
Gold number is the measure of:
[A] stability of colloidal system
[B] coagulating power of a colloid
[C] size of colloidal particles
[D] efficiency of the protective colloid
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: The term gold number is used in colloidal chemistry. It is generally used to explain the strength of lyophilic substances. It is different for every substance and it serves the purpose of protection.
Complete step by step answer:
Gold number is the amount of a protective colloid in milligrams required to prevent the coagulation of 10ml of a standard hydro gold sol when 1ml of 10% sodium chloride solution is added to it.
Coagulation of gold sol is indicated by the colour change from red to blue or purple when the size of particle increases.
Higher is the gold number, lower is the protective power of the lyophilic colloid as it means a higher amount of the colloid is required.
In simpler words, we can write that the gold number is the measure of the minimum amount of lyophilic protective coating on a lyophobic particle which will prevent the change of colour from red to purple.
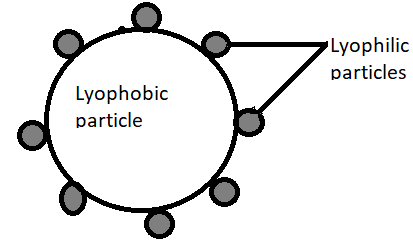
Lyophilic particles attached to the surface of the lyophobic particles as we can see in the above diagram.
Lyophilic particles are the protecting particles, which prohibits the colour changing phenomenon.
Example of lyophilic substances: gelatin, haemoglobin etc.
As it is clear from the above discussion, we can say that the gold number is a measure for the lyophilic substances, which are the protecting colloids.
Or we can say that it is the measure for the efficiency of protective colloids.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Gelatin is a commonly used protective colloid because its gold number is very low $\sim $0.005-0.1 mg/cL.
It is important here to know that gold number is a measure of efficiency of protective colloids and it is different for every substance. As the gold number increases, the requirement of amount of the colloid also increases. Therefore, particles with lower gold number are preferred.
Complete step by step answer:
Gold number is the amount of a protective colloid in milligrams required to prevent the coagulation of 10ml of a standard hydro gold sol when 1ml of 10% sodium chloride solution is added to it.
Coagulation of gold sol is indicated by the colour change from red to blue or purple when the size of particle increases.
Higher is the gold number, lower is the protective power of the lyophilic colloid as it means a higher amount of the colloid is required.
In simpler words, we can write that the gold number is the measure of the minimum amount of lyophilic protective coating on a lyophobic particle which will prevent the change of colour from red to purple.

Lyophilic particles attached to the surface of the lyophobic particles as we can see in the above diagram.
Lyophilic particles are the protecting particles, which prohibits the colour changing phenomenon.
Example of lyophilic substances: gelatin, haemoglobin etc.
As it is clear from the above discussion, we can say that the gold number is a measure for the lyophilic substances, which are the protecting colloids.
Or we can say that it is the measure for the efficiency of protective colloids.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Gelatin is a commonly used protective colloid because its gold number is very low $\sim $0.005-0.1 mg/cL.
It is important here to know that gold number is a measure of efficiency of protective colloids and it is different for every substance. As the gold number increases, the requirement of amount of the colloid also increases. Therefore, particles with lower gold number are preferred.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




