
Graphite and diamonds are made up of carbon atoms. Graphite, however, is soft and can be used to write with while diamonds are the hardest substance known to man and are the only substances that can be used to cut other diamonds. What is the main reason for this difference?
A) The carbon atoms in graphite are covalently bonded while carbon atoms in diamonds are ionically bonded.
B) The bonds within a layer of graphite are relatively strong but the bonds between the layers of the graphite are relatively weaker. The bonds between the carbon atoms of a diamond are relatively strong throughout the entire structure.
C) The bonds within the layers of graphite are relatively weak, allowing for the atoms to slide past each other. The bonds between the atoms in diamond have a limited capacity to slide.
D) Graphite is held together by covalent bonds while diamond is held together by London Dispersion Forces.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: We know that physical as well as chemical properties are the result from the characteristic structure of a given compound which is why even compounds made from the same element can have different properties.
Complete answer:
Graphite and diamond are two quite known allotropes of carbon. Both the graphite as well as diamond are made up of carbon atoms but have very different properties. So, in order to be able to understand and explain these, we have to look at their structures for structures to a great extent.
Let’s have a look at the crystalline structure of graphite. In graphite, each carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ hybridized and bonded to three other carbon atoms forming hexagonal rings which are planar that can be shown as follows:

These hexagonal rings form sheets giving graphite a layered structure in which Van der Waals forces hold these sheets together and make graphite soft and slippery. The layered structure can be shown as follows:
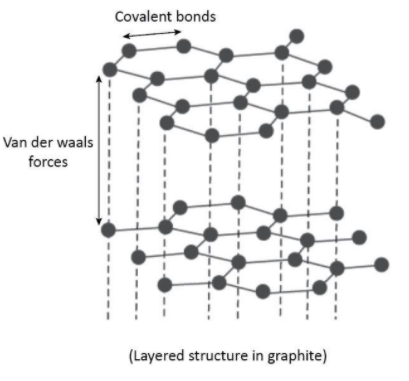
The three electrons of each carbon atom are used in bonding whereas one electron from each carbon is involved in $\pi $ bonding and these are delocalized. These delocalized electrons make graphite a good electric conductor.
Now, we will have a look at the crystalline structure of diamond. In diamond, each carbon atom is $s{p^3}$ hybridized and bonded to four other carbon atoms that can be shown as follows:
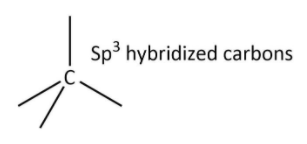
These tetrahedrons are extended in 3-D giving diamond an extended and rigid structure in which there are directional covalent bonds only and make diamond, the hardest substance known to us. The extended structure can be shown as follows:

All four electrons of each carbon atom are used in bonding so there is no delocalization as we saw in graphite.
From the above discussion, we can conclude that there is covalent bonding between the carbon atoms in both the graphite as well as diamond but it is the weaker Van der Waals forces acting between the layers in graphite which make it soft whereas no such layers or weaker forces are there in diamond.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The difference in the crystal structure of graphite and diamond leads to many other different properties such as diamond having the highest melting and boiling point even when it is made from a non-metal or graphite being a good conductor of electricity and used as electrode.
Complete answer:
Graphite and diamond are two quite known allotropes of carbon. Both the graphite as well as diamond are made up of carbon atoms but have very different properties. So, in order to be able to understand and explain these, we have to look at their structures for structures to a great extent.
Let’s have a look at the crystalline structure of graphite. In graphite, each carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ hybridized and bonded to three other carbon atoms forming hexagonal rings which are planar that can be shown as follows:

These hexagonal rings form sheets giving graphite a layered structure in which Van der Waals forces hold these sheets together and make graphite soft and slippery. The layered structure can be shown as follows:

The three electrons of each carbon atom are used in bonding whereas one electron from each carbon is involved in $\pi $ bonding and these are delocalized. These delocalized electrons make graphite a good electric conductor.
Now, we will have a look at the crystalline structure of diamond. In diamond, each carbon atom is $s{p^3}$ hybridized and bonded to four other carbon atoms that can be shown as follows:

These tetrahedrons are extended in 3-D giving diamond an extended and rigid structure in which there are directional covalent bonds only and make diamond, the hardest substance known to us. The extended structure can be shown as follows:

All four electrons of each carbon atom are used in bonding so there is no delocalization as we saw in graphite.
From the above discussion, we can conclude that there is covalent bonding between the carbon atoms in both the graphite as well as diamond but it is the weaker Van der Waals forces acting between the layers in graphite which make it soft whereas no such layers or weaker forces are there in diamond.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The difference in the crystal structure of graphite and diamond leads to many other different properties such as diamond having the highest melting and boiling point even when it is made from a non-metal or graphite being a good conductor of electricity and used as electrode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




