
Here, 2,4,6-tribromoaniline is a product of-
(A) electrophilic addition on ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$
(B) electrophilic substitution on ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$
(C) nucleophilic addition on ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$
(D) nucleophilic substitution on ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: $N{{H}_{2}}$ group attached to the benzene ring is an electron donating group. As a result, electron density increases at ortho and para positions of aniline. 2,4,6-tribromoaniline is a result of bromination of aniline.
Complete answer:
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$ is a chemical formula of anilines, also called as aminobenzene or phenylamine.
Electrophilic substitution reaction is an organic substitution reaction in which an electrophile substitutes another electrophile in an organic compound. Anilines(${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$)undergo the electrophilic substitution reactions such as halogenation, nitration and sulphonation. Bromination is an example of halogenation reaction.
The functional group (-$N{{H}_{2}}$) associated with aniline is an electron donating group and thus is very activating towards the electrophilic substitution reaction.
Due to various resonating structures of aniline, there is an excess of electron density at ortho- and para- positions of the benzene ring as compared to the meta- position. Hence, anilines are o- and p- directing towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
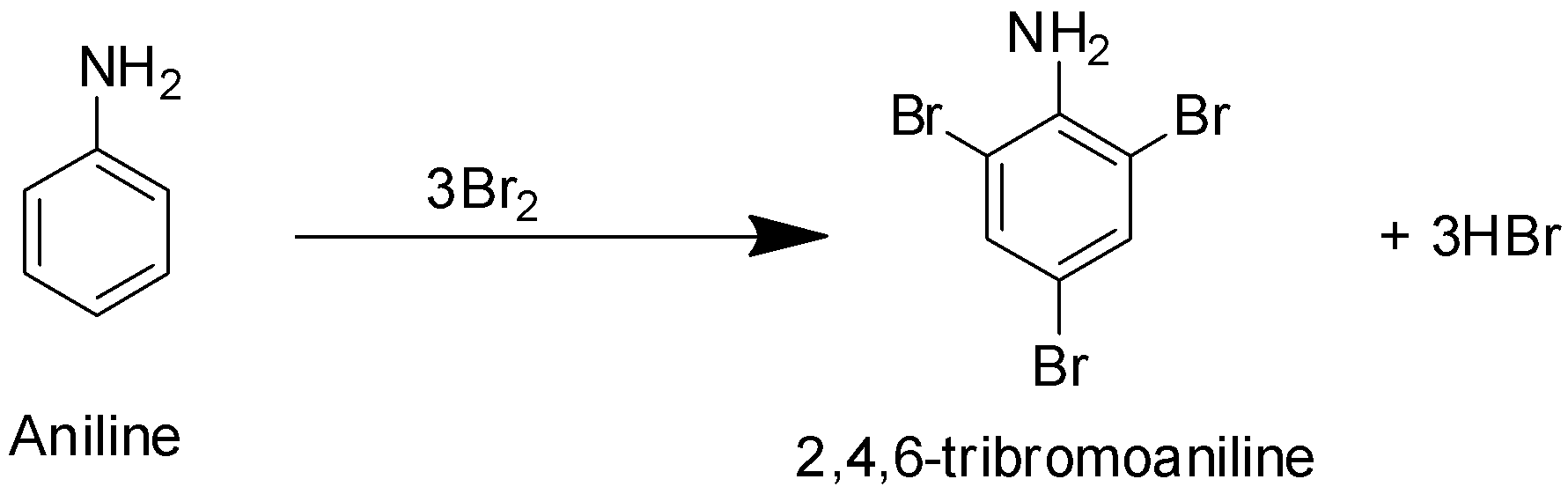
In this reaction shown above, when aniline comes close to bromine water, the bromine molecule develops a polarity within itself and $B{{r}^{+}}$ acts as an electrophile(electron loving specie) and attacks the electron rich ortho and para positions of ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$. Bromine water gets decolourized and white precipitate 2,4,6-tribromoaniline is obtained at room temperature.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Additional information:
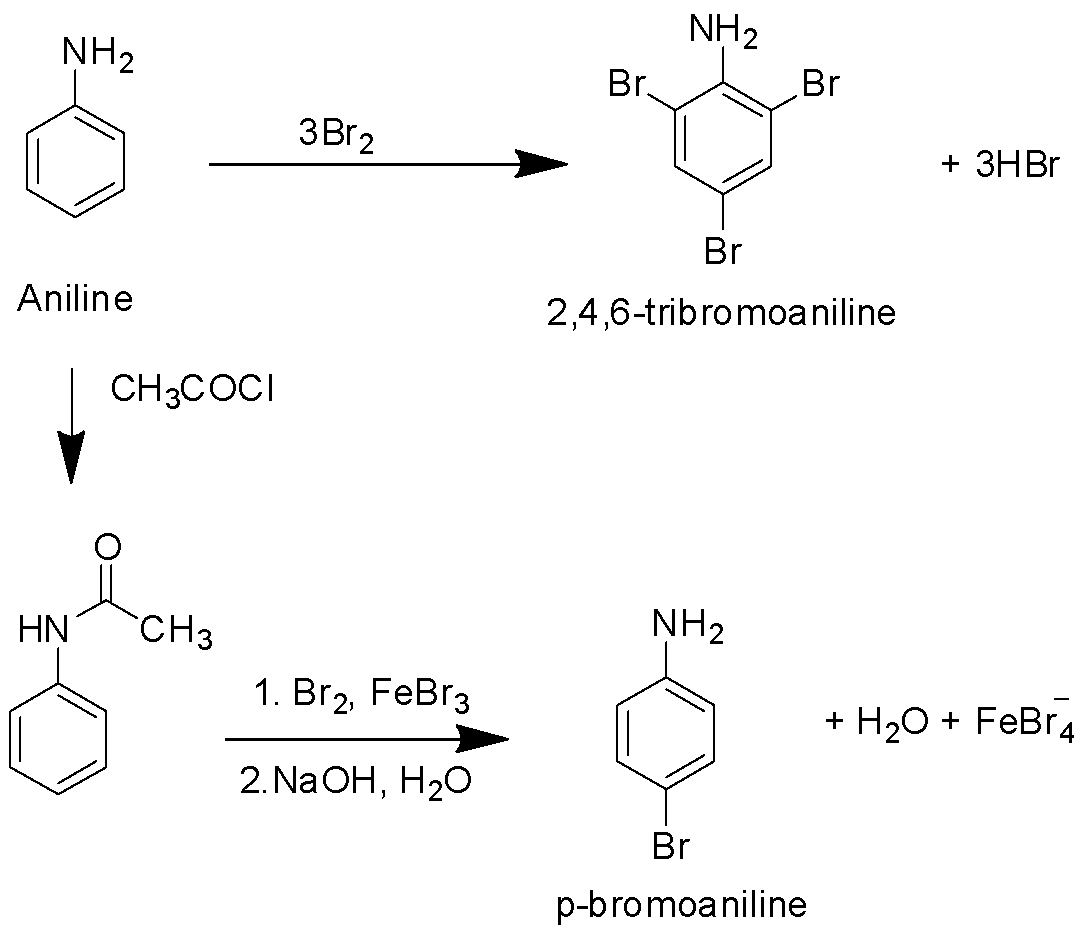
In order to generate the mono-substituted product, a protection with acetyl chloride is required as shown below-
Note:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is a chemical reaction where one nucleophile replaces another nucleophile.
