
What happens to electrons when a polar covalent bond forms?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: In chemistry, chemical bonds are three types of classification. This classification is based on electron binding in the bond. There are covalent bonds, ionic bonds and coordinate bonds. We must remember that the covalent bond is nothing but the mutually sharing of electrons between the two atoms in the molecule. The ionic bond is nothing but highly electronegativity pulls the electrons towards itself, least electronegativity atom loss the electrons in the molecule. The coordinate bond is nothing but the pair of the electrons from one atom to another atom in the molecule. It is mainly seen in coordination chemistry.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that the polar covalent bond means, in molecules having some polar bonds because dipole-dipole interaction and direction cancel each other.
For example, methane is a well known covalent molecule. But it has four polar bonds. In methane, polar bonds are formed between carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms. The electronegativity of the carbon is greater than hydrogen. Hence, in methane carbon acts as an electronegativity atom. The one electron in each hydrogen carbon attracts towards itself. That is the reason here four polar bonds are rising. But the directions of the polar bond are opposite to each other. The two polar bonds cancel another two polar bonds because of the direction of bond.
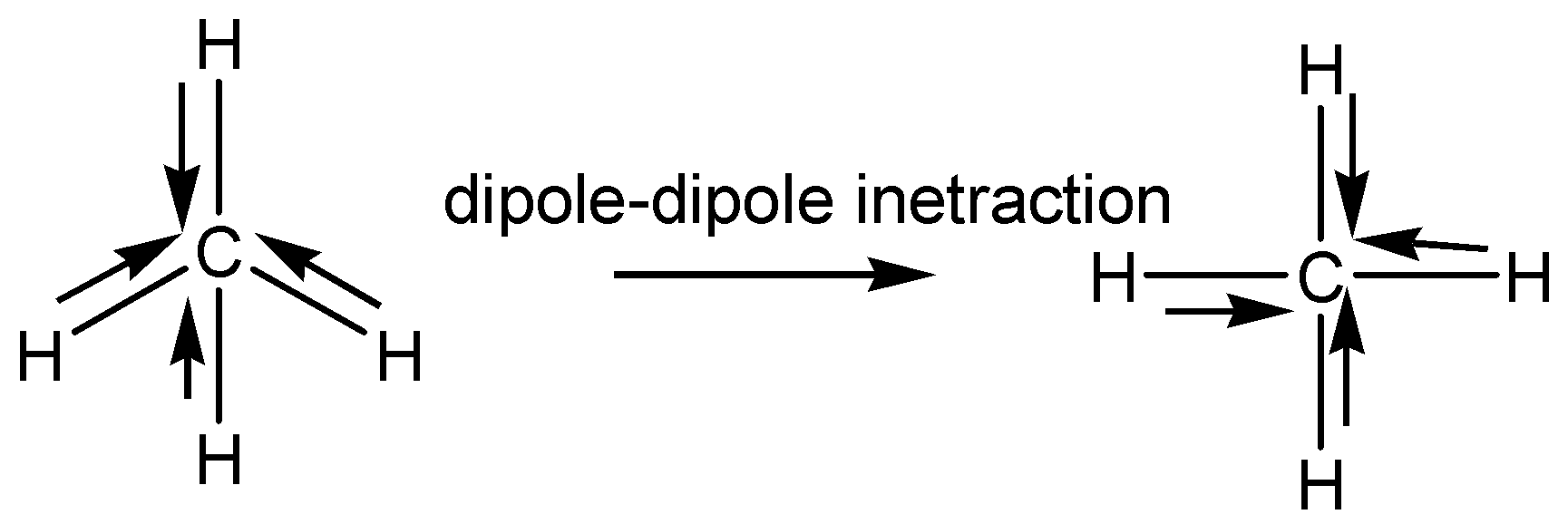
Note: We represent the arrows by using the dipole-dipole interaction direction in the molecule. The electronegativity difference in the bonded atom plays a vital role whether the bond is ionic or covalent or polar covalent bond. The electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms is lesser than \[1.7\], which means it is considered a covalent bond. If the electronegativity difference between the bonded atom is equal to \[1.7\], it is considered a polar covalent bond. If the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms is greater than\[1.7\], it means it is considered a polar bond.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that the polar covalent bond means, in molecules having some polar bonds because dipole-dipole interaction and direction cancel each other.
For example, methane is a well known covalent molecule. But it has four polar bonds. In methane, polar bonds are formed between carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms. The electronegativity of the carbon is greater than hydrogen. Hence, in methane carbon acts as an electronegativity atom. The one electron in each hydrogen carbon attracts towards itself. That is the reason here four polar bonds are rising. But the directions of the polar bond are opposite to each other. The two polar bonds cancel another two polar bonds because of the direction of bond.

Note: We represent the arrows by using the dipole-dipole interaction direction in the molecule. The electronegativity difference in the bonded atom plays a vital role whether the bond is ionic or covalent or polar covalent bond. The electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms is lesser than \[1.7\], which means it is considered a covalent bond. If the electronegativity difference between the bonded atom is equal to \[1.7\], it is considered a polar covalent bond. If the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms is greater than\[1.7\], it means it is considered a polar bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




