
Given,${{N}_{2}}$ gas will not be evolved upon the reaction of $HN{{O}_{2}}$ with which of the following amines?
(A)- ${{1}^{o}}$
(B)- ${{2}^{o}}$
(C)- ${{3}^{o}}$
(D)- Both B and C
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Primary (${{1}^{o}}$), secondary (${{2}^{o}}$) and tertiary (${{3}^{o}}$) amines, all react with nitrous acid ($HN{{O}_{2}}$) but in different ways. Alkane Diazonium salts are very unstable and decompose to give alcohols and release nitrogen (${{N}_{2}}$) gas. Diazonium salts are formed from primary amines only.
Complete answer:
Both aromatic and aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts at 273 -278 K temperature. Nitrous acid is quite unstable and thus it is generally formed immediately before its use in a reaction.
Reaction of aromatic primary amines with cold solution of nitrous acid to form arenediazonium salts is called diazotization. On increasing the temperature above 278 K, diazonium salts decompose with the evolution of ${{N}_{2}}$ gas to form phenols. The chemical reaction of aniline aromatic (${{1}^{o}}$ aromatic amine) with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ is given below:
\[NaN{{O}_{2}}+HCl\to HN{{O}_{2}}+NaCl\]
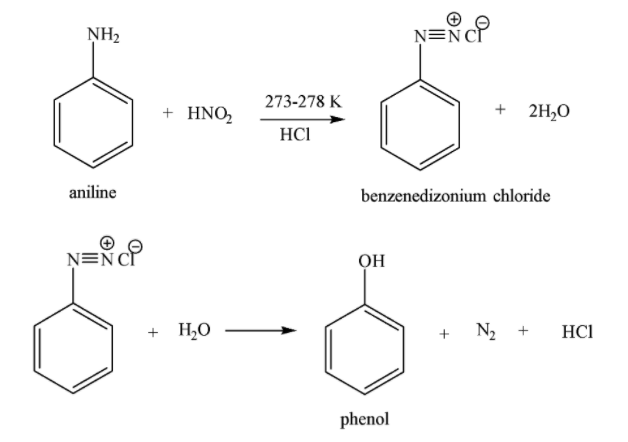
Similarly, aliphatic ${{1}^{o}}$ amines react with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ to form alkane diazonium salts which are unstable even at low temperature and thus decompose immediately to form alcohol and evolve ${{N}_{2}}$ gas.
\[R-N{{H}_{2}}+HN{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{273-278K}R-OH+{{N}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Secondary amines react with nitrous acid to form yellow coloured oily compounds called N-nitrosamines which are insoluble in mineral acids. Both aromatic and aliphatic ${{2}^{o}}$ amines form these oily compounds with $HN{{O}_{2}}$. Reaction of ${{2}^{o}}$ amine with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ is given below:
\[{{R}_{2}}NH+HN{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{273K}{{R}_{2}}N-NO+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Tertiary amines form ammonium salts with nitrous acid. Aromatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amines form nitroso ($-N=O$) substituted compounds whereas aliphatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amine form water soluble nitrite salts.
Aromatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amines:
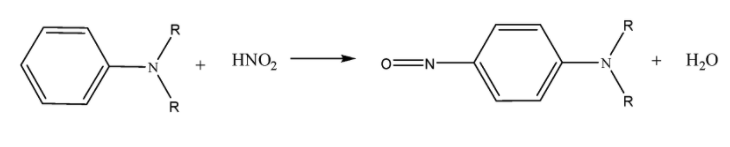
Aliphatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amines:
\[{{R}_{3}}N+HN{{O}_{2}}\to {{R}_{3}}N{{H}^{+}}NO_{2}^{-}\]
From the above discussion, it is clear that only primary (${{1}^{o}}$) amines evolve ${{N}_{2}}$ gas on reaction with $HN{{O}_{2}}$.
Since ${{N}_{2}}$ is not released upon the reaction of both ${{2}^{o}}$ and ${{3}^{o}}$ amines with $HN{{O}_{2}}$, therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Note that ${{1}^{o}}$ amines immediately evolve ${{N}_{2}}$ on reaction with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ whereas aromatic ${{1}^{o}}$ amines only release ${{N}_{2}}$ at a temperature higher than reaction temperature. Reaction of amines with nitrous acid is often used as a test to distinguish ${{1}^{o}}$, ${{2}^{o}}$ and ${{3}^{o}}$ amines. In some cases, it is even possible to distinguish aromatic amines from aliphatic amines using $HN{{O}_{2}}$.
Complete answer:
Both aromatic and aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts at 273 -278 K temperature. Nitrous acid is quite unstable and thus it is generally formed immediately before its use in a reaction.
Reaction of aromatic primary amines with cold solution of nitrous acid to form arenediazonium salts is called diazotization. On increasing the temperature above 278 K, diazonium salts decompose with the evolution of ${{N}_{2}}$ gas to form phenols. The chemical reaction of aniline aromatic (${{1}^{o}}$ aromatic amine) with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ is given below:
\[NaN{{O}_{2}}+HCl\to HN{{O}_{2}}+NaCl\]

Similarly, aliphatic ${{1}^{o}}$ amines react with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ to form alkane diazonium salts which are unstable even at low temperature and thus decompose immediately to form alcohol and evolve ${{N}_{2}}$ gas.
\[R-N{{H}_{2}}+HN{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{273-278K}R-OH+{{N}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Secondary amines react with nitrous acid to form yellow coloured oily compounds called N-nitrosamines which are insoluble in mineral acids. Both aromatic and aliphatic ${{2}^{o}}$ amines form these oily compounds with $HN{{O}_{2}}$. Reaction of ${{2}^{o}}$ amine with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ is given below:
\[{{R}_{2}}NH+HN{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{273K}{{R}_{2}}N-NO+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Tertiary amines form ammonium salts with nitrous acid. Aromatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amines form nitroso ($-N=O$) substituted compounds whereas aliphatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amine form water soluble nitrite salts.
Aromatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amines:

Aliphatic ${{3}^{o}}$ amines:
\[{{R}_{3}}N+HN{{O}_{2}}\to {{R}_{3}}N{{H}^{+}}NO_{2}^{-}\]
From the above discussion, it is clear that only primary (${{1}^{o}}$) amines evolve ${{N}_{2}}$ gas on reaction with $HN{{O}_{2}}$.
Since ${{N}_{2}}$ is not released upon the reaction of both ${{2}^{o}}$ and ${{3}^{o}}$ amines with $HN{{O}_{2}}$, therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Note that ${{1}^{o}}$ amines immediately evolve ${{N}_{2}}$ on reaction with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ whereas aromatic ${{1}^{o}}$ amines only release ${{N}_{2}}$ at a temperature higher than reaction temperature. Reaction of amines with nitrous acid is often used as a test to distinguish ${{1}^{o}}$, ${{2}^{o}}$ and ${{3}^{o}}$ amines. In some cases, it is even possible to distinguish aromatic amines from aliphatic amines using $HN{{O}_{2}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




