
How do you graph $2x+3y=3$ using intercepts?
Answer
555.9k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we must have prior knowledge about intercepts of a straight-line and how they are represented in the equation of a line. We will find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the given equation of straight. Further, we will plot those on a graph and create the graph of the given function.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The x-intercept is the distance from origin of the point on the given function where the value of y is zero. This point logically lies on the x-axis and is given as $\left( a,0 \right)$ where $a$ is called the x-intercept.
The y-intercept is the distance from origin of the point on the given function where the value of x is zero. This point logically lies on the y-axis and is given as $\left( 0,b \right)$ where $b$ is called the y-intercept.
We are given the function, $2x+3y=3$.
In order to find the x-intercept, we will put $y=0$ and solve the equation accordingly. Hence, putting $y=0$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x+3\left( 0 \right)=3 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=3 \\
\end{align}$
Taking 2 on the right-hand side, we get
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}$
Therefore, the x-intercept is equal to $\dfrac{3}{2}.$
In order to find the y-intercept, we will put $x=0$ and solve the equation accordingly. Hence, putting $x=0$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\left( 0 \right)+3y=3 \\
& \Rightarrow 3y=3 \\
\end{align}$
Taking 3 on the right-hand side, we get
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{3}{3}$
$\Rightarrow y=1$
Therefore, the y-intercept is equal to $1.$
Hence, we get our two points as $\left( \dfrac{3}{2},0 \right)$ and $\left( 0,1 \right)$.
Therefore, we get our graph as:
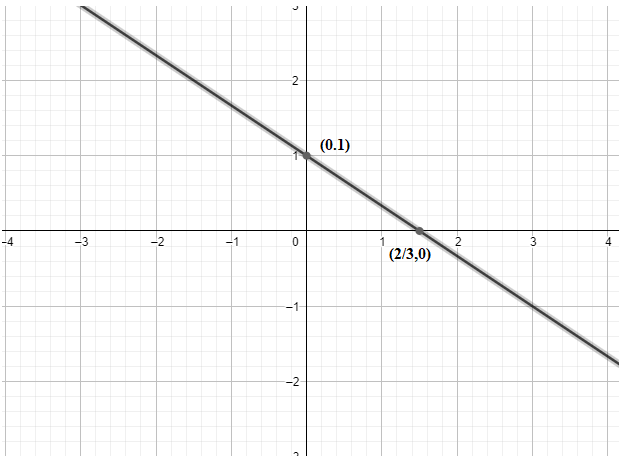
Note:
The equation of a straight line is expressed especially in an intercept form which is given as $\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1$ where $a$ is the x-intercept of line and $b$ is the y-intercept of the line as mentioned before. One essential feature of the intercept form of line is that its constant term is always equal to 1.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The x-intercept is the distance from origin of the point on the given function where the value of y is zero. This point logically lies on the x-axis and is given as $\left( a,0 \right)$ where $a$ is called the x-intercept.
The y-intercept is the distance from origin of the point on the given function where the value of x is zero. This point logically lies on the y-axis and is given as $\left( 0,b \right)$ where $b$ is called the y-intercept.
We are given the function, $2x+3y=3$.
In order to find the x-intercept, we will put $y=0$ and solve the equation accordingly. Hence, putting $y=0$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x+3\left( 0 \right)=3 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=3 \\
\end{align}$
Taking 2 on the right-hand side, we get
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}$
Therefore, the x-intercept is equal to $\dfrac{3}{2}.$
In order to find the y-intercept, we will put $x=0$ and solve the equation accordingly. Hence, putting $x=0$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\left( 0 \right)+3y=3 \\
& \Rightarrow 3y=3 \\
\end{align}$
Taking 3 on the right-hand side, we get
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{3}{3}$
$\Rightarrow y=1$
Therefore, the y-intercept is equal to $1.$
Hence, we get our two points as $\left( \dfrac{3}{2},0 \right)$ and $\left( 0,1 \right)$.
Therefore, we get our graph as:

Note:
The equation of a straight line is expressed especially in an intercept form which is given as $\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1$ where $a$ is the x-intercept of line and $b$ is the y-intercept of the line as mentioned before. One essential feature of the intercept form of line is that its constant term is always equal to 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




