
How do you graph the parabola ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=-8\left( y-1 \right)$ using vertex, intercepts, and additional points?
Answer
536.7k+ views
Hint: To solve these types of questions, first write the given equation in the standard form and then by comparing the coefficients of both equations find the value of the vertex of the parabola and then plot the required points to get the graph of the parabola.
Complete step by step solution:
Given the equation: ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=-8\left( y-1 \right)$
First of all, write the given equation in the general form of a parabola, which can be given as,
$y=a{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+k$ .
So, rewriting the given equation in the general form of a parabola we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$ …$\left( i \right)$
The above equation has been obtained by taking the opening parenthesis on the right-hand side of the equation and then writing the equation in terms of $x$ .
Now on comparing the above equation and the general equation, we can see that $a=\dfrac{-1}{8}$ , $h=-2$ and $k=1$ .
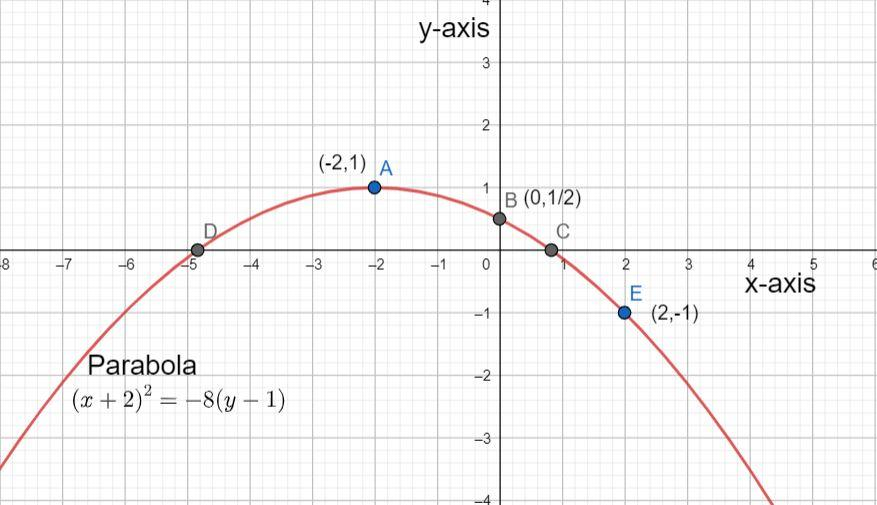
The vertex of the parabola is given by $\left( h,k \right)$ and therefore, the vertex of this parabola will be $\left( -2,1 \right)$ and will be point A in the graph.
Now, the $y$ - intercept can be defined as the value of $y$ coordinate when$x=0$ . So, to calculate the $y$ intercept substituting $x=0$ and solving for$y$ , we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( 0+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}\times 4+1$
Cancelling the required terms and simplifying, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{-1}{8}\times 4 \right)+1=\dfrac{-1}{2}+1$
On further simplification, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, we get the $y$ - intercept as $\left( 0,\dfrac{1}{2} \right)$ . To get the graph of the parabola, plot this point as well, which will be point B.
Similarly, we can also find the $x$ - intercept by taking the $y$ coordinate as zero this time. To find the $x$ - intercept we have to first convert the equation of the parabola from vertex to standard form.
To write the equation in the standard form, expand the expression ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}$ to ${{x}^{2}}+4x+4$ in the equation $y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$ .
Therefore, we get the following equation,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}\left( {{x}^{2}}+4x+4 \right)+1$
On further simplifying the above equation, by opening the parenthesis, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}\left( {{x}^{2}}+4x+4 \right)+1=\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{8}-\dfrac{4x}{8}-\dfrac{4}{8}+1$
Simplifying by cancelling terms with a common factor,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{8}-\dfrac{4x}{8}-\dfrac{4}{8}+1$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{8}-\dfrac{x}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}+1$
Arranging the terms and writing in the standard form by taking out common, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+x-1 \right)$
Now, calculate the value of $x$ - intercept by putting $y=0$ to get,
$\Rightarrow 0=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+x-1 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+x-1 \right)=0$
Simplify the above equation, to get,
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+4x-4=0$
By using the quadratic formula to solve the above equation, we get,
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
Substituting the values,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-4\times 1\times \left( -4 \right)}}{2\times 1}$
Simplifying to get,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{32}}{2\times 1}$
Prime factorization $32$ to get,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{2\times 2\times 2\times 2\times 2}}{2}$
Simplifying further by forming pairs and taking under root, we get,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm 4\sqrt{2}}{2}$
Therefore, the possible values of $x$ are: $x=\dfrac{-4+4\sqrt{2}}{2}$ and $x=\dfrac{-4-4\sqrt{2}}{2}$
Simplifying the values further,
$x=-2+2\sqrt{2}$ And $x=-2-2\sqrt{2}$ .
