
What happens to cells during osmosis?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Osmosis is the movement of solvent across a semipermeable membrane toward a region of higher concentration of solute. The main difference between osmosis and diffusion is that diffusion does not require a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis is a biophysical phenomenon occurring in biological systems.
Complete answer:
In biological systems, the water molecules pass through the cell membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration to facilitate the entry and exit of important nutrients. For example, if a cell is submerged in saltwater, water molecules move out of the cell. If a cell is submerged in freshwater, water molecules move into the cell. The turgor pressure of a cell is maintained by osmosis across the cell membrane between the cell interior and its hypotonic environment. When the cell membrane has a volume of pure water on both the sides, water molecules pass in and out in each direction at exactly the same rate. There will be no net flow of water through the membrane. An animal cell has thin walls whereas a plant cell has thick walls. Due to its thick walls, plant cells require more water. The cells won’t burst when placed in a hypotonic solution. In fact, a hypotonic solution is the ideal solution for a plant cell. On the other hand, an animal cell will survive only in an isotonic solution. The leaves of a plant, however, will droop when kept in an isotonic solution. Osmosis is the process by means of which cells maintain their water content and its turgidity.
Note:
In biological systems, the solvent is usually water, but osmosis can occur in other liquids, supercritical liquids, and even gases. Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall. Isotonic solution and hypotonic solution are two types of osmotic solutions, the other one being hypertonic solution. Isotonic indicates the same concentration of solution inside and outside the cell whereas hypertonic indicates higher concentration of solution outside the cell. Hypotonic solution is the one that has higher concentration of solution inside the cell.
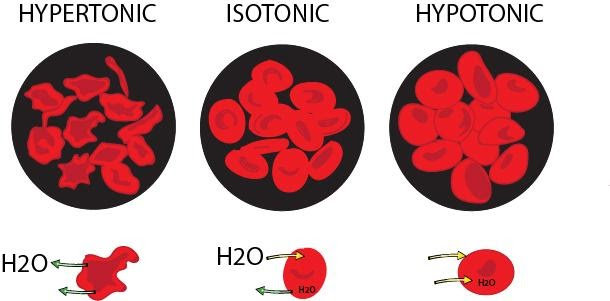
Figure 1: Types of solutions
Complete answer:
In biological systems, the water molecules pass through the cell membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration to facilitate the entry and exit of important nutrients. For example, if a cell is submerged in saltwater, water molecules move out of the cell. If a cell is submerged in freshwater, water molecules move into the cell. The turgor pressure of a cell is maintained by osmosis across the cell membrane between the cell interior and its hypotonic environment. When the cell membrane has a volume of pure water on both the sides, water molecules pass in and out in each direction at exactly the same rate. There will be no net flow of water through the membrane. An animal cell has thin walls whereas a plant cell has thick walls. Due to its thick walls, plant cells require more water. The cells won’t burst when placed in a hypotonic solution. In fact, a hypotonic solution is the ideal solution for a plant cell. On the other hand, an animal cell will survive only in an isotonic solution. The leaves of a plant, however, will droop when kept in an isotonic solution. Osmosis is the process by means of which cells maintain their water content and its turgidity.
Note:
In biological systems, the solvent is usually water, but osmosis can occur in other liquids, supercritical liquids, and even gases. Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall. Isotonic solution and hypotonic solution are two types of osmotic solutions, the other one being hypertonic solution. Isotonic indicates the same concentration of solution inside and outside the cell whereas hypertonic indicates higher concentration of solution outside the cell. Hypotonic solution is the one that has higher concentration of solution inside the cell.

Figure 1: Types of solutions
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




