
What is the height of the cone which is formed by joining the two ends of a sector of circle with radius r and angle $60{}^\circ $ .
(A). $\dfrac{\sqrt{35}}{6}r$
(B). $\dfrac{\sqrt{25}}{6}r$
(C). $\dfrac{r}{\sqrt{3}}$
(D). $\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{\sqrt{3}}$
Answer
610.2k+ views
Hint: Focus on the point that area of the circle of radius r is equal to the curved/lateral surface area of the cone formed using the sector and radius of the circle is the slant height of the cone.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us start by drawing a representative figure of the sector and the cone..
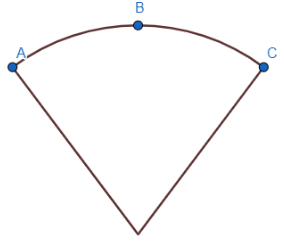
Now, if we join the points A and C of the sector, we get a cone with slant height equal to r and curved surface area equal to the area of the sector.
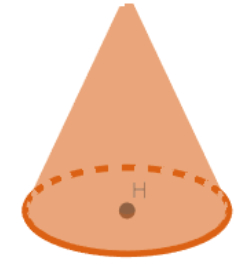
Let the height of the cone be h units and radius be x units.
Now, we know that the slant height of the cone is equal to the root of the squares of the height and the radius.
$\therefore l=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$
Also, from the question, we have deduced that slant height is equal to r.
$\therefore r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}..................(i)$
Now, as we know that the curved surface area of the cone is equal to the area of the sector, the equation we get is:
Curved surface area of cone = area of the sector.
$\pi xl=\dfrac{\theta }{360}\pi {{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow xl=\dfrac{60}{360}{{r}^{2}}$
As we mentioned earlier, the slant height of the cone is equal to r. So, using the value in our equation, we get
$xr=\dfrac{60}{360}{{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{6}r$
Now if we substitute the value of x in equation (i), we get
$r=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{6}r \right)}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$
Now we will square both sides of the equation. On doing so, we get
${{r}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{1}{6}r \right)}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=\dfrac{35}{36}{{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow h=\sqrt{\dfrac{35}{36}{{r}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{\sqrt{35}}{6}r$ units
Hence, the answer to the above question is option (a).
Note: Make sure to convert all the dimensions to a standardized system of units; this decreases the chance of errors. Also, you need to remember all the basic formulas for surface area and volume of the general 3-D shapes like the cone, cube, cylinder, etc.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us start by drawing a representative figure of the sector and the cone..

Now, if we join the points A and C of the sector, we get a cone with slant height equal to r and curved surface area equal to the area of the sector.

Let the height of the cone be h units and radius be x units.
Now, we know that the slant height of the cone is equal to the root of the squares of the height and the radius.
$\therefore l=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$
Also, from the question, we have deduced that slant height is equal to r.
$\therefore r=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}..................(i)$
Now, as we know that the curved surface area of the cone is equal to the area of the sector, the equation we get is:
Curved surface area of cone = area of the sector.
$\pi xl=\dfrac{\theta }{360}\pi {{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow xl=\dfrac{60}{360}{{r}^{2}}$
As we mentioned earlier, the slant height of the cone is equal to r. So, using the value in our equation, we get
$xr=\dfrac{60}{360}{{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{6}r$
Now if we substitute the value of x in equation (i), we get
$r=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{6}r \right)}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$
Now we will square both sides of the equation. On doing so, we get
${{r}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{1}{6}r \right)}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=\dfrac{35}{36}{{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow h=\sqrt{\dfrac{35}{36}{{r}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{\sqrt{35}}{6}r$ units
Hence, the answer to the above question is option (a).
Note: Make sure to convert all the dimensions to a standardized system of units; this decreases the chance of errors. Also, you need to remember all the basic formulas for surface area and volume of the general 3-D shapes like the cone, cube, cylinder, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