Therefore, the $x$ - intercepts are $\left( -2+2\sqrt{2},0 \right)$ and $\left( -2-2\sqrt{2},0 \right)$
Plot these points as well by taking their approximate values which will be represented by points C and D.
For additional point, take any value of $x$ and calculate the value of $y$ by substituting the value of $x$ in equation $\left( i \right)$ that is, $y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$.
Let$x=2$, then,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( 2+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+1$
Simplifying, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{-1}{8}\times 16 \right)+1=-2+1=-1$
Therefore, the additional point is $\left( 2,-1 \right)$and will be represented by point E . Plot this point as well to get the graph of the parabola as given below:
Note: These questions can become very lengthy while solving, so one must remember to mark the equations correctly and keep in mind all the values that have to be calculated. Also, keep checking if the calculations are correct by taking the correct signs and applying the correct formulae.
Complete step by step solution:
Given the equation: ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=-8\left( y-1 \right)$
First of all, write the given equation in the general form of a parabola, which can be given as,
$y=a{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+k$ .
So, rewriting the given equation in the general form of a parabola we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$ …$\left( i \right)$
The above equation has been obtained by taking the opening parenthesis on the right-hand side of the equation and then writing the equation in terms of $x$ .
Now on comparing the above equation and the general equation, we can see that $a=\dfrac{-1}{8}$ , $h=-2$ and $k=1$ .
The vertex of the parabola is given by $\left( h,k \right)$ and therefore, the vertex of this parabola will be $\left( -2,1 \right)$ and will be point A in the graph.
Now, the $y$ - intercept can be defined as the value of $y$ coordinate when$x=0$ . So, to calculate the $y$ intercept substituting $x=0$ and solving for$y$ , we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( 0+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}\times 4+1$
Cancelling the required terms and simplifying, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{-1}{8}\times 4 \right)+1=\dfrac{-1}{2}+1$
On further simplification, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, we get the $y$ - intercept as $\left( 0,\dfrac{1}{2} \right)$ . To get the graph of the parabola, plot this point as well, which will be point B.
Similarly, we can also find the $x$ - intercept by taking the $y$ coordinate as zero this time. To find the $x$ - intercept we have to first convert the equation of the parabola from vertex to standard form.
To write the equation in the standard form, expand the expression ${{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}$ to ${{x}^{2}}+4x+4$ in the equation $y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$ .
Therefore, we get the following equation,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}\left( {{x}^{2}}+4x+4 \right)+1$
On further simplifying the above equation, by opening the parenthesis, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}\left( {{x}^{2}}+4x+4 \right)+1=\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{8}-\dfrac{4x}{8}-\dfrac{4}{8}+1$
Simplifying by cancelling terms with a common factor,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{8}-\dfrac{4x}{8}-\dfrac{4}{8}+1$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{8}-\dfrac{x}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}+1$
Arranging the terms and writing in the standard form by taking out common, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+x-1 \right)$
Now, calculate the value of $x$ - intercept by putting $y=0$ to get,
$\Rightarrow 0=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+x-1 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+x-1 \right)=0$
Simplify the above equation, to get,
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+4x-4=0$
By using the quadratic formula to solve the above equation, we get,
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
Substituting the values,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-4\times 1\times \left( -4 \right)}}{2\times 1}$
Simplifying to get,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{32}}{2\times 1}$
Prime factorization $32$ to get,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{2\times 2\times 2\times 2\times 2}}{2}$
Simplifying further by forming pairs and taking under root, we get,
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4\pm 4\sqrt{2}}{2}$
Therefore, the possible values of $x$ are: $x=\dfrac{-4+4\sqrt{2}}{2}$ and $x=\dfrac{-4-4\sqrt{2}}{2}$
Simplifying the values further,
$x=-2+2\sqrt{2}$ And $x=-2-2\sqrt{2}$ .
Therefore, the $x$ - intercepts are $\left( -2+2\sqrt{2},0 \right)$ and $\left( -2-2\sqrt{2},0 \right)$
Plot these points as well by taking their approximate values which will be represented by points C and D.
For additional point, take any value of $x$ and calculate the value of $y$ by substituting the value of $x$ in equation $\left( i \right)$ that is, $y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$.
Let$x=2$, then,
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( 2+2 \right)}^{2}}+1$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-1}{8}{{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+1$
Simplifying, we get,
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{-1}{8}\times 16 \right)+1=-2+1=-1$
Therefore, the additional point is $\left( 2,-1 \right)$and will be represented by point E . Plot this point as well to get the graph of the parabola as given below:

Note: These questions can become very lengthy while solving, so one must remember to mark the equations correctly and keep in mind all the values that have to be calculated. Also, keep checking if the calculations are correct by taking the correct signs and applying the correct formulae.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




