
What is heart? What is its function and structure?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: The human coronary heart is one of the most quintessential organs responsible for maintaining life. It is a four- chambered muscular organ. The measurement of the coronary heart is about the clenched fist.
Complete answer:
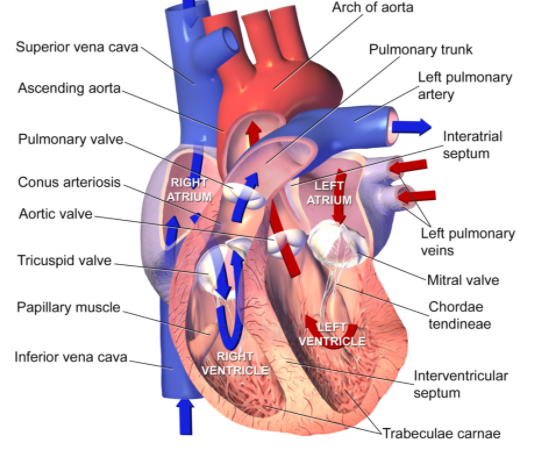
- The human heart is divided into four chambers, particularly two ventricles and two atria, and is about the size of a human fist.
- The ventricles are the chambers that pump blood and the chambers that get hold of blood are the atrium chambers. Both the proper atrium and the ventricle make up the "right heart," and the "left heart" is made up of the left atrium and ventricle. The heart structure also homes the biggest artery in the body, the aorta.
The heart's right and left regions are separated via a muscle wall called the septum. For re-oxygenation, the right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs.
Between the ventricles and atria are auriculoventricular valves. The valve between the right ventricle and proper atrium is the tricuspid valve, and the one which is placed between the left ventricle and left atrium is acknowledged as the mitral valve. Between the left ventricle and aorta lies the semilunar valve.
The heart performs the subsequent vital functions:
- The foremost operation of the middle is to pump blood during the body.
- It presents atomic variety 8 and vitamins to the tissues and gets rid of greenhouse emission and wastes from the blood.
- It moreover helps to preserve up adequate indispensable signs at some stage in the body.
- The arteries receive ventilated blood from the core and provide it at some point of the body. Whereas, the veins carry the deoxygenated blood from all the body factors to the middle for action.
The coronary heart functions inside the following ways:
- The proper atrium receives blood from the veins and pumps it to the applicable ventricle. The proper ventricle pumps the blood acquired from the applicable atrium to the lungs.
Note: Valves are flaps of fibrous tissues located between the veins in the cardiac chambers. They direct the blood flows in a single (unidirectional) direction. Flaps also prevent the backward glide of blood.
Complete answer:
- The human heart is divided into four chambers, particularly two ventricles and two atria, and is about the size of a human fist.
- The ventricles are the chambers that pump blood and the chambers that get hold of blood are the atrium chambers. Both the proper atrium and the ventricle make up the "right heart," and the "left heart" is made up of the left atrium and ventricle. The heart structure also homes the biggest artery in the body, the aorta.
The heart's right and left regions are separated via a muscle wall called the septum. For re-oxygenation, the right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs.
Between the ventricles and atria are auriculoventricular valves. The valve between the right ventricle and proper atrium is the tricuspid valve, and the one which is placed between the left ventricle and left atrium is acknowledged as the mitral valve. Between the left ventricle and aorta lies the semilunar valve.

The heart performs the subsequent vital functions:
- The foremost operation of the middle is to pump blood during the body.
- It presents atomic variety 8 and vitamins to the tissues and gets rid of greenhouse emission and wastes from the blood.
- It moreover helps to preserve up adequate indispensable signs at some stage in the body.
- The arteries receive ventilated blood from the core and provide it at some point of the body. Whereas, the veins carry the deoxygenated blood from all the body factors to the middle for action.
The coronary heart functions inside the following ways:
- The proper atrium receives blood from the veins and pumps it to the applicable ventricle. The proper ventricle pumps the blood acquired from the applicable atrium to the lungs.
Note: Valves are flaps of fibrous tissues located between the veins in the cardiac chambers. They direct the blood flows in a single (unidirectional) direction. Flaps also prevent the backward glide of blood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




