
How do you factor $64{x^3} + 8 = 0$?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: To factorise a given cubic polynomial, we first assume the given polynomial to be $p\left( x \right)$. Then, make the coefficient of ${x^3}$ equal to one if it is not one and then find the constant term. Then, find all the factors of constant term. Then, check at which factor of constant term, $p\left( x \right)$ is zero by using trial method and get one factor of $p\left( x \right)$.Then, write $p\left( x \right)$ as the product of this factor and a quadratic polynomial. This will be the desired factor of the given polynomial.
Complete step by step solution:
Given cubic polynomial: $64{x^3} + 8$
We have to factorize this cubic polynomial.
So, assuming a given polynomial to be $p\left( x \right)$.
Let $p\left( x \right) = 64{x^3} + 8$
Next step is to make the coefficient of ${x^3}$ equal to one if it is not one.
So, $p\left( x \right) = 64\left( {{x^3} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right)$
Next step is to find the constant term and all the factors of the constant term.
So, we have to find the constant term of $p\left( x \right)$ and all its factors.
Constant term is $\dfrac{1}{8}$ and all factors of $\dfrac{1}{8}$ are \[ \pm 1, \pm \dfrac{1}{2}, \pm \dfrac{1}{4}, \pm \dfrac{1}{8}\].
Next step is to check at which factor of constant term, $p\left( x \right)$ is zero by using trial method and get one factor of $p\left( x \right)$.
So, put $x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$ in $p\left( x \right) = 64\left( {{x^3} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right)$.
$p\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 64\left[ {{{\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}^3} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow p\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 64\left[ { - \dfrac{1}{8} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow p\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 0$
So, $\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$ is a factor of $p\left( x \right)$.
Next step is to write $p\left( x \right)$ as the product of this factor and a quadratic polynomial.
So, divide $p\left( x \right)$ by $\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$.
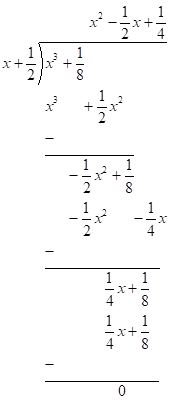
$ \Rightarrow p\left( x \right) = 64\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - \dfrac{1}{2}x + \dfrac{1}{4}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 64{x^3} + 8 = 8\left( {2x + 1} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right)$
Therefore, $64{x^3} + 8 = 0$ can be factored as $8\left( {2x + 1} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right) = 0$.
Note: We can also factorise given cubic polynomial using algebraic identity ${a^3} + {b^3} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {{a^2} - ab + {b^2}} \right)$.
Since, $64{x^3}$ can be written as ${\left( {4x} \right)^3}$ and $8$ can be written as ${2^3}$.
So, both terms are perfect cubes in $64{x^3} + 8$. Thus, factor using the algebraic identity ${a^3} + {b^3} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {{a^2} - ab + {b^2}} \right)$ by substituting $a = 4x$ and $b = 2$.
$ \Rightarrow 64{x^3} + 8 = \left( {4x + 2} \right)\left( {16{x^2} - 8x + 4} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 64{x^3} + 8 = 8\left( {2x + 1} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right)$
Complete step by step solution:
Given cubic polynomial: $64{x^3} + 8$
We have to factorize this cubic polynomial.
So, assuming a given polynomial to be $p\left( x \right)$.
Let $p\left( x \right) = 64{x^3} + 8$
Next step is to make the coefficient of ${x^3}$ equal to one if it is not one.
So, $p\left( x \right) = 64\left( {{x^3} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right)$
Next step is to find the constant term and all the factors of the constant term.
So, we have to find the constant term of $p\left( x \right)$ and all its factors.
Constant term is $\dfrac{1}{8}$ and all factors of $\dfrac{1}{8}$ are \[ \pm 1, \pm \dfrac{1}{2}, \pm \dfrac{1}{4}, \pm \dfrac{1}{8}\].
Next step is to check at which factor of constant term, $p\left( x \right)$ is zero by using trial method and get one factor of $p\left( x \right)$.
So, put $x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$ in $p\left( x \right) = 64\left( {{x^3} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right)$.
$p\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 64\left[ {{{\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}^3} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow p\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 64\left[ { - \dfrac{1}{8} + \dfrac{1}{8}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow p\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 0$
So, $\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$ is a factor of $p\left( x \right)$.
Next step is to write $p\left( x \right)$ as the product of this factor and a quadratic polynomial.
So, divide $p\left( x \right)$ by $\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$.
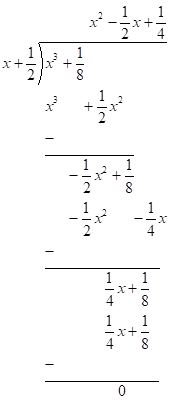
$ \Rightarrow p\left( x \right) = 64\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - \dfrac{1}{2}x + \dfrac{1}{4}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 64{x^3} + 8 = 8\left( {2x + 1} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right)$
Therefore, $64{x^3} + 8 = 0$ can be factored as $8\left( {2x + 1} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right) = 0$.
Note: We can also factorise given cubic polynomial using algebraic identity ${a^3} + {b^3} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {{a^2} - ab + {b^2}} \right)$.
Since, $64{x^3}$ can be written as ${\left( {4x} \right)^3}$ and $8$ can be written as ${2^3}$.
So, both terms are perfect cubes in $64{x^3} + 8$. Thus, factor using the algebraic identity ${a^3} + {b^3} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {{a^2} - ab + {b^2}} \right)$ by substituting $a = 4x$ and $b = 2$.
$ \Rightarrow 64{x^3} + 8 = \left( {4x + 2} \right)\left( {16{x^2} - 8x + 4} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 64{x^3} + 8 = 8\left( {2x + 1} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




