
\[{{H}_{2}}O\] is liquid but \[{{H}_{2}}S\] is gas. This is because of:
(A)- larger size of S
(B)- acidic nature of \[{{H}_{2}}S\]
(C)- hydrogen bonding
(D)- small size of O
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: Hydrogen bonding is a type of weak interaction between a hydrogen atom bonded to an atom of high electron affinity (e.g. N, O, and F) and an electron rich atom with high electron affinity. It is, therefore, a weak bond between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom bonded to another electronegative atom.
Complete step by step solution:
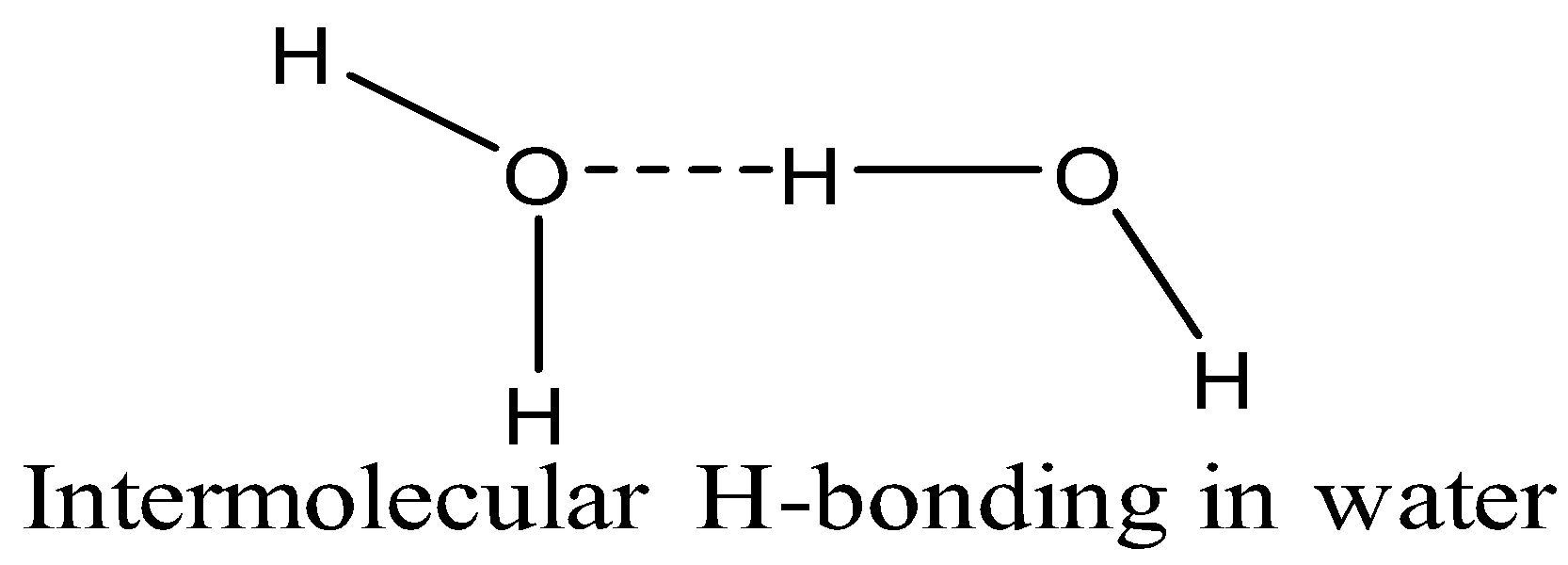
\[{{H}_{2}}O\] and \[{{H}_{2}}S\] are the hydrides of group 16. The hydride of oxygen i.e. \[{{H}_{2}}O\] is liquid whereas the hydride of sulphur is in gaseous state. The reason for this difference in their physical states is the ability of water molecules to undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
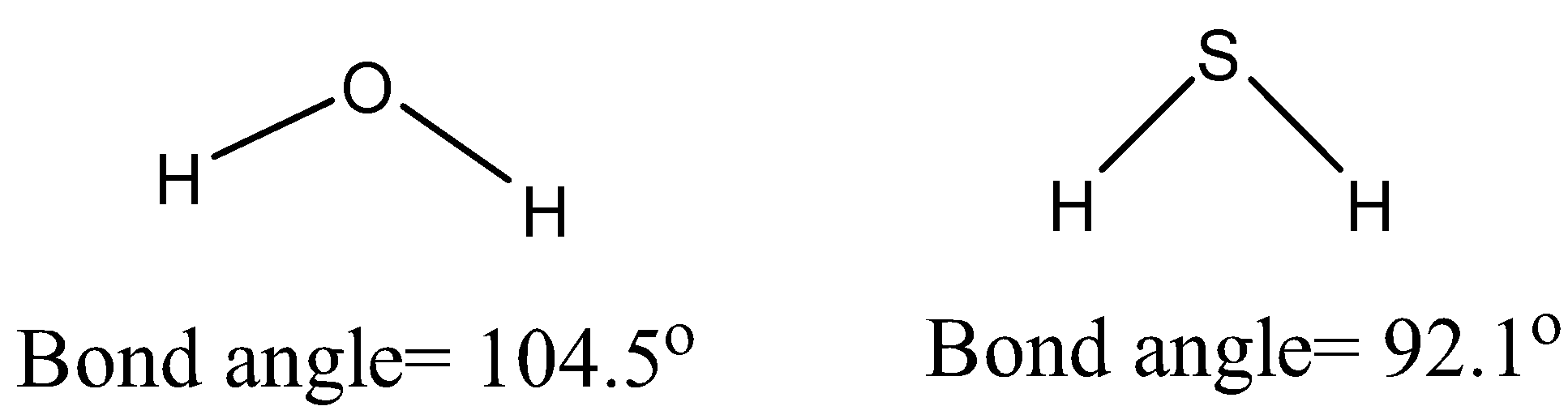
Oxygen is the most electronegative of all the elements in group 16. Since it has more electron affinity than sulphur, its hydride i.e. \[{{H}_{2}}O\], undergoes intermolecular hydrogen bonding. O of one \[{{H}_{2}}O\] molecule is bonded with the hydrogen of another \[{{H}_{2}}O\]molecule. In this way, \[{{H}_{2}}O\] molecules are held together by H-bonding. No such interactions are present among \[{{H}_{2}}S\] molecules and are only held together by weak van der Waals forces of attraction.
As electronegativity decreases with the increase in sizes down the group, other elements including S, Se, and Te do not form hydrogen bonds. Therefore, their hydrides are all in gaseous state.
 The correct option is (C).
The correct option is (C).
Additional Information: The hydrides of other elements of group 16 excluding \[{{H}_{2}}O\] are poisonous, unpleasant and foul smelling gases. They all are volatile and \[{{H}_{2}}O\] has the highest boiling point.
