
How do you graph using the intercepts for\[6x-y=4\]?
Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint: In order to graph plot for the equation,\[6x-y=4\], we need the points to be plotted in the graph, however here, we need to draw using the intercepts , for this, we can find the two intercepts , \[x-\]and \[y-\]intercepts by putting \[x\]and \[y\]zero one by one and then simply plotting the intercepts.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Firstly let us write the equation, for which we need to plot the graph
\[6x-y=4\]
Let us find the \[x-\]and \[y-\]intercepts
Now, to find the\[x-\]intercept, put \[y=0\]in the equation
i.e.
\[
6x-y=4 \\
\Rightarrow 6x-0=4 \\
\Rightarrow 6x=4 \\
\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{6}=\dfrac{2}{3} \;
\]
Therefore, the \[x-\]intercept is \[\dfrac{2}{3}\]
Now, let us find the\[y-\]intercept
For this, let us put \[x=0\]in the equation
\[
6x-y=4 \\
\Rightarrow 6\left( 0 \right)-y=4 \\
\Rightarrow -y=4 \\
\Rightarrow y=-4 \;
\]
Thus, we get the \[y-\]intercept, which is \[-4\]
Therefore, we get the intercept points as
\[\left( \dfrac{2}{3},0 \right)\]and\[\left( 0,-4 \right)\]
Now, if we plot these two points in the graph, we get
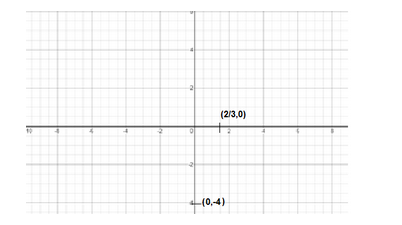
Now, this equation is for a straight line graph for which the intercepts have been drawn
If we join the two points, we get the graph as required
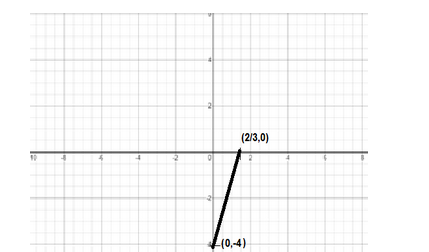
Hence, the graph is plotted.
Note: The formula used for the graph is for finding the intercepts. For finding \[x-\]intercept, first put \[y=0\]in the equation and in order to find the \[y-\]intercept, put \[x=0\], in this way the two points for the graph are found and then plotted to get a straight line graph.
Alternatively, this can also be solved by looking at the equation,
\[
6x-y=4 \\
y=6x-4 \;
\]
This equation is of the form \[y=mx+c\]
Where, \[m\]is the slope and \[c\]is the\[y-\] intercept,
And \[x-\]intercept is found in the same way as before.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Firstly let us write the equation, for which we need to plot the graph
\[6x-y=4\]
Let us find the \[x-\]and \[y-\]intercepts
Now, to find the\[x-\]intercept, put \[y=0\]in the equation
i.e.
\[
6x-y=4 \\
\Rightarrow 6x-0=4 \\
\Rightarrow 6x=4 \\
\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{6}=\dfrac{2}{3} \;
\]
Therefore, the \[x-\]intercept is \[\dfrac{2}{3}\]
Now, let us find the\[y-\]intercept
For this, let us put \[x=0\]in the equation
\[
6x-y=4 \\
\Rightarrow 6\left( 0 \right)-y=4 \\
\Rightarrow -y=4 \\
\Rightarrow y=-4 \;
\]
Thus, we get the \[y-\]intercept, which is \[-4\]
Therefore, we get the intercept points as
\[\left( \dfrac{2}{3},0 \right)\]and\[\left( 0,-4 \right)\]
Now, if we plot these two points in the graph, we get

Now, this equation is for a straight line graph for which the intercepts have been drawn
If we join the two points, we get the graph as required

Hence, the graph is plotted.
Note: The formula used for the graph is for finding the intercepts. For finding \[x-\]intercept, first put \[y=0\]in the equation and in order to find the \[y-\]intercept, put \[x=0\], in this way the two points for the graph are found and then plotted to get a straight line graph.
Alternatively, this can also be solved by looking at the equation,
\[
6x-y=4 \\
y=6x-4 \;
\]
This equation is of the form \[y=mx+c\]
Where, \[m\]is the slope and \[c\]is the\[y-\] intercept,
And \[x-\]intercept is found in the same way as before.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




