
Hooke’s law, the constant of proportionality signifies
Answer
474.6k+ views
Hint: When English scientist Robert Hooke was studying springs and elasticity in the 19th century, he observed that numerous materials had a similar feature when the stress-strain connection was analyzed. The force required to stretch the material was proportional to the extension of the material in a linear region. This is known as Hooke's Law.
Complete answer:
Hooke's law is a law, which asserts that the displacement or magnitude of deformation is directly proportional to the deforming force or load for relatively minor deformations of an object. The item returns to its original shape and dimensions when the load is removed under these conditions. The fact that minor displacements of their constituent molecules, atoms, or ions from normal locations are proportional to the force that generates the displacement explains the elastic behavior of solids according to Hooke's equation.
Hooke’s law:
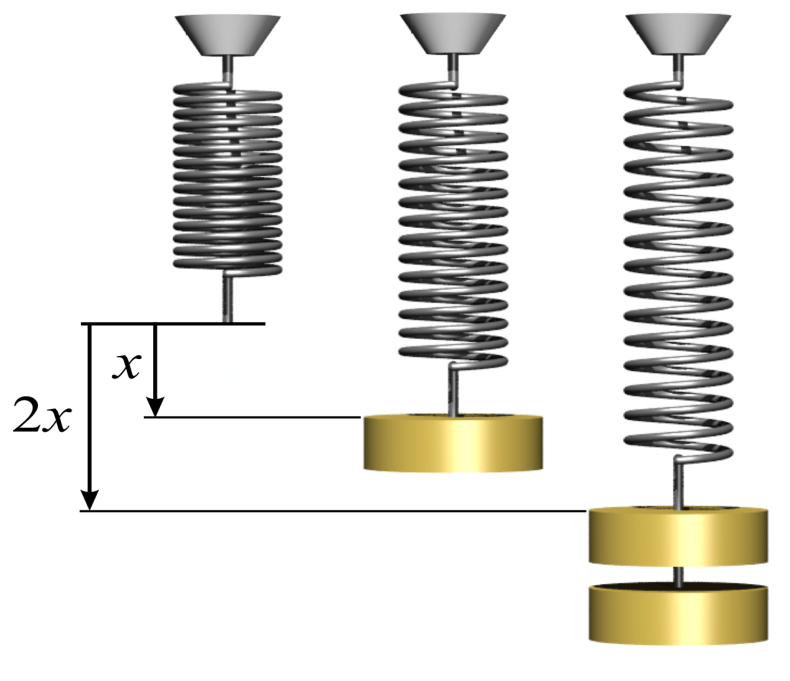
According to Hooke's law, within the elastic limit of the material, the strain is proportional to the applied stress.
In simple words, \[{\text{Stress}} \propto {\text{strain}}\]
\[{\text{Stress = modulus of elasticity x strain}}\]
Hooke’s Law can be:
\[F = - kx\]
\[F\] - force
\[x\] - extension length
\[k\] -The spring constant is a proportionality constant $\dfrac{N}{m}$.
Note:
This law had numerous practical uses, including the development of a balancing wheel, which enabled the development of mechanical clocks, portable timepieces, spring scales, and manometers (aka. the pressure gauge). Furthermore, because it is a near approximation of all solid bodies (as long as the forces of deformation are minimal enough), Hooke's law is credited to several disciplines of science and engineering. Seismology, molecular mechanics, and acoustics are among these sciences.
Complete answer:
Hooke's law is a law, which asserts that the displacement or magnitude of deformation is directly proportional to the deforming force or load for relatively minor deformations of an object. The item returns to its original shape and dimensions when the load is removed under these conditions. The fact that minor displacements of their constituent molecules, atoms, or ions from normal locations are proportional to the force that generates the displacement explains the elastic behavior of solids according to Hooke's equation.
Hooke’s law:
According to Hooke's law, within the elastic limit of the material, the strain is proportional to the applied stress.
In simple words, \[{\text{Stress}} \propto {\text{strain}}\]
\[{\text{Stress = modulus of elasticity x strain}}\]
Hooke’s Law can be:
\[F = - kx\]
\[F\] - force
\[x\] - extension length
\[k\] -The spring constant is a proportionality constant $\dfrac{N}{m}$.

Note:
This law had numerous practical uses, including the development of a balancing wheel, which enabled the development of mechanical clocks, portable timepieces, spring scales, and manometers (aka. the pressure gauge). Furthermore, because it is a near approximation of all solid bodies (as long as the forces of deformation are minimal enough), Hooke's law is credited to several disciplines of science and engineering. Seismology, molecular mechanics, and acoustics are among these sciences.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




