
How do you evaluate $\cos {{145}^{\circ }}$? \[\]
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: We recall trigonometric ratios of sine and cosine. We use the shift by half turn or right angle angle formula $\cos \left( \theta +{{90}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin \theta $ to express the value in sine. We convert theta $\theta $ in degree to radian and use the sine series $\sin x=x-\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3!}+\dfrac{{{x}^{5}}}{5!}+...$ to evaluate the required value. \[\]
Complete answer:
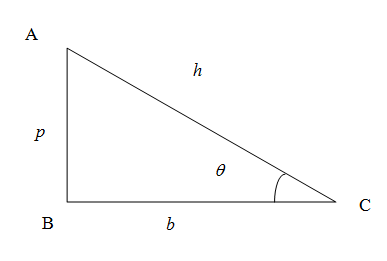
We know that in right angled triangle the side opposite to right angled triangle is called hypotenuse denoted as $h$, the vertical side is called perpendicular denoted as $p$ and the horizontal side is called the base denoted as $b$.\[\]
We know from the trigonometric ratios in a right angled triangle the sine of any angle is given by the ratio of side opposite to the angle to the hypotenuse. In the figure the sine of the angle $\theta $ is given by
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{p}{h}...(1)\]
Similarly the cosine of an angle is the ratio of side adjacent to the angle (excluding hypotenuse) to the hypotenuse. So we have cosine of angle $\theta $
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{b}{h}...(2)\]
We know that when angle is shifted by a full turn $\left( {{360}^{\circ }} \right)$, half turn $\left( {{180}^{\circ }} \right)$or quarter turn $\left( {{90}^{\circ }} \right)$ the trigonometric ratios return the value of their complementary trigonometric value with positive or negative sign . We write a shift formula for cosine.
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \left( \theta +{{90}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin \theta \\
& \cos \left( \theta +{{180}^{\circ }} \right)=-\cos \theta \\
& \cos \left( \theta +{{360}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \theta \\
\end{align}\]
We are asked to evaluate$\cos {{145}^{\circ }}$. We can write it as shift by quarter turn and use the formula $\cos \left( \theta +{{90}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin \theta $as
\[\cos \left( {{145}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+{{55}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin {{55}^{\circ }}\]
We convert the ${{55}^{\circ }}$into radian to have
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{c}}=\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}\times {{\theta }^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}\times {{55}^{\circ }}\simeq 0.96 \\
\end{align}\]
We use the sine power series to evaluate the value as
\[\begin{align}
& \sin x=x-\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3!}+\dfrac{{{x}^{5}}}{5!}+... \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \left( {{55}^{\circ }} \right)\simeq \sin \left( 0.96 \right)=0.96-\dfrac{{{\left( 0.96 \right)}^{3}}}{6}+\dfrac{{{\left( 0.96 \right)}^{5}}}{120} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \left( {{55}^{\circ }} \right)\simeq 0.8191 \\
\end{align}\]
So the required value is
\[\cos {{145}^{\circ }}=-\sin {{55}^{\circ }}=-0.8124\]
Note: We can also find the approximate value of $\cos {{145}^{\circ }}$with cosine power series$\cos x=1-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2!}+\dfrac{{{x}^{4}}}{4!}+...$. . We can only calculate accurately with a calculator and the accurate value up to fourth decimal is $\cos {{145}^{\circ }}\simeq 0.8838$. The shift formulas for sine is given by $\sin \left( \theta +{{90}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \theta ,\sin \left( \theta +{{180}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin \theta ,\sin \left( \theta +{{360}^{\circ }} \right)=\sin \theta $.
Complete answer:

We know that in right angled triangle the side opposite to right angled triangle is called hypotenuse denoted as $h$, the vertical side is called perpendicular denoted as $p$ and the horizontal side is called the base denoted as $b$.\[\]
We know from the trigonometric ratios in a right angled triangle the sine of any angle is given by the ratio of side opposite to the angle to the hypotenuse. In the figure the sine of the angle $\theta $ is given by
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{p}{h}...(1)\]
Similarly the cosine of an angle is the ratio of side adjacent to the angle (excluding hypotenuse) to the hypotenuse. So we have cosine of angle $\theta $
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{b}{h}...(2)\]
We know that when angle is shifted by a full turn $\left( {{360}^{\circ }} \right)$, half turn $\left( {{180}^{\circ }} \right)$or quarter turn $\left( {{90}^{\circ }} \right)$ the trigonometric ratios return the value of their complementary trigonometric value with positive or negative sign . We write a shift formula for cosine.
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \left( \theta +{{90}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin \theta \\
& \cos \left( \theta +{{180}^{\circ }} \right)=-\cos \theta \\
& \cos \left( \theta +{{360}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \theta \\
\end{align}\]
We are asked to evaluate$\cos {{145}^{\circ }}$. We can write it as shift by quarter turn and use the formula $\cos \left( \theta +{{90}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin \theta $as
\[\cos \left( {{145}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+{{55}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin {{55}^{\circ }}\]
We convert the ${{55}^{\circ }}$into radian to have
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{c}}=\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}\times {{\theta }^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}\times {{55}^{\circ }}\simeq 0.96 \\
\end{align}\]
We use the sine power series to evaluate the value as
\[\begin{align}
& \sin x=x-\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3!}+\dfrac{{{x}^{5}}}{5!}+... \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \left( {{55}^{\circ }} \right)\simeq \sin \left( 0.96 \right)=0.96-\dfrac{{{\left( 0.96 \right)}^{3}}}{6}+\dfrac{{{\left( 0.96 \right)}^{5}}}{120} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \left( {{55}^{\circ }} \right)\simeq 0.8191 \\
\end{align}\]
So the required value is
\[\cos {{145}^{\circ }}=-\sin {{55}^{\circ }}=-0.8124\]
Note: We can also find the approximate value of $\cos {{145}^{\circ }}$with cosine power series$\cos x=1-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2!}+\dfrac{{{x}^{4}}}{4!}+...$. . We can only calculate accurately with a calculator and the accurate value up to fourth decimal is $\cos {{145}^{\circ }}\simeq 0.8838$. The shift formulas for sine is given by $\sin \left( \theta +{{90}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \theta ,\sin \left( \theta +{{180}^{\circ }} \right)=-\sin \theta ,\sin \left( \theta +{{360}^{\circ }} \right)=\sin \theta $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




