
What is the heat of the following reaction?
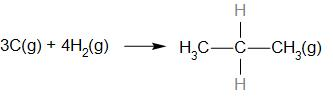
Given that BE of H-H = x, H-C = y and C-C = z.
(A) $ 4x-2z-8y $
(B) $ x-y-z $
(C) $ 4x-{\text{2}}y-2z $
(D) $ 4y + 5x-z $

Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: Enthalpy is a property of the thermodynamic system. Enthalpy is a state function. We shall calculate the number of bonds of each type and use it to relate it in the form of the equations given.
Complete Step by step solution
Thermodynamics system is a body or matter or radiation. It is confined in space with defined permeability which separates it from its surroundings. There are three types of thermodynamics systems:
-Isolated thermodynamic system
-Closed thermodynamics system
-Open thermodynamics system
Isolated thermodynamics system is confined by walls that are non-conductive of heat and perfectly reflective of all radiation. Closed thermodynamic system is confirmed by walls that are impermeable to matter. Open thermodynamic system is permeable to one chemical substance as well as to radiation.
Enthalpy is a state function and hence it depends on the final configuration of internal energy, pressure and volume and not on the path taken to achieve it. The unit of enthalpy in the international system of units is Joule. Enthalpy of ideal gas depends on temperature and not on its pressure. Heat of reaction is a change in the enthalpy of the chemical reaction that occurs at the constant pressure. The amount of energy per mole released or produced in a reaction is calculated with the help of heat of reaction. Heat of reaction is also enthalpy and hence it is a state function. Heat of reaction is positive then the reaction is endothermic and if the heat of reaction is negative it is exothermic. Heat of reaction is the amount of heat that must be added or removed during chemical reaction so that all the substances are present at the same temperature.
Bond energy is also known as mean bond enthalpy or average bond enthalpy. It is the measure of strength in a chemical bond. Bond enthalpy is defined as the total amount of energy required to break one mole of that chemical bond. Breaking of any chemical bond is always an endothermic process as energy must be supplied to break that chemical bond of the molecule.
Heat of the reaction can be calculated by subtracting the bond enthalpy of the bonds in reactant side with bond enthalpy of bonds in product side.
It is given that BE of H-H = x, H-C = y and C-C = z.
$ \Delta {\text{H}} = {\text{Reactant}}-{\text{Product}} = 4\left( x \right)-\left( {2z + 8y} \right) = 4x-2z-8y $
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note
Path dependent function depends on the path followed and state dependent function does not depend on the path followed. For example, pressure, temperature, internal energy are state functions while work done, heat absorbed are path functions.
Complete Step by step solution
Thermodynamics system is a body or matter or radiation. It is confined in space with defined permeability which separates it from its surroundings. There are three types of thermodynamics systems:
-Isolated thermodynamic system
-Closed thermodynamics system
-Open thermodynamics system
Isolated thermodynamics system is confined by walls that are non-conductive of heat and perfectly reflective of all radiation. Closed thermodynamic system is confirmed by walls that are impermeable to matter. Open thermodynamic system is permeable to one chemical substance as well as to radiation.
Enthalpy is a state function and hence it depends on the final configuration of internal energy, pressure and volume and not on the path taken to achieve it. The unit of enthalpy in the international system of units is Joule. Enthalpy of ideal gas depends on temperature and not on its pressure. Heat of reaction is a change in the enthalpy of the chemical reaction that occurs at the constant pressure. The amount of energy per mole released or produced in a reaction is calculated with the help of heat of reaction. Heat of reaction is also enthalpy and hence it is a state function. Heat of reaction is positive then the reaction is endothermic and if the heat of reaction is negative it is exothermic. Heat of reaction is the amount of heat that must be added or removed during chemical reaction so that all the substances are present at the same temperature.
Bond energy is also known as mean bond enthalpy or average bond enthalpy. It is the measure of strength in a chemical bond. Bond enthalpy is defined as the total amount of energy required to break one mole of that chemical bond. Breaking of any chemical bond is always an endothermic process as energy must be supplied to break that chemical bond of the molecule.
Heat of the reaction can be calculated by subtracting the bond enthalpy of the bonds in reactant side with bond enthalpy of bonds in product side.
It is given that BE of H-H = x, H-C = y and C-C = z.
$ \Delta {\text{H}} = {\text{Reactant}}-{\text{Product}} = 4\left( x \right)-\left( {2z + 8y} \right) = 4x-2z-8y $
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note
Path dependent function depends on the path followed and state dependent function does not depend on the path followed. For example, pressure, temperature, internal energy are state functions while work done, heat absorbed are path functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