Nucleophilic addition reaction is an additional reaction wherein a chemical species with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile.
An electrophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction in which a substrate is attacked by an electrophile.
Complete answer:
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$ is a chemical formula of anilines, also called as aminobenzene or phenylamine.
Electrophilic substitution reaction is an organic substitution reaction in which an electrophile substitutes another electrophile in an organic compound. Anilines(${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$)undergo the electrophilic substitution reactions such as halogenation, nitration and sulphonation. Bromination is an example of halogenation reaction.
The functional group (-$N{{H}_{2}}$) associated with aniline is an electron donating group and thus is very activating towards the electrophilic substitution reaction.
Due to various resonating structures of aniline, there is an excess of electron density at ortho- and para- positions of the benzene ring as compared to the meta- position. Hence, anilines are o- and p- directing towards electrophilic substitution reaction.

In this reaction shown above, when aniline comes close to bromine water, the bromine molecule develops a polarity within itself and $B{{r}^{+}}$ acts as an electrophile(electron loving specie) and attacks the electron rich ortho and para positions of ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$. Bromine water gets decolourized and white precipitate 2,4,6-tribromoaniline is obtained at room temperature.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Additional information:
In order to generate the mono-substituted product, a protection with acetyl chloride is required as shown below-

Note:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is a chemical reaction where one nucleophile replaces another nucleophile.
Nucleophilic addition reaction is an additional reaction wherein a chemical species with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile.
An electrophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction in which a substrate is attacked by an electrophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define peptide linkage class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which compound gives positive iodoform test A2pentanone class 12 chemistry CBSE

Write the different structural and functional differences class 12 chemistry CBSE




