept point for X-axis is \[\left( \dfrac{-4\pm 3\sqrt{15}}{4},0 \right)\].
Note: The minimum point of the function $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$ is $\left( -1,9-\dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)$. The graph is bounded at that point. But on the other side the curve is open and not bounded. The general case of parabolic curve is to be bounded at one side to mark the vertex.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given equation $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$ is an elliptic curve.
We convert the equation into a square form and get
$\begin{align}
& 16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 4x+4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-9 \right)}^{2}}=216={{\left( 6\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-9 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( 6\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}}=1 \\
\end{align}$
We equate $\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-9 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( 6\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}}=1$ with the general equation of parabola \[\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]. We can also see that ${{b}^{2}}>{{a}^{2}}$. The formula changes if ${{b}^{2}}<{{a}^{2}}$.
For the general equation $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$ is the centre. The vertices are $\left( \alpha ,\beta \pm a \right)$. The coordinates of the foci are $\left( \alpha ,\beta \pm be \right)$. Here \[e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}}\] is the eccentricity.
This gives the centre as $\left( -1,9 \right)$. The vertices are $\left( -1,9\pm \dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)$.
Here $e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{1}{16}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{15}}{4}$ is the eccentricity value.
The coordinates of the foci are $\left( -1,9\pm 9 \sqrt{\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)$.

We first find the Y-axis intercepts. In that case for the Y-axis, we have to take the coordinate values of x as 0. Putting the value of $x=0$ in the equation $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}-18y-119=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{18\pm \sqrt{{{18}^{2}}-4\times \left( -119 \right)\times 1}}{2\times 1}=\dfrac{18\pm \sqrt{800}}{2}=9\pm 10\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
So, the intercept point for Y-axis is $\left( 0,9\pm 10\sqrt{2} \right)$.
We find the X-axis intercepts. In that case for X-axis, we have to take the coordinate values of y as 0. Putting the value of $y=0$ in the equation $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$, we get
\[\begin{align}
& 16{{x}^{2}}+32x-119=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-32\pm \sqrt{{{32}^{2}}-4\times \left( -119 \right)\times 16}}{2\times 16}=\dfrac{-32\pm \sqrt{8640}}{32}=\dfrac{-4\pm 3\sqrt{15}}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
The intercept point for X-axis is \[\left( \dfrac{-4\pm 3\sqrt{15}}{4},0 \right)\].
Note: The minimum point of the function $16{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+32x-18y=119$ is $\left( -1,9-\dfrac{3\sqrt{6}}{2} \right)$. The graph is bounded at that point. But on the other side the curve is open and not bounded. The general case of parabolic curve is to be bounded at one side to mark the vertex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




