
How do you graph \[y = 3{x^2} + 1\] and its inverse?
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: To find the graph of an equation, we have to first convert it to the standard form. The general equation of a parabola is of the form $ a{x^2} + bx + c $ , a parabola is defined as a curve in which every point is at a fixed distance from a fixed point and a fixed straight line. The fixed point is called the focus and the fixed straight line is called the directrix. After comparing the given equation with the standard form, we will find the coordinates of the vertex of the parabola and the coordinates of at least two points through which this parabola passes.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to graph \[y = 3{x^2} + 1\]
At $ x = 0,\,y = 3{(0)^2} + 1 = 1 $
So the vertex of the given parabola is at $ (0,1) $
The standard form of the parabolic equation is $ a{x^2} + bx + c $ , on comparing the given equation with the standard form, we get – $ a = 3,\,b = 0,\,c = 1 $ . Since $ a $ is positive, the graph opens upwards.
At $ x = 1,\,y = 3{(1)^2} + 1 = 4 $
At $ x = 2,\,y = 3{(2)^2} + 1 = 13 $
At $ x = - 1,\,y = 3{( - 1)^2} + 1 = 4 $
At $ x = - 2,\,y = 3{( - 2)^2} + 1 = 13 $
Using these points, we can plot the graph of $ y = 3{x^2} + 1 $ .
The inverse of this function can be found as follows –
$
y = 3{x^2} + 1 \\
\Rightarrow y - 1 = 3{x^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - \dfrac{{y - 1}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow x = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{y - 1}}{3}} \\
\Rightarrow {f^{ - 1}}(x) = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3}} \\
\Rightarrow y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3}} \;
$
At $ x = 1 $ , $ y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{1 - 1}}{3}} = 0 $
At $ x = 4 $ , $ y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{4 - 1}}{3}} = \pm 1 $
At $ x = 13 $ , $ y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{13 - 1}}{3}} = \pm 2 $
Using these points, we can plot the graph of \[y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3}} \]
This way we can graph $ y = 3{x^2} + 1 $ and its inverse as –
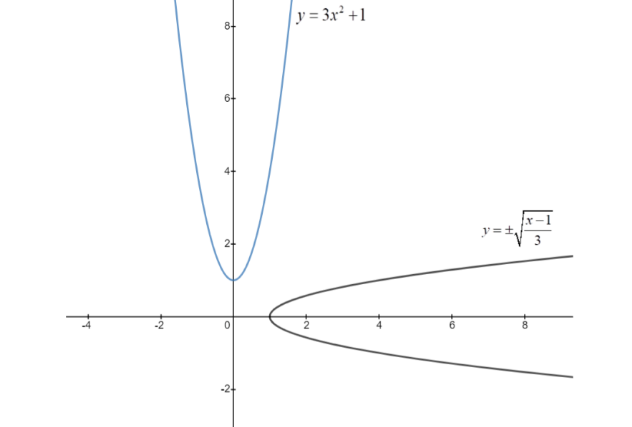
Note: To plot the graph of inverse of this function, we will simply reverse the values of the coordinates, that is, $ (1,4) $ lies on $ y = 3{x^2} + 1 $ then $ (4,1) $ lies on its inverse. To find the graph of a straight line, coordinates of two points lying on the straight line are enough but to find the graph of a curve, we need more coordinates to observe the pattern.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to graph \[y = 3{x^2} + 1\]
At $ x = 0,\,y = 3{(0)^2} + 1 = 1 $
So the vertex of the given parabola is at $ (0,1) $
The standard form of the parabolic equation is $ a{x^2} + bx + c $ , on comparing the given equation with the standard form, we get – $ a = 3,\,b = 0,\,c = 1 $ . Since $ a $ is positive, the graph opens upwards.
At $ x = 1,\,y = 3{(1)^2} + 1 = 4 $
At $ x = 2,\,y = 3{(2)^2} + 1 = 13 $
At $ x = - 1,\,y = 3{( - 1)^2} + 1 = 4 $
At $ x = - 2,\,y = 3{( - 2)^2} + 1 = 13 $
Using these points, we can plot the graph of $ y = 3{x^2} + 1 $ .
The inverse of this function can be found as follows –
$
y = 3{x^2} + 1 \\
\Rightarrow y - 1 = 3{x^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - \dfrac{{y - 1}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow x = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{y - 1}}{3}} \\
\Rightarrow {f^{ - 1}}(x) = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3}} \\
\Rightarrow y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3}} \;
$
At $ x = 1 $ , $ y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{1 - 1}}{3}} = 0 $
At $ x = 4 $ , $ y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{4 - 1}}{3}} = \pm 1 $
At $ x = 13 $ , $ y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{13 - 1}}{3}} = \pm 2 $
Using these points, we can plot the graph of \[y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{x - 1}}{3}} \]
This way we can graph $ y = 3{x^2} + 1 $ and its inverse as –

Note: To plot the graph of inverse of this function, we will simply reverse the values of the coordinates, that is, $ (1,4) $ lies on $ y = 3{x^2} + 1 $ then $ (4,1) $ lies on its inverse. To find the graph of a straight line, coordinates of two points lying on the straight line are enough but to find the graph of a curve, we need more coordinates to observe the pattern.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




