
How do you factor ${x^3} - {x^2} - 4x + 4$?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint:To order to determine the factors of the above cubic equation first pick our common from first two terms and last two and use the formula $\left( {{A^2} - {B^2}} \right) = \left( {A - B} \right)\left( {A + B} \right)$to find all the factors .
Complete step by step solution:
Given a Cubic equation${x^3} - {x^2} - 4x + 4$,let it be $f(x)$
$f(x) = {x^3} - {x^2} - 4x + 4$
Comparing the equation with the standard cubic equation $a{x^3} + b{x^2}cx + d$
a becomes 1
b becomes -1
c becomes -4
and d becomes 4
To find the cubic factorization,
Taking common ${x^2}$from the first two terms and $ - 4$from the last two terms
$
f(x) = {x^2}(x - 1) - 4(x - 1) \\
= (x - 1)({x^2} - 4) \\
= (x - 1)({x^2} - {2^2}) \\
$Again pull out common$(x - 1)$ from both the terms .
Consider $x$as A and $2$as B and Applying Identity $\left( {{A^2} - {B^2}} \right) = \left( {A - B}
\right)\left( {A + B} \right)$
Now our equation becomes
$f\left( x \right) = (x - 1)(x - 2)(x + 2)$
Hence, we have successfully factorized our cubic equation.
Therefore, the factors are $(x - 1)(x - 2)(x + 2)$
Additional Information:
Cubic Equation: A cubic equation is a equation which can be represented in the form of $a{x^3} + b{x^2}cx + d$where $x$is the unknown variable and a,b,c,d are the numbers known where $a \ne 0$.If $a = 0$then the equation will become a quadratic equation and will no longer be cubic.
The degree of the quadratic equation is of the order 3.
Every Cubic equation has 3 roots.
The Graph of any cubic polynomial is symmetric with respect to the inflection point of the
polynomial.
Graph to cubic polynomial $y = {x^3} - {x^2} - 4x + 4$
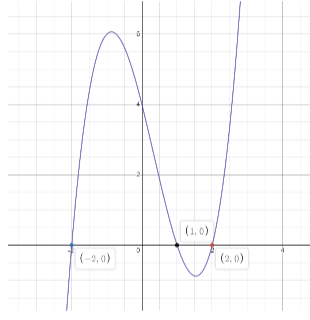
The points at which the graph touches the x-axis are the roots of the polynomial.
Note: 1. One must be careful while calculating the answer as calculation error may come.
2.Don’t forget to compare the given cubic equation with the standard one every time.
Complete step by step solution:
Given a Cubic equation${x^3} - {x^2} - 4x + 4$,let it be $f(x)$
$f(x) = {x^3} - {x^2} - 4x + 4$
Comparing the equation with the standard cubic equation $a{x^3} + b{x^2}cx + d$
a becomes 1
b becomes -1
c becomes -4
and d becomes 4
To find the cubic factorization,
Taking common ${x^2}$from the first two terms and $ - 4$from the last two terms
$
f(x) = {x^2}(x - 1) - 4(x - 1) \\
= (x - 1)({x^2} - 4) \\
= (x - 1)({x^2} - {2^2}) \\
$Again pull out common$(x - 1)$ from both the terms .
Consider $x$as A and $2$as B and Applying Identity $\left( {{A^2} - {B^2}} \right) = \left( {A - B}
\right)\left( {A + B} \right)$
Now our equation becomes
$f\left( x \right) = (x - 1)(x - 2)(x + 2)$
Hence, we have successfully factorized our cubic equation.
Therefore, the factors are $(x - 1)(x - 2)(x + 2)$
Additional Information:
Cubic Equation: A cubic equation is a equation which can be represented in the form of $a{x^3} + b{x^2}cx + d$where $x$is the unknown variable and a,b,c,d are the numbers known where $a \ne 0$.If $a = 0$then the equation will become a quadratic equation and will no longer be cubic.
The degree of the quadratic equation is of the order 3.
Every Cubic equation has 3 roots.
The Graph of any cubic polynomial is symmetric with respect to the inflection point of the
polynomial.
Graph to cubic polynomial $y = {x^3} - {x^2} - 4x + 4$

The points at which the graph touches the x-axis are the roots of the polynomial.
Note: 1. One must be careful while calculating the answer as calculation error may come.
2.Don’t forget to compare the given cubic equation with the standard one every time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