Note: Due to the smaller size of O, its electronegativity is higher than S. But intermolecular hydrogen bonding is the most adequate explanation for the difference in physical states of \[{{H}_{2}}O\] and\[{{H}_{2}}S\].
Complete step by step solution:
\[{{H}_{2}}O\] and \[{{H}_{2}}S\] are the hydrides of group 16. The hydride of oxygen i.e. \[{{H}_{2}}O\] is liquid whereas the hydride of sulphur is in gaseous state. The reason for this difference in their physical states is the ability of water molecules to undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Oxygen is the most electronegative of all the elements in group 16. Since it has more electron affinity than sulphur, its hydride i.e. \[{{H}_{2}}O\], undergoes intermolecular hydrogen bonding. O of one \[{{H}_{2}}O\] molecule is bonded with the hydrogen of another \[{{H}_{2}}O\]molecule. In this way, \[{{H}_{2}}O\] molecules are held together by H-bonding. No such interactions are present among \[{{H}_{2}}S\] molecules and are only held together by weak van der Waals forces of attraction.
As electronegativity decreases with the increase in sizes down the group, other elements including S, Se, and Te do not form hydrogen bonds. Therefore, their hydrides are all in gaseous state.


Additional Information: The hydrides of other elements of group 16 excluding \[{{H}_{2}}O\] are poisonous, unpleasant and foul smelling gases. They all are volatile and \[{{H}_{2}}O\] has the highest boiling point.
Note: Due to the smaller size of O, its electronegativity is higher than S. But intermolecular hydrogen bonding is the most adequate explanation for the difference in physical states of \[{{H}_{2}}O\] and\[{{H}_{2}}S\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




