
How can I interpret phase diagrams?
Answer
547.2k+ views
Hint: Phase diagrams consist of three single phases, for solid, liquid and gas. The slopes gradually increase and solid has the highest slope which means it has the highest density.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about phase diagrams. Phase diagrams can be used for the interpretation for the range of thermodynamic figures on the basis of when a pure sample of matter exists at a specific phase. A typical phase diagram shows the graph between pressure and temperature. It is divided into three regions, which correspond to the solid, liquid and gaseous state respectively. Phase diagrams can be also used to give reason for the behaviour of materials that is exhibited at the critical point. Let us see a typical phase diagram:
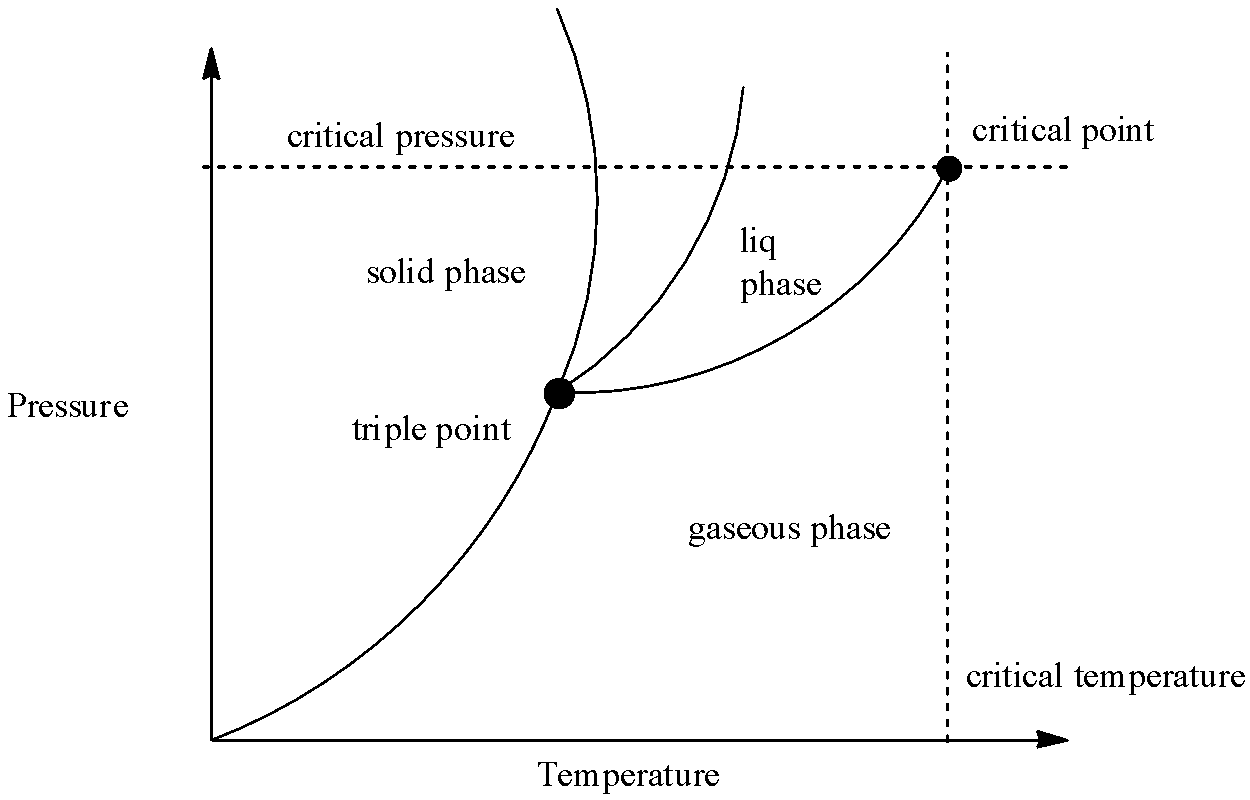
Now, in the phase diagram, there are three separate phases for solid, liquid and gas. However, there is a point where the critical temperature and critical pressure intersects. This is called the critical point and at this stage, the liquid and solid state of the substance becomes indistinguishable, meaning that both the phases have the same density. We can see that the solid phase has the highest slope, followed by liquid and gaseous state, which is because the density of solid is maximum among the three phases. From the phase diagram, we can interpret some observations which are:
(1) Solid state is preferred if the pressure is kept high and temperature is kept low
(2) If both the pressure and temperature are kept moderate, then liquid state is favoured.
(3) If temperature is kept high and pressure is kept low, then gaseous state is preferred.
Note:
The solid liquid phase boundary for water has a negative slope, which can be explained by the floating of solid ice in liquid water, meaning that ice has lower density than liquid water.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about phase diagrams. Phase diagrams can be used for the interpretation for the range of thermodynamic figures on the basis of when a pure sample of matter exists at a specific phase. A typical phase diagram shows the graph between pressure and temperature. It is divided into three regions, which correspond to the solid, liquid and gaseous state respectively. Phase diagrams can be also used to give reason for the behaviour of materials that is exhibited at the critical point. Let us see a typical phase diagram:

Now, in the phase diagram, there are three separate phases for solid, liquid and gas. However, there is a point where the critical temperature and critical pressure intersects. This is called the critical point and at this stage, the liquid and solid state of the substance becomes indistinguishable, meaning that both the phases have the same density. We can see that the solid phase has the highest slope, followed by liquid and gaseous state, which is because the density of solid is maximum among the three phases. From the phase diagram, we can interpret some observations which are:
(1) Solid state is preferred if the pressure is kept high and temperature is kept low
(2) If both the pressure and temperature are kept moderate, then liquid state is favoured.
(3) If temperature is kept high and pressure is kept low, then gaseous state is preferred.
Note:
The solid liquid phase boundary for water has a negative slope, which can be explained by the floating of solid ice in liquid water, meaning that ice has lower density than liquid water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




