
Haplo-diplontic life cycle is found in
a. Bryophytes
b. Pteridophytes
c. Fungi
d. Both (A) & (B)
Answer
523.1k+ views
Hint: In haplo-diplontic, the mitosis takes place in both diploid and haploid cells. Such an organism shows "alternation of the generation" during their life cycle where the gametophyte is multicellular and haploid, while the sporophyte is multicellular and diploid.
Complete answer:
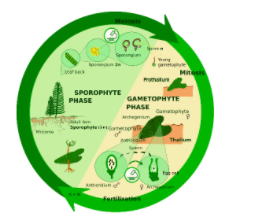
Haplo-diplontic life cycle involves the alternation of generations between a haploid gametophyte and a diploid sporophyte. Bryophytes and pteridophytes exhibit this life cycle.
Features of haplo-diplontic life cycle:
> The life cycle has two phases
> One phase is haploid gametophyte and the other is diploid sporophyte
> Diploid structure or zygote develops into diploid sporophytic generation
> Sporophyte produce sporangia that by meiosis produce haploid zoospores
> Zoospores develop into a haploid gametophytic generation
> Gametophyte produce gametes
> Male and female gametes fuse to form the diploid zygote
> There are two types of the haplodiplontic life cycle: a) Isomorphic b) Heteromorphic
So, the correct answer is option (D) Both A and B
Note: A haploid gametophyte represents a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, thalloid or erect phase. The dominant phase alternates with the short-lived multicellular sporophyte. The sporophyte is totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte for anchorage and nutrition. All bryophytes represent this pattern. In the case of the pteridophytes, the sporophyte is the dominant phase and represents an independent, photosynthetic, vascular plant body. This alternates with gametophyte which is haploid, multicellular, saprophytic/autotrophic, independent and short-lived. This pattern represents a haplo-diplontic life cycle. All pteridophytes exhibit this pattern. Example- Exceptionally Algae such as Ectocarpus, Polysiphonia, kelps. Pteridophytes example- Lycopodium, Selaginella, Equisetum, Pteris, Dryopteris, Adiantum. Bryophytes example- Moss and liverworts
Complete answer:

Haplo-diplontic life cycle involves the alternation of generations between a haploid gametophyte and a diploid sporophyte. Bryophytes and pteridophytes exhibit this life cycle.
Features of haplo-diplontic life cycle:
> The life cycle has two phases
> One phase is haploid gametophyte and the other is diploid sporophyte
> Diploid structure or zygote develops into diploid sporophytic generation
> Sporophyte produce sporangia that by meiosis produce haploid zoospores
> Zoospores develop into a haploid gametophytic generation
> Gametophyte produce gametes
> Male and female gametes fuse to form the diploid zygote
> There are two types of the haplodiplontic life cycle: a) Isomorphic b) Heteromorphic
So, the correct answer is option (D) Both A and B
Note: A haploid gametophyte represents a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, thalloid or erect phase. The dominant phase alternates with the short-lived multicellular sporophyte. The sporophyte is totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte for anchorage and nutrition. All bryophytes represent this pattern. In the case of the pteridophytes, the sporophyte is the dominant phase and represents an independent, photosynthetic, vascular plant body. This alternates with gametophyte which is haploid, multicellular, saprophytic/autotrophic, independent and short-lived. This pattern represents a haplo-diplontic life cycle. All pteridophytes exhibit this pattern. Example- Exceptionally Algae such as Ectocarpus, Polysiphonia, kelps. Pteridophytes example- Lycopodium, Selaginella, Equisetum, Pteris, Dryopteris, Adiantum. Bryophytes example- Moss and liverworts
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




