
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is $30^\circ $.Find
i) Polarising angle, and
ii) Refractive index of medium.
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Just remember, When light is incident at the polarising angle of a medium, the part of the light is reflected and becomes polarised. Some part of the ray is refracted and becomes slightly polarised. The $\tan $ of the polarising angle is simply the refractive index of the medium.
Complete step by step solution:
This situation can be best described by the following diagram.
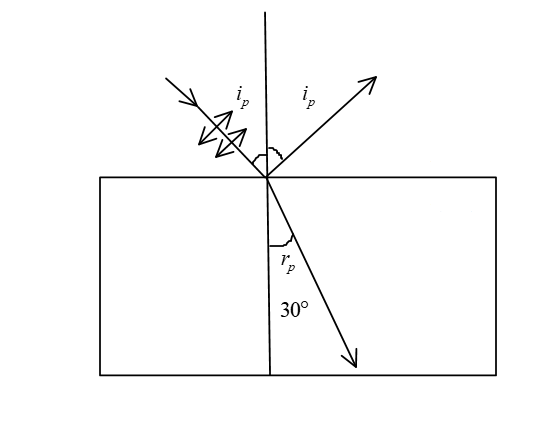
Here, the incident light is at a polarizing angle on the transparent medium. First, we need to realize what happens when light is incident at a polarizing angle and what is a polarizing angle.
The Polarizing angle is the angle of incidence such that, after the incidence, the refracted ray and the reflected ray makes an angle of ${90^ \circ }$. When an unpolarised light is incident on the glass, the reflected light will be perfectly polarised and refracted light will be slightly polarised.
i) Now, as we can see in the diagram, the reflected and refracted ray make an angle of ${90^ \circ }$, by simple geometry, we can write:
${i_p} + {r_p} = {90^ \circ }$, or
$ \Rightarrow {i_p} = {90^ \circ } - {r_p}$
Here, the angle of refraction is given, ${r_p} = 30^\circ $. Hence we can simply find the angle of incidence or polarizing angle ${i_p}$ by,
${i_p} = {90^ \circ } - {30^\circ } = 60^\circ $
Therefore, the polarizing angle or the angle of incidence is $60^\circ$.
ii) Refractive index
Now we know that,
${i_p} + {r_p} = {90^ \circ }$
Where, ${i_p}$ is the angle of incidence and ${r_p}$ is the angle of refraction. Hence we can apply Snell’s law which states that,
${n_1}\sin {i_p} = {n_2}\sin {r_p}$
Where, ${n_1}$ and ${n_2}$ are the refractive indices of the medium 1 and 2.
Now, we also know that, ${r_p} = {90^ \circ } - {i_p}$ , on substituting ${r_p}$ in the Snell’s law equation, we get,
${n_1}\sin {i_p} = {n_2}\sin ({90^ \circ } - {i_p})$, or
$ \Rightarrow {n_1}\sin {i_p} = {n_2}\cos {i_p}$
Hence, finally, we can write the refractive index of the medium as given below,
$\mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} = \tan {i_p}$
Now, we have derived the formula for the refractive index, we can simply put the value of ${i_p}$ and get the result.
$\mu = \tan {60^ \circ } = 1.732$
Therefore, the refractive index of the medium is 1.732
Note: The polarizing angle is also known as Brewster’s angle. It is important to note that the angle between the refracted and reflected ray is ${90^ \circ }$. The reflected ray is completely polarised as opposed to the refracted ray which is slightly polarised.
Complete step by step solution:
This situation can be best described by the following diagram.

Here, the incident light is at a polarizing angle on the transparent medium. First, we need to realize what happens when light is incident at a polarizing angle and what is a polarizing angle.
The Polarizing angle is the angle of incidence such that, after the incidence, the refracted ray and the reflected ray makes an angle of ${90^ \circ }$. When an unpolarised light is incident on the glass, the reflected light will be perfectly polarised and refracted light will be slightly polarised.
i) Now, as we can see in the diagram, the reflected and refracted ray make an angle of ${90^ \circ }$, by simple geometry, we can write:
${i_p} + {r_p} = {90^ \circ }$, or
$ \Rightarrow {i_p} = {90^ \circ } - {r_p}$
Here, the angle of refraction is given, ${r_p} = 30^\circ $. Hence we can simply find the angle of incidence or polarizing angle ${i_p}$ by,
${i_p} = {90^ \circ } - {30^\circ } = 60^\circ $
Therefore, the polarizing angle or the angle of incidence is $60^\circ$.
ii) Refractive index
Now we know that,
${i_p} + {r_p} = {90^ \circ }$
Where, ${i_p}$ is the angle of incidence and ${r_p}$ is the angle of refraction. Hence we can apply Snell’s law which states that,
${n_1}\sin {i_p} = {n_2}\sin {r_p}$
Where, ${n_1}$ and ${n_2}$ are the refractive indices of the medium 1 and 2.
Now, we also know that, ${r_p} = {90^ \circ } - {i_p}$ , on substituting ${r_p}$ in the Snell’s law equation, we get,
${n_1}\sin {i_p} = {n_2}\sin ({90^ \circ } - {i_p})$, or
$ \Rightarrow {n_1}\sin {i_p} = {n_2}\cos {i_p}$
Hence, finally, we can write the refractive index of the medium as given below,
$\mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} = \tan {i_p}$
Now, we have derived the formula for the refractive index, we can simply put the value of ${i_p}$ and get the result.
$\mu = \tan {60^ \circ } = 1.732$
Therefore, the refractive index of the medium is 1.732
Note: The polarizing angle is also known as Brewster’s angle. It is important to note that the angle between the refracted and reflected ray is ${90^ \circ }$. The reflected ray is completely polarised as opposed to the refracted ray which is slightly polarised.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




