
How do you evaluate $\tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}$?
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: Here we are asked to find the tangent of an angle. We have to remember that a tangent function is a periodic function with periodicity $\pi $ . Therefore we can write,
$\tan \left( {\pi + x} \right) = \tan x$ , where $0 \leqslant x \leqslant \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Formula used:
$\tan \left( {\pi + x} \right) = \tan x$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are asked to evaluate $\tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}$. The angle is $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}\,radians$ or $270^\circ $.
Since we are making use of the periodicity of tangent function, let us split $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}$ as follows:
$\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \pi + \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Therefore, we can write question as
$\tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \tan \left( {\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$
$\tan \left( {\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
That is,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Now, we know that, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$ , $\theta $ is any angle.
Therefore, we have to find $\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2},\cos \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Consider a right angled triangle, $\Delta AOB$ , right angled at $\angle O$.
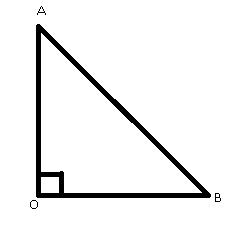
From definition of sine, we have
$\sin \left( {\angle AOB} \right) = \dfrac{{opposite\,side}}{{hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AB}} = 1$
Now, consider $\angle B$ . If we bring the vertex $B$ along the side $OB$ so that $B$ coincides with $O$ , we then will have $BC = 0$ .
Now from definition of cosine, we have
$\cos \left( {\angle AOB} \right) = \dfrac{{adjacent\,side}}{{hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{0}{1} = 0$
Therefore, we have
$\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2} = \dfrac{{\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2}}}{{\cos \dfrac{\pi }{2}}} = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\angle AOB} \right)}}{{\cos \left( {\angle AOB} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{0}$
We know that $\dfrac{1}{0}$ is undefined.
That is, $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2} = undefined$
Therefore, going back to our original problem, we have,
$\tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2} = undefined$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right) = undefined$.
Note: The same result can be obtained graphically by plotting the graph of tangent function.The trigonometric function takes in angles as their input and gives out the ratio of sides of a triangle. Thus, these provide a link between angles and sides.
$\tan \left( {\pi + x} \right) = \tan x$ , where $0 \leqslant x \leqslant \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Formula used:
$\tan \left( {\pi + x} \right) = \tan x$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are asked to evaluate $\tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}$. The angle is $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}\,radians$ or $270^\circ $.
Since we are making use of the periodicity of tangent function, let us split $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}$ as follows:
$\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \pi + \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Therefore, we can write question as
$\tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \tan \left( {\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$
$\tan \left( {\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
That is,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Now, we know that, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$ , $\theta $ is any angle.
Therefore, we have to find $\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2},\cos \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Consider a right angled triangle, $\Delta AOB$ , right angled at $\angle O$.

From definition of sine, we have
$\sin \left( {\angle AOB} \right) = \dfrac{{opposite\,side}}{{hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AB}} = 1$
Now, consider $\angle B$ . If we bring the vertex $B$ along the side $OB$ so that $B$ coincides with $O$ , we then will have $BC = 0$ .
Now from definition of cosine, we have
$\cos \left( {\angle AOB} \right) = \dfrac{{adjacent\,side}}{{hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{0}{1} = 0$
Therefore, we have
$\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2} = \dfrac{{\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2}}}{{\cos \dfrac{\pi }{2}}} = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\angle AOB} \right)}}{{\cos \left( {\angle AOB} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{0}$
We know that $\dfrac{1}{0}$ is undefined.
That is, $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2} = undefined$
Therefore, going back to our original problem, we have,
$\tan \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2} = undefined$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right) = undefined$.
Note: The same result can be obtained graphically by plotting the graph of tangent function.The trigonometric function takes in angles as their input and gives out the ratio of sides of a triangle. Thus, these provide a link between angles and sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




