
How do you graph the parabola \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3\] using vertex, intercept and the additional points.
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: We are given \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3\] and we know that it is the second quadrant equation as it has square over x only, so it is a parabola. To sketch the graph of this, we will need the following terms: we find the vertex, y-intercept and x-intercept. Once we find them we will then locate their point on the graph, once they are located we will join the point and sketch the required graph. We will use the general equation \[y=a{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+k\] to compare so that we find the vertex (h, k).
Complete answer:
We are given an equation as \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3.\] We are asked to draw the graph of this solution. As we can see that, it is a quadratic equation in which x has the highest power of 2 while y is only linear. So our equation is a kind of parabola. As we have to plot this, we should know that to plot any parabola, we should simplify the equation and reduce it. We are given the equation as \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3.\] We will simplify and reduce it using completing the square method. As we have,
\[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3\]
Add and subtract 4, we get,
\[\Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-4x+4-4+3\]
So, we have,
\[\Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-2\times 2\times x+{{2}^{2}}-4+3\left[ \text{As }4={{2}^{2}}\text{ and }4x=2\times 2\times x \right]\]
Now as \[{{x}^{2}}-2\times 2\times x+{{2}^{2}}={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}\] so we get, \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
So, we get an equation \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3\] that becomes \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
Now, comparing this with \[y=a{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+k,\] we get h = 2, k = – 1 and a = 1. So, we get the vertex coordinate as (2, – 1).
Now, we find the y – intercept, the y – intercept is the point at which the graph cut y – axis. To find y intercept we put x = 0 in our equation \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\] So, putting x = 0, we get, \[y={{\left( 0-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
Simplifying, we get, y = 4 – 1. Therefore, y intercept is 3. So, the graph cut y – axis at 3. Now, we will find the x – intercept. For x – intercept we put y = 0 and solve for x. We have \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
Putting y = 0, we get,
\[0={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1\]
Simplifying, we get,
\[\Rightarrow 1={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}\]
Taking the square root on both the sides, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \pm \sqrt{1}=x-2\]
So, we get,
\[\Rightarrow x=2\pm 1\left[ \text{As }\sqrt{1}=1 \right]\]
So, x = 3 and x = 1.
So, x-intercepts at (3, 0) and (1, 0). Now we have y-intercept as (0, 3), x-intercept at (3, 0) and (1, 0) and vertex as (2, – 1). We put all these on the graph and then join the coordinate, once we join the graph formed is our required answer.
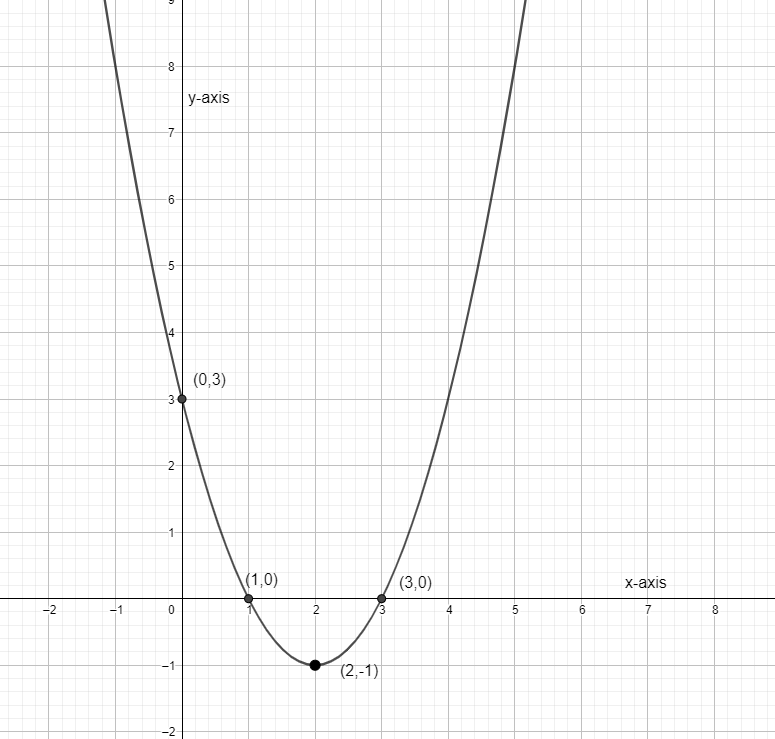
Note: Symmetric points are called the point which is equidistant from the axis of symmetry and lies on the x-axis, they are mostly calculated as the x-intercept. While simplifying the root also remember that, \[{{y}^{2}}=x\] will always give \[y=\pm \sqrt{x}\] the two possibilities as the answer.
Complete answer:
We are given an equation as \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3.\] We are asked to draw the graph of this solution. As we can see that, it is a quadratic equation in which x has the highest power of 2 while y is only linear. So our equation is a kind of parabola. As we have to plot this, we should know that to plot any parabola, we should simplify the equation and reduce it. We are given the equation as \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3.\] We will simplify and reduce it using completing the square method. As we have,
\[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3\]
Add and subtract 4, we get,
\[\Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-4x+4-4+3\]
So, we have,
\[\Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-2\times 2\times x+{{2}^{2}}-4+3\left[ \text{As }4={{2}^{2}}\text{ and }4x=2\times 2\times x \right]\]
Now as \[{{x}^{2}}-2\times 2\times x+{{2}^{2}}={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}\] so we get, \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
So, we get an equation \[y={{x}^{2}}-4x+3\] that becomes \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
Now, comparing this with \[y=a{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+k,\] we get h = 2, k = – 1 and a = 1. So, we get the vertex coordinate as (2, – 1).
Now, we find the y – intercept, the y – intercept is the point at which the graph cut y – axis. To find y intercept we put x = 0 in our equation \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\] So, putting x = 0, we get, \[y={{\left( 0-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
Simplifying, we get, y = 4 – 1. Therefore, y intercept is 3. So, the graph cut y – axis at 3. Now, we will find the x – intercept. For x – intercept we put y = 0 and solve for x. We have \[y={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1.\]
Putting y = 0, we get,
\[0={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-1\]
Simplifying, we get,
\[\Rightarrow 1={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}\]
Taking the square root on both the sides, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \pm \sqrt{1}=x-2\]
So, we get,
\[\Rightarrow x=2\pm 1\left[ \text{As }\sqrt{1}=1 \right]\]
So, x = 3 and x = 1.
So, x-intercepts at (3, 0) and (1, 0). Now we have y-intercept as (0, 3), x-intercept at (3, 0) and (1, 0) and vertex as (2, – 1). We put all these on the graph and then join the coordinate, once we join the graph formed is our required answer.

Note: Symmetric points are called the point which is equidistant from the axis of symmetry and lies on the x-axis, they are mostly calculated as the x-intercept. While simplifying the root also remember that, \[{{y}^{2}}=x\] will always give \[y=\pm \sqrt{x}\] the two possibilities as the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




