
Guttation is a process of water loss
in
(a) Liquid form containing dissolved minerals
(b) Liquid form without dissolved minerals
(c) Vapour form with minerals
(d) Vapour form without minerals
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Guttation is an adaptation for the elimination of surplus water. Usually, it occurs from the margins of tips of leaves through stomata like pores, called hydathodes, or 'water stomata’. Exudation sometimes occurs through scars and lenticels of the stem also. By guttation, fully turgid plants remove extra water.
Complete answer:
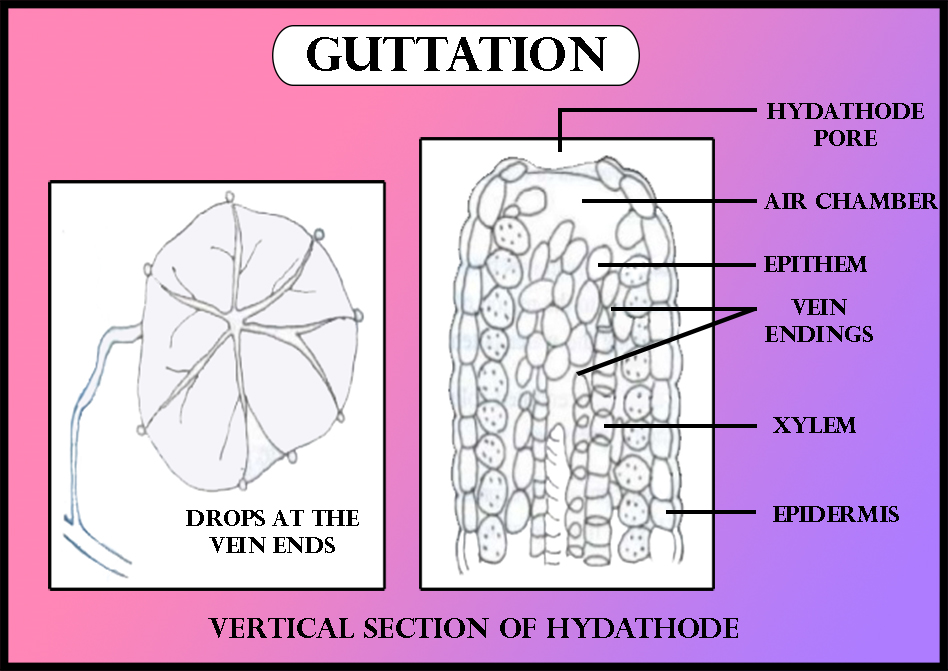
Guttation is the exudation of liquid drops with dissolved inorganic solutes from uninjured xylem endings. So the plant loses water in liquid form. It is common in tropical herbaceous plants, growing under conditions of high atmospheric humidity, high water absorption, and very low transpiration. Root pressure is the major cause of guttation. Guttation water exudes through hydathodes or water stomata, seen at xylem terminals of leaves. It occurs in some plants like grasses, tomatoes, colocasia, etc. The amount of the exudate may vary from a few too many drops. Its quality also varies from pure water to a dilute solution of organic and inorganic solutes, such as aspartic acid, asparagine, several sugars, and various inorganic compounds. Thus, guttation is a process of water loss in liquid form containing dissolved minerals. Guttation is less important to plants. High humidity and low transpiration increase guttation.
Additional Information: -Guttation is the process of expulsion of excess water from plants through hydathodes or water stomata.
-Hydathodes are stomata-like pores generally present at the tips or margins of the leaves of those plants, which grows in moist shady places.
-Water pores are present over a mass of loosely arranged cells, called epithem.
- In between the cells are intercellular spaces.
-The driving force of guttation is the root pressure that develops in the xylem sap of roots.
-It pushes up the xylem sap and forces it out through the intercellular spaces of the epithem and the hydathodes.
-Guttation water is a solution of inorganic and organic solutes such as aspartic acid, asparagine, several sugars, and other organic compounds.
So, the correct answer is ‘Liquid form containing dissolved minerals.’
Note: Guttation occurs particularly at night under conditions of high humidity. It is an unregulated process. Morning dews on grasses, colocasia, tomato, etc., are often due to guttation. Sometimes, it may cause injury to the leaf margins by salt deposition due to the evaporation of exudate. This may invite pathogenic organisms, such as fungi and bacteria.
Complete answer:
Guttation is the exudation of liquid drops with dissolved inorganic solutes from uninjured xylem endings. So the plant loses water in liquid form. It is common in tropical herbaceous plants, growing under conditions of high atmospheric humidity, high water absorption, and very low transpiration. Root pressure is the major cause of guttation. Guttation water exudes through hydathodes or water stomata, seen at xylem terminals of leaves. It occurs in some plants like grasses, tomatoes, colocasia, etc. The amount of the exudate may vary from a few too many drops. Its quality also varies from pure water to a dilute solution of organic and inorganic solutes, such as aspartic acid, asparagine, several sugars, and various inorganic compounds. Thus, guttation is a process of water loss in liquid form containing dissolved minerals. Guttation is less important to plants. High humidity and low transpiration increase guttation.
Additional Information: -Guttation is the process of expulsion of excess water from plants through hydathodes or water stomata.
-Hydathodes are stomata-like pores generally present at the tips or margins of the leaves of those plants, which grows in moist shady places.
-Water pores are present over a mass of loosely arranged cells, called epithem.
- In between the cells are intercellular spaces.
-The driving force of guttation is the root pressure that develops in the xylem sap of roots.
-It pushes up the xylem sap and forces it out through the intercellular spaces of the epithem and the hydathodes.
-Guttation water is a solution of inorganic and organic solutes such as aspartic acid, asparagine, several sugars, and other organic compounds.
So, the correct answer is ‘Liquid form containing dissolved minerals.’
Note: Guttation occurs particularly at night under conditions of high humidity. It is an unregulated process. Morning dews on grasses, colocasia, tomato, etc., are often due to guttation. Sometimes, it may cause injury to the leaf margins by salt deposition due to the evaporation of exudate. This may invite pathogenic organisms, such as fungi and bacteria.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




