
How do you find the area of a kite?
Answer
561k+ views
Hint:Kite is a special quadrilateral in which each pair of the consecutive sides congruent, but the opposite sides are not congruent. Convert the shape of the kit into any of the known shapes let say square or rectangle and find the area.
Complete step by step solution:
A kite can be viewed as a pair of congruent triangles with a common base. Diagonal of a kite
intersect each other at right angles. The longer diagonal is the perpendicular bisector of the shorter diagonal. The shorter diagonal divides the kite into two isosceles triangles.
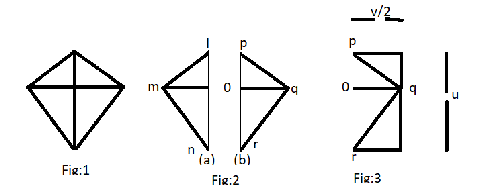
Let’s consider the following diagram to find the area of a kite. Fig:1 shows the shape of the kite, which nearly look alike as a rhombus.
In Fig: 2 the kite is divides into two half and we can see from the fig: 2 that we have four triangles, where $\angle 0lm = \angle 0qp$ and$\angle 0mn = \angle0qr$.
Now rotate the upper triangle in the Fig: 2 (a) ${180^ \circ }$ anticlockwise again rotate ${180^ \circ }$ upwards.
Repeat this process for lower triangle also, so that we can get a shape of a
rectangle as shown in the Fig: 3.
Now the Fig: 3 resemble as a rectangle and we already know that the area of the rectangle= Length * Breadth, which also can be said as the area of the kite and also it will be the multiple of the larger diagonal and half of the smaller diagonal.
And hence the area of kite will be equal to $u*\dfrac{v}{2}$, which also can be written as the Area of the kite$ = \dfrac{1}{2}uv$. This is the required solution.
Note: Area of the kite is equal to the area of the rhombus, there is only one property that will differ between them, is their sides. In rhombus all the four sides are equal whereas in kite all the four sides are not equal. Angle between them is unequal.
Complete step by step solution:
A kite can be viewed as a pair of congruent triangles with a common base. Diagonal of a kite
intersect each other at right angles. The longer diagonal is the perpendicular bisector of the shorter diagonal. The shorter diagonal divides the kite into two isosceles triangles.

Let’s consider the following diagram to find the area of a kite. Fig:1 shows the shape of the kite, which nearly look alike as a rhombus.
In Fig: 2 the kite is divides into two half and we can see from the fig: 2 that we have four triangles, where $\angle 0lm = \angle 0qp$ and$\angle 0mn = \angle0qr$.
Now rotate the upper triangle in the Fig: 2 (a) ${180^ \circ }$ anticlockwise again rotate ${180^ \circ }$ upwards.
Repeat this process for lower triangle also, so that we can get a shape of a
rectangle as shown in the Fig: 3.
Now the Fig: 3 resemble as a rectangle and we already know that the area of the rectangle= Length * Breadth, which also can be said as the area of the kite and also it will be the multiple of the larger diagonal and half of the smaller diagonal.
And hence the area of kite will be equal to $u*\dfrac{v}{2}$, which also can be written as the Area of the kite$ = \dfrac{1}{2}uv$. This is the required solution.
Note: Area of the kite is equal to the area of the rhombus, there is only one property that will differ between them, is their sides. In rhombus all the four sides are equal whereas in kite all the four sides are not equal. Angle between them is unequal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




