
Glycolate metabolism occurs in
(a) Lysosome
(b) Ribosomes
(c) Glyoxysomes
(d) Peroxisome
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: This is a small organelle present in the cytoplasm of most of the eukaryotic cells. These contain the reducing enzymes that oxidize certain molecules normally found in the cell.
Phosphoglycolate is transformed into glycolate which is transferred to peroxisomes. In the chloroplasts, glycolate biosynthesis occurs where glycolate is oxidized to glyoxylate with oxygen uptake by glycolate oxidase. With the help of glutamate i.e. glyoxylate aminotransferase, the glyoxylate is converted to glycine. All this happens within peroxisomes. Further metabolism of glycine does not occur here. The excess glyoxylate left in the peroxisomes can return to the chloroplasts so that it can be reduced to glycolate. It is or also oxidized to account for part of the carbon dioxide loss during photorespiration.
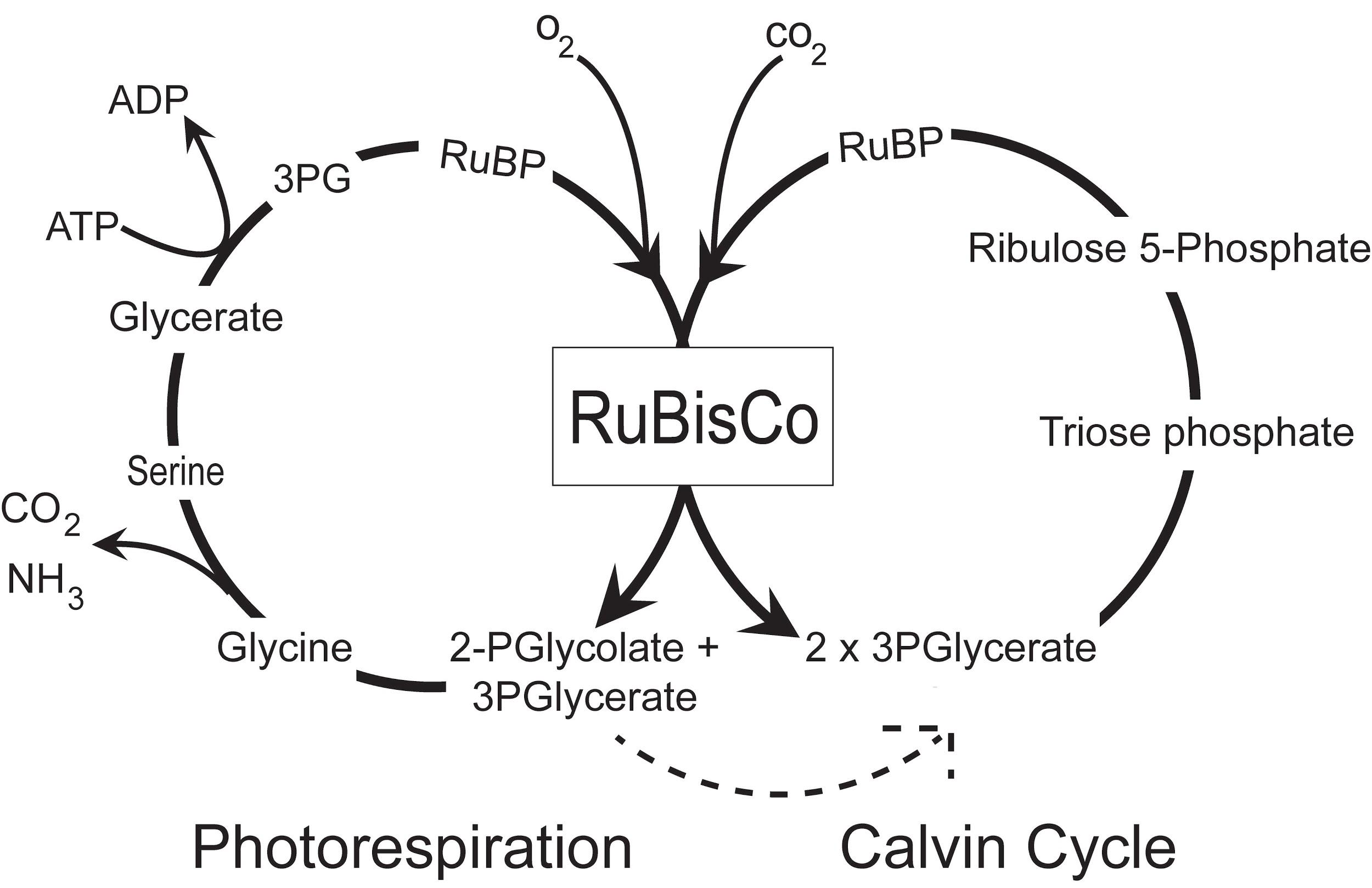
Peroxisomes oxidize certain molecules found in cells, especially the fatty acids and amino acids. The name for this comes from the basis of their reaction to produce hydrogen peroxide. But this hydrogen peroxide is toxic to the eukaryotic cells, so peroxisomes contain even catalase which gives water and oxygen from hydrogen peroxide. Thus providing a safe place for the oxidation metabolism of molecules. They also help in the biosynthesis of membrane lipids known as plasmalogens. In the cells of plants peroxisomes carry out additional functions and special types of peroxisomes have been identified in them.
So, the correct answer is 'Peroxisome'.
Note: In humans, plasmalogens are the primary ether lipids that have one or more ether linkages distinguishing them from other lipids present. The peroxisomes catalyze the synthesis of an ether precursor that undergoes further synthesis and results in a plasmalogen. Plasmalogen is associated with severe developmental conditions like rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, Zellweger syndrome, and reduced levels of plasmalogens that have been observed in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the brain.
Phosphoglycolate is transformed into glycolate which is transferred to peroxisomes. In the chloroplasts, glycolate biosynthesis occurs where glycolate is oxidized to glyoxylate with oxygen uptake by glycolate oxidase. With the help of glutamate i.e. glyoxylate aminotransferase, the glyoxylate is converted to glycine. All this happens within peroxisomes. Further metabolism of glycine does not occur here. The excess glyoxylate left in the peroxisomes can return to the chloroplasts so that it can be reduced to glycolate. It is or also oxidized to account for part of the carbon dioxide loss during photorespiration.

Peroxisomes oxidize certain molecules found in cells, especially the fatty acids and amino acids. The name for this comes from the basis of their reaction to produce hydrogen peroxide. But this hydrogen peroxide is toxic to the eukaryotic cells, so peroxisomes contain even catalase which gives water and oxygen from hydrogen peroxide. Thus providing a safe place for the oxidation metabolism of molecules. They also help in the biosynthesis of membrane lipids known as plasmalogens. In the cells of plants peroxisomes carry out additional functions and special types of peroxisomes have been identified in them.
So, the correct answer is 'Peroxisome'.
Note: In humans, plasmalogens are the primary ether lipids that have one or more ether linkages distinguishing them from other lipids present. The peroxisomes catalyze the synthesis of an ether precursor that undergoes further synthesis and results in a plasmalogen. Plasmalogen is associated with severe developmental conditions like rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, Zellweger syndrome, and reduced levels of plasmalogens that have been observed in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the brain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




