
Here, $Al{{H}_{3}}$ is:
(A)- pyramidal
(B)- trigonal planar
(C)- linear
(D)- tetrahedral
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: The geometry of the molecule is derived from the orientation of the hybrid orbitals, in order to minimize the repulsion between the adjacent orbitals, leading to ease in overlapping with the orbitals of the atoms to be bonded. Thus, forming a stable covalent bond.
Complete answer:
The shape of aluminium trihydride can be obtained by determining the hybridisation of the molecule, using the VSEPR theory. In the aluminium atom, with configuration $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{1}}$ and having three valence electrons.
In order to bond with three hydrogen atoms, the aluminium atom in its excited state, one electron from the 3s-orbitals jumps to the 3p-orbital. Thus, having three unpaired electrons. It undergoes hybridisation of the one 3s and the two 3p-orbitals to form three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals with one electron each and have similar energy. The $3{{p}_{z}}$ orbital is empty and is perpendicular to the $s{{p}^{2}}$hybrid orbitals.
These hybrid orbitals align themselves in the corners of the triangle (at ${{120}^{\circ }}$ angle) to minimise the repulsion, thus, forming the trigonal geometry.
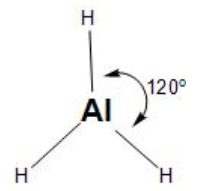
Then, the three $s{{p}^{2}}$orbitals overlap with the 1s orbital of the three hydrogen atoms, in the trigonal planar structure.
Therefore, the aluminium hydride has option (B)- trigonal planar geometry.
Note:
The octet of the aluminium atom is incomplete, having only six electrons. This is due to the empty $3{{p}_{z}}$ orbital. Hence, the stable hydride is an electron-deficient molecule and a good Lewis acid.
The hydride and its derivatives are often used in the reduction of carbonyl compounds like aldehyde, ketones, esters etc, to alcohols.
Complete answer:
The shape of aluminium trihydride can be obtained by determining the hybridisation of the molecule, using the VSEPR theory. In the aluminium atom, with configuration $\left[ Ne \right]3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{1}}$ and having three valence electrons.
In order to bond with three hydrogen atoms, the aluminium atom in its excited state, one electron from the 3s-orbitals jumps to the 3p-orbital. Thus, having three unpaired electrons. It undergoes hybridisation of the one 3s and the two 3p-orbitals to form three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals with one electron each and have similar energy. The $3{{p}_{z}}$ orbital is empty and is perpendicular to the $s{{p}^{2}}$hybrid orbitals.
These hybrid orbitals align themselves in the corners of the triangle (at ${{120}^{\circ }}$ angle) to minimise the repulsion, thus, forming the trigonal geometry.

Then, the three $s{{p}^{2}}$orbitals overlap with the 1s orbital of the three hydrogen atoms, in the trigonal planar structure.
Therefore, the aluminium hydride has option (B)- trigonal planar geometry.
Note:
The octet of the aluminium atom is incomplete, having only six electrons. This is due to the empty $3{{p}_{z}}$ orbital. Hence, the stable hydride is an electron-deficient molecule and a good Lewis acid.
The hydride and its derivatives are often used in the reduction of carbonyl compounds like aldehyde, ketones, esters etc, to alcohols.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




