
How do you graph \[y=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\]?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: In order to find the graph of the given equation in the question that is \[y=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\], find the points that satisfy this equation and then plot them in the graph.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation in the question is as follows
\[y=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\]
Consider the above equation as the function\[f\left( x \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\]
To find the points that satisfy this equation first consider the point at \[x=-3\]
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[-3\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -3 \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{-3}{3} \right)=\pi \]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -3 \right)=\pi \]
Now consider the point at \[x=\dfrac{-3}{2}\]
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[\dfrac{-3}{2}\]in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{2}}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and multiply the numerator by the reciprocal of the denominator.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( -\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Cancel the common factor of \[3\] to do this follow the following steps:
Move the leading negative in \[\dfrac{-3}{2}\]into the numerator.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( -\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Factor \[3\] out of \[-3\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{3\left( -1 \right)}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Cancel the common factor.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{{3}\cdot -1}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{{{3}}} \right)\]
Rewrite the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)\]
Move the negative in front of the fraction.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\] is \[\dfrac{2\pi }{3}\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}\]
After this consider the point at \[x=0\]
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[0\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{0}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and divide \[0\] by \[3\], we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=\arccos \left( 0 \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( 0 \right)\] is \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Now find for the point at \[x=\dfrac{3}{2}\].
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[\dfrac{3}{2}\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{\dfrac{3}{2}}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and multiply the numerator by the reciprocal of the denominator.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{3}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Cancel the common factor of \[3\], we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)\]is \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
Now at last find the point at \[x=3\]
Replace the variable \[x\]with \[3\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 3 \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{3}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and divide \[3\] by \[3\], we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 3 \right)=\arccos \left( 1 \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( 1 \right)\]is \[0\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 3 \right)=0\]
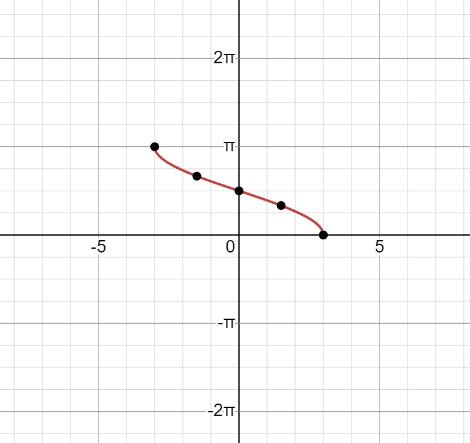
Now list all the points in a table and this trigonometric function can be graphed by plotting these points.
\[\begin{matrix}
x & f\left( x \right) \\
-3 & \pi \\
-\dfrac{3}{2} & \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \\
0 & \dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\dfrac{3}{2} & \dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
3 & 0 \\
\end{matrix}\]
The graph of the function \[f\left( x \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\] is as follows:
Note: Students generally make calculation mistakes while calculating the points that satisfy the graph. It's important to remember the trigonometric values and recheck the calculations once done.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation in the question is as follows
\[y=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\]
Consider the above equation as the function\[f\left( x \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\]
To find the points that satisfy this equation first consider the point at \[x=-3\]
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[-3\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -3 \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{-3}{3} \right)=\pi \]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -3 \right)=\pi \]
Now consider the point at \[x=\dfrac{-3}{2}\]
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[\dfrac{-3}{2}\]in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{2}}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and multiply the numerator by the reciprocal of the denominator.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( -\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Cancel the common factor of \[3\] to do this follow the following steps:
Move the leading negative in \[\dfrac{-3}{2}\]into the numerator.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{-3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( -\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Factor \[3\] out of \[-3\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{3\left( -1 \right)}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Cancel the common factor.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{{3}\cdot -1}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{{{3}}} \right)\]
Rewrite the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)\]
Move the negative in front of the fraction.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( -\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\] is \[\dfrac{2\pi }{3}\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}\]
After this consider the point at \[x=0\]
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[0\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{0}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and divide \[0\] by \[3\], we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=\arccos \left( 0 \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( 0 \right)\] is \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Now find for the point at \[x=\dfrac{3}{2}\].
Replace the variable \[x\] with \[\dfrac{3}{2}\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{\dfrac{3}{2}}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and multiply the numerator by the reciprocal of the denominator.
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{3}{2}\cdot \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\]
Cancel the common factor of \[3\], we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)\]is \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
Now at last find the point at \[x=3\]
Replace the variable \[x\]with \[3\] in the expression, we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 3 \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{3}{3} \right)\]
Simplify it further and divide \[3\] by \[3\], we get:
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 3 \right)=\arccos \left( 1 \right)\]
The exact value of \[\arccos \left( 1 \right)\]is \[0\].
\[\Rightarrow f\left( 3 \right)=0\]
Now list all the points in a table and this trigonometric function can be graphed by plotting these points.
\[\begin{matrix}
x & f\left( x \right) \\
-3 & \pi \\
-\dfrac{3}{2} & \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \\
0 & \dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\dfrac{3}{2} & \dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
3 & 0 \\
\end{matrix}\]
The graph of the function \[f\left( x \right)=\arccos \left( \dfrac{x}{3} \right)\] is as follows:

Note: Students generally make calculation mistakes while calculating the points that satisfy the graph. It's important to remember the trigonometric values and recheck the calculations once done.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




