
What happened when:
$B{{F}_{3}}$ is reacted with ammonia?
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: The $B{{F}_{3}}$ is a Lewis acid i.e. an electron deficient species and $N{{H}_{3}}$ is a Lewis base, a species which consists of lone pairs that can be donated for the formation of bonds.
- $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule consists of a lone pair of electrons .
Complete Solution :
So here in the question we are asked to predict what happens when $N{{H}_{3}}$ and $B{{F}_{3}}$ reacts together.
Before predicting the product let’s see some characteristics of ammonia and boron trifluoride.
So in $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule B is the central atom and we know that the$B{{F}_{3}}$ is a Lewis acid i.e. an electron deficient species.
- The atomic number of B is 5 and has an electronic configuration:
$\text{E}\text{.C}\,\text{of}\,\text{B=1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{1}}}$
- The valency possessed by the B atom is +3.
- The hybridization of $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and hence having a planar structure.
- In $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule, N is the central atom having the atomic number 7 and the electronic configuration is,
$\text{E}\text{.C}\,\text{of}\,\text{N=1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$
Ammonia is a $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized molecule in which one lone pair is present and hence having a trigonal pyramidal structure.
So as we discussed earlier $B{{F}_{3}}$ is a Lewis acid and requires two electrons for B to obtain the octet configuration and $N{{H}_{3}}$ consists of one lone pair of electron and it acts as the Lewis base according to Lewis theory.
Hence the $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule donates its lone pair of electrons to the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule and forms a coordinate bond.
So the ammonia and boron trifluoride on reactions forms an adduct.
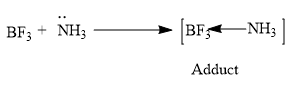
$N{{H}_{3}}$ The hybridization of this adduct formed is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized adduct.
Note: The hybridization of a molecule is calculate using the formulae,
$\text{steric number = No}\text{. of bps + No}\text{.of lps}$
Bps refers to bond pairs and lps refers to lone pairs and the steric number obtained will give an idea about the hybridization of the molecule.
- $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule consists of a lone pair of electrons .
Complete Solution :
So here in the question we are asked to predict what happens when $N{{H}_{3}}$ and $B{{F}_{3}}$ reacts together.
Before predicting the product let’s see some characteristics of ammonia and boron trifluoride.
So in $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule B is the central atom and we know that the$B{{F}_{3}}$ is a Lewis acid i.e. an electron deficient species.
- The atomic number of B is 5 and has an electronic configuration:
$\text{E}\text{.C}\,\text{of}\,\text{B=1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{1}}}$
- The valency possessed by the B atom is +3.
- The hybridization of $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and hence having a planar structure.
- In $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule, N is the central atom having the atomic number 7 and the electronic configuration is,
$\text{E}\text{.C}\,\text{of}\,\text{N=1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$
Ammonia is a $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized molecule in which one lone pair is present and hence having a trigonal pyramidal structure.
So as we discussed earlier $B{{F}_{3}}$ is a Lewis acid and requires two electrons for B to obtain the octet configuration and $N{{H}_{3}}$ consists of one lone pair of electron and it acts as the Lewis base according to Lewis theory.
Hence the $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule donates its lone pair of electrons to the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule and forms a coordinate bond.
So the ammonia and boron trifluoride on reactions forms an adduct.

$N{{H}_{3}}$ The hybridization of this adduct formed is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized adduct.
Note: The hybridization of a molecule is calculate using the formulae,
$\text{steric number = No}\text{. of bps + No}\text{.of lps}$
Bps refers to bond pairs and lps refers to lone pairs and the steric number obtained will give an idea about the hybridization of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




