
What happens in internal respiration?
Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: Respiration is the process of taking in oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide. The oxygen is used to oxidise glucose so as to liberate energy in the form of ATP. Respiration is of two types external and internal. In internal respiration, the gaseous exchange occurs between the blood and the cells.
Complete answer:
The main organ of respiration in our body is the lungs. We breathe in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. The gaseous exchange takes place at the alveoli where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the alveoli and the blood. This is known as external respiration. The gaseous exchange further takes place between the blood and the cells. This is termed internal respiration.
Let us discuss in detail internal respiration-
The gaseous exchange mainly occurs through diffusion. The carbon dioxide is given out as waste and oxygen are taken in. In internal respiration, the oxygen from the blood diffuses to the cells of the body. The oxygen is transported by the haemoglobin present in the blood. It is further transported to various cells through the blood stream.
The diffusion takes place between the bloodstream and the cells. Once the oxygen reaches every cell, the glucose is metabolised by the process of glycolysis in the cytoplasm and further, the release of energy takes place in mitochondria. The energy released is utilised by the cells to carry out other metabolic activities.
The diffusion of gases is shown in the figure below.
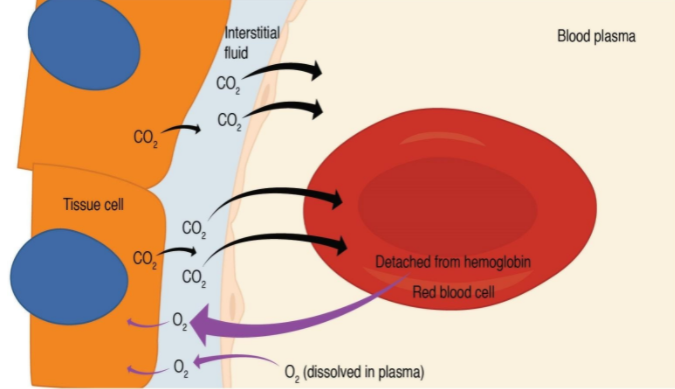
Note: The respiration which takes place in the presence of oxygen is known as aerobic respiration. In certain cases, like during strenuous exercise, due to lack of oxygen, the muscles respire anaerobically and forms lactate. This lactate is deposited in the muscles is the main reason cause fatigue.
Complete answer:
The main organ of respiration in our body is the lungs. We breathe in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. The gaseous exchange takes place at the alveoli where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the alveoli and the blood. This is known as external respiration. The gaseous exchange further takes place between the blood and the cells. This is termed internal respiration.
Let us discuss in detail internal respiration-
The gaseous exchange mainly occurs through diffusion. The carbon dioxide is given out as waste and oxygen are taken in. In internal respiration, the oxygen from the blood diffuses to the cells of the body. The oxygen is transported by the haemoglobin present in the blood. It is further transported to various cells through the blood stream.
The diffusion takes place between the bloodstream and the cells. Once the oxygen reaches every cell, the glucose is metabolised by the process of glycolysis in the cytoplasm and further, the release of energy takes place in mitochondria. The energy released is utilised by the cells to carry out other metabolic activities.
The diffusion of gases is shown in the figure below.

Note: The respiration which takes place in the presence of oxygen is known as aerobic respiration. In certain cases, like during strenuous exercise, due to lack of oxygen, the muscles respire anaerobically and forms lactate. This lactate is deposited in the muscles is the main reason cause fatigue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




