
When heated in air, brown copper powder turns black. This powder would turn brown again when heated with:
A. \[{\text{CO}}\]
B. \[{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
C. \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]
D. \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: We must understand that the reaction of change of colour of copper powder into black and turns back to brown is due to the change in the oxidation of copper. In metallic form copper is brown in colour that has zero oxidation state. However, when it gets exposed to air its oxidation state changes to +2 and turns black.
Complete step by step solution:
First part of the question ‘When heated in air, brown copper powder turns black’; here oxidation of copper takes place.
This is the most commonly seen chemical reaction that occurs to copper. When copper gets exposed to air or heated in air, it results in the darkening of copper's surface. The formula for copper oxidation is
\[{\text{2Cu + }}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{}} \to 2{\text{CuO (black)}}\]
\[{\text{CuO}}\] is a black powder, to this if hydrogen is passed, hydrogen displaces oxygen from oxide which restores the brown colour of the copper. Basically, hydrogen removes the oxygen and it acts as a reducing agent.
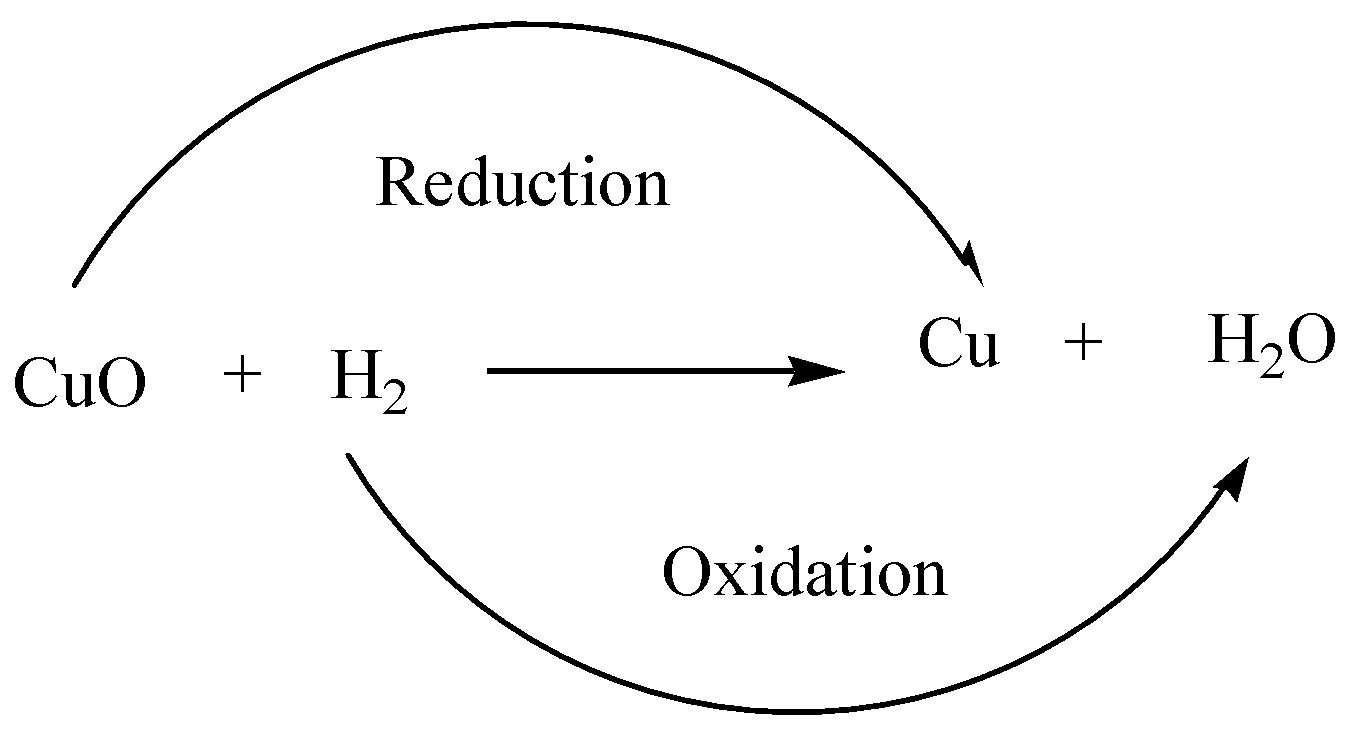
\[{\text{CuO + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{Cu + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
Note that in the above chemical reaction copper oxide (\[{\text{CuO}}\]) is reduced to copper (\[{\text{Cu}}\]) while hydrogen (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]) gets oxidised to water (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]). Hence, we can conclude that the option C is correct.
Note: 1. Hydrogen gas is a reducing agent when it reacts with nonmetals and an oxidizing agent when it reacts with metals.
2.\[{\text{CuO + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{Cu + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\], this is a type of redox reaction.
3. In oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, involves a transfer of electrons between two species.
4. Because \[{\text{CuO}}\] is reduced to \[{\text{Cu}}\]and hydrogen is oxidised to \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\].Both oxidation and reduction is taken place at the same time so it is redox reaction. We can also explain in this way, in the reaction \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] is oxidized since it has lost electrons and \[{\text{Cu}}\] is reduced since it has gained electrons.
Complete step by step solution:
First part of the question ‘When heated in air, brown copper powder turns black’; here oxidation of copper takes place.
This is the most commonly seen chemical reaction that occurs to copper. When copper gets exposed to air or heated in air, it results in the darkening of copper's surface. The formula for copper oxidation is
\[{\text{2Cu + }}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{}} \to 2{\text{CuO (black)}}\]
\[{\text{CuO}}\] is a black powder, to this if hydrogen is passed, hydrogen displaces oxygen from oxide which restores the brown colour of the copper. Basically, hydrogen removes the oxygen and it acts as a reducing agent.
\[{\text{CuO + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{Cu + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
Note that in the above chemical reaction copper oxide (\[{\text{CuO}}\]) is reduced to copper (\[{\text{Cu}}\]) while hydrogen (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]) gets oxidised to water (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]). Hence, we can conclude that the option C is correct.
Note: 1. Hydrogen gas is a reducing agent when it reacts with nonmetals and an oxidizing agent when it reacts with metals.
2.\[{\text{CuO + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{Cu + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\], this is a type of redox reaction.
3. In oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, involves a transfer of electrons between two species.
4. Because \[{\text{CuO}}\] is reduced to \[{\text{Cu}}\]and hydrogen is oxidised to \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\].Both oxidation and reduction is taken place at the same time so it is redox reaction. We can also explain in this way, in the reaction \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] is oxidized since it has lost electrons and \[{\text{Cu}}\] is reduced since it has gained electrons.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




