
How do Grignard reagents react with alcohols?
Answer
522.3k+ views
Hint :Grignard reagent: It is a very useful organometallic compound which consists of magnesium atoms bonded to a halogen and an alkyl group. General formula of Grignard reagent is $ R - Mg - X $ . It is used in various specific tests to determine functional groups of unknown compounds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The haloalkane when react to magnesium in the presence of vinyl or aryl halides, formation of a very important organometallic compound i.e., Grignard reagent takes place as follows:
The mechanism for the formation of Grignard reagents is as follows:
Step-1: Homolytic cleavage of $ R - X $ bond takes place in haloalkanes.
$ R - X \to {R^ \bullet } + {X^ \bullet } $
Step-2: Attack of halogen radical on magnesium atoms.
$ {X^ \bullet } + Mg \to {}^ \bullet MgX $
Step-3: Attack of $ {R^ \bullet } $ on the product formed in step-2.
$ {R^ \bullet } + {}^ \bullet MgX \to R - Mg - X $
Grignard reagent is a good nucleophile as well as a strong base, so it can react with compounds having functional groups like epoxide, ketone, aldehydic, and alcohol. When alcohols react with Grignard reagent, then the acid-base reaction takes place and formation of magnesium alkoxide and respective alkane takes place. The reaction is as follows:
$ R - OH + R'MgX \to R - OMgX + R' - H $
Hence Grignard reagent reacts with alcohols to form respective alkanes.
Additional Information:
Reaction of Grignard reagent with compounds having carbonyl groups to give alcohol as a product:
Grignard reagent attacks at carbonyl centres of the compounds to form an intermediate which on further reaction forms alcohol and hydroxy-magnesium halide. The reaction proceeds as follows:
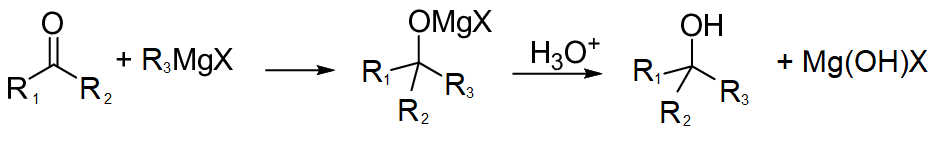
Note :
Grignard reagent acts as both a nucleophile as well as a base. But at priority, it will act as a good base rather than nucleophile because acid-base reactions are very fast as compared to other reactions.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The haloalkane when react to magnesium in the presence of vinyl or aryl halides, formation of a very important organometallic compound i.e., Grignard reagent takes place as follows:
The mechanism for the formation of Grignard reagents is as follows:
Step-1: Homolytic cleavage of $ R - X $ bond takes place in haloalkanes.
$ R - X \to {R^ \bullet } + {X^ \bullet } $
Step-2: Attack of halogen radical on magnesium atoms.
$ {X^ \bullet } + Mg \to {}^ \bullet MgX $
Step-3: Attack of $ {R^ \bullet } $ on the product formed in step-2.
$ {R^ \bullet } + {}^ \bullet MgX \to R - Mg - X $
Grignard reagent is a good nucleophile as well as a strong base, so it can react with compounds having functional groups like epoxide, ketone, aldehydic, and alcohol. When alcohols react with Grignard reagent, then the acid-base reaction takes place and formation of magnesium alkoxide and respective alkane takes place. The reaction is as follows:
$ R - OH + R'MgX \to R - OMgX + R' - H $
Hence Grignard reagent reacts with alcohols to form respective alkanes.
Additional Information:
Reaction of Grignard reagent with compounds having carbonyl groups to give alcohol as a product:
Grignard reagent attacks at carbonyl centres of the compounds to form an intermediate which on further reaction forms alcohol and hydroxy-magnesium halide. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Note :
Grignard reagent acts as both a nucleophile as well as a base. But at priority, it will act as a good base rather than nucleophile because acid-base reactions are very fast as compared to other reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




