
What happens in the following? Give reasons for your answer.
A. $Fe + CuS{O_4} \to $
B. $Cu + FeS{O_4} \to $
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: In the reactivity series, iron (Fe) is above copper (Cu), hence it will replace the copper in the copper sulphate compound, so the reaction will take place but copper (Cu) is below iron in the reactivity series. It is less reactive than iron, so it won’t replace the iron (Fe) in the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
The reactivity series of metals is shown below:
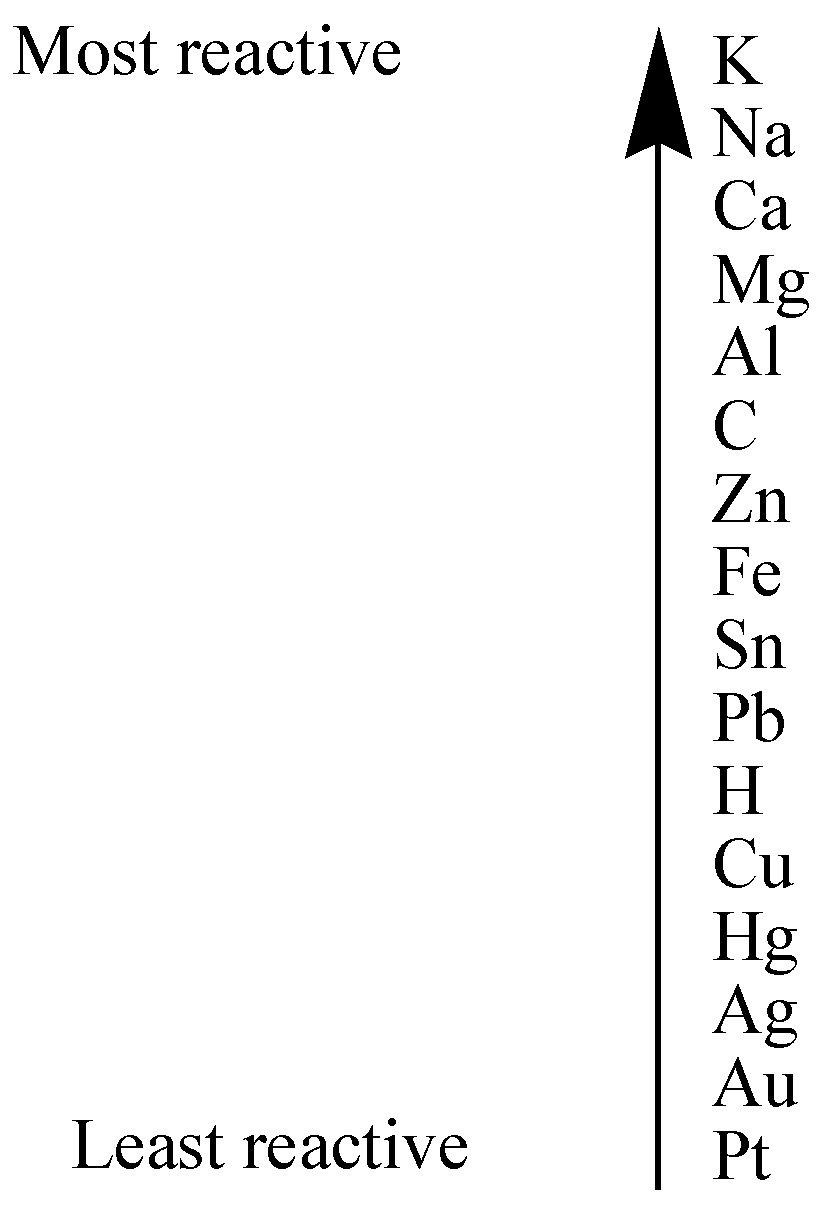
Metals that are present on top of the other metal in a reactivity series can displace the metal that are present at the bottom from its salt solution.
In the first equation,
$Fe + CuS{O_4} \to FeS{O_4} + Cu$
Since, Iron (Fe) is present on top of Copper (Cu) in the reactivity series, so it means Iron (Fe) is more reactive than copper (Cu), thus it has a greater tendency to lose electrons and form positive ion, displacing copper ion in copper sulphate solution.
Iron (Fe) will displace copper from its sulphate solution $(CuS{O_4})$ and form Ferrous sulphate $(FeS{O_4})$. This is a typical example of a single displacement reaction where one metal displaces another is the reaction between iron and copper sulphate, Therefore, Fe is more reactive than Cu.
Reactivity of Iron (Fe) > Reactivity of Copper (Cu).
In the second equation,
$Cu + FeS{O_4} \to $ no reaction
However, since Copper (Cu) is below iron (Fe) in the reactivity series, therefore it is less reactive than iron and therefore unable to displace the ferrous ion $(F{e^{2 + }})$ in ferrous sulphate solution. Hence, the reaction will not occur in this situation.
Note: Iron (Fe) forms 2 types of ions i.e. $F{e^{2 + }}$ and $F{e^{3 + }}$. We will then use the stoichiometric principles to determine which of these ions is formed in the reaction between iron and copper (II) sulphate solution.
Complete step by step answer:
The reactivity series of metals is shown below:

Metals that are present on top of the other metal in a reactivity series can displace the metal that are present at the bottom from its salt solution.
In the first equation,
$Fe + CuS{O_4} \to FeS{O_4} + Cu$
Since, Iron (Fe) is present on top of Copper (Cu) in the reactivity series, so it means Iron (Fe) is more reactive than copper (Cu), thus it has a greater tendency to lose electrons and form positive ion, displacing copper ion in copper sulphate solution.
Iron (Fe) will displace copper from its sulphate solution $(CuS{O_4})$ and form Ferrous sulphate $(FeS{O_4})$. This is a typical example of a single displacement reaction where one metal displaces another is the reaction between iron and copper sulphate, Therefore, Fe is more reactive than Cu.
Reactivity of Iron (Fe) > Reactivity of Copper (Cu).
In the second equation,
$Cu + FeS{O_4} \to $ no reaction
However, since Copper (Cu) is below iron (Fe) in the reactivity series, therefore it is less reactive than iron and therefore unable to displace the ferrous ion $(F{e^{2 + }})$ in ferrous sulphate solution. Hence, the reaction will not occur in this situation.
Note: Iron (Fe) forms 2 types of ions i.e. $F{e^{2 + }}$ and $F{e^{3 + }}$. We will then use the stoichiometric principles to determine which of these ions is formed in the reaction between iron and copper (II) sulphate solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




