
Given the following sequence of reaction:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}I\xrightarrow{{NaCN}}A\xrightarrow[{Partial{\text{ }}hydrolysis}]{{O{H^ - }}}B\xrightarrow{{B{r_2}/NaOH}}C$
The major product C is:
(a)$C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}$
(b)$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - COON{H_4}$
(c)$C{H_3}C{H_2} - COON{H_4}$
(d)$C{H_3} - C{H_2}CO - NB{r_2}$
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint: To start this question, you can recall the concept of nucleophilic substitution reactions. nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which an electron pair donor (i.e. a nucleophile say ‘Y’:) reacts with an electron pair acceptor (i.e. a substrate, say ‘R-X’) and which substitutes for the ‘X’ group (i.e. a leaving group). Let us look at the following generalized equation for nucleophilic substitution:
$Y{:^ - } + R - X \to Y - R + :{X^ - }$
Here, R can be an alkyl or an aryl group.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Sodium cyanide is used to substitute cyanide ions into the given which it reacts with. It does a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Bromine in presence of sodium hydroxide is used in bromamide degradation synthesis.
Now, let us solve the given question in a step-wise manner:
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}I\] in the presence of \[NaCN\] would lead to the formation of \[C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\] via nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction would be as follows:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}I\xrightarrow{{NaCN}}C{H_3}C{H_2}CN$
Thus, the product A is \[C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\]
Now, we know that hydrolysis of nitriles lead to the production of amide (ethanamide in the present case) as depicted below:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\xrightarrow[{Partial{\text{ }}hydrolysis}]{{O{H^ - }}}C{H_3}C{H_2}CON{H_2}$
Thus, the product B is $C{H_3}C{H_2}CON{H_2}$
Now, ethanamide in the presence of \[B{r_2}/NaOH\]will lead to the formation of primary amine (with one less carbon atom) via hofmann rearrangement. The reaction is depicted below:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}CON{H_2}\xrightarrow{{B{r_2}/NaOH}}C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}$
The mechanism of this reaction is also demonstrated below:
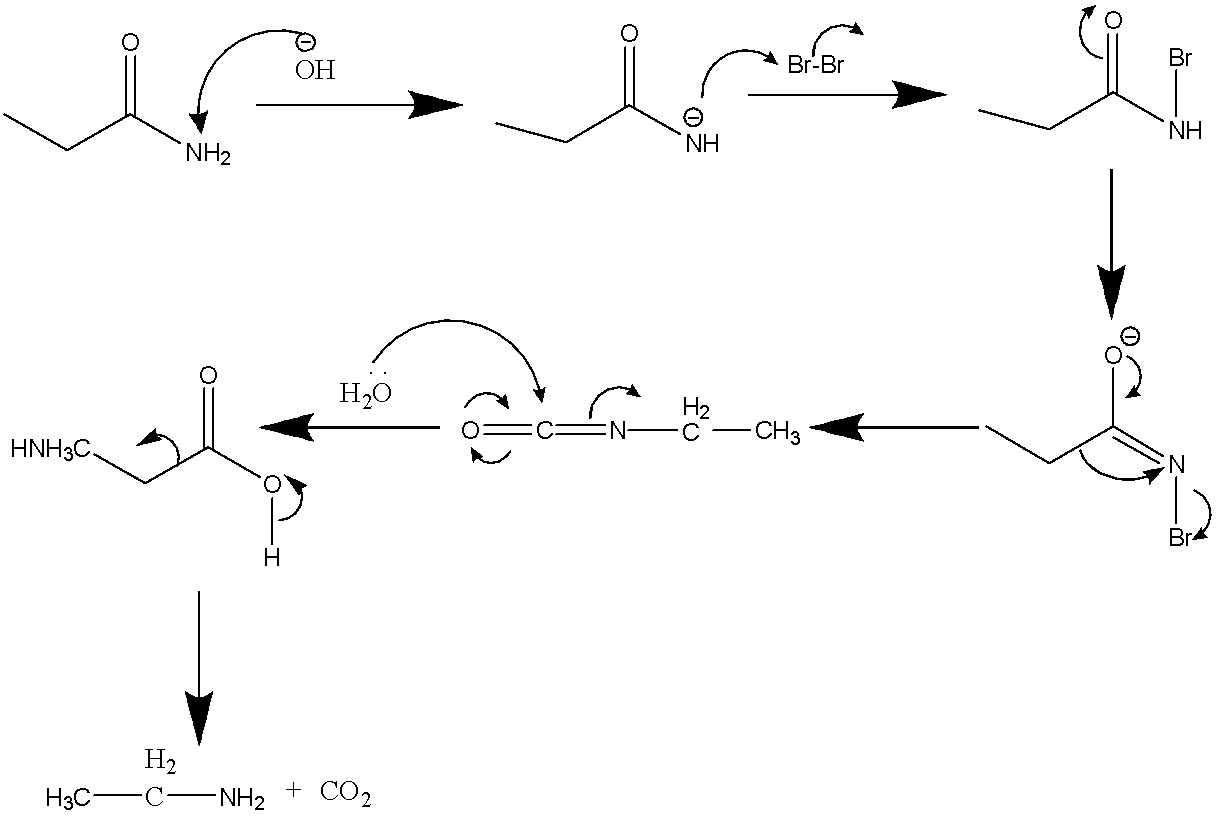
Therefore the major product C is ethyl amine that is $C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}$
The following reaction sequence would be followed:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}I\xrightarrow{{NaCN}}C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\xrightarrow[{Partial{\text{ }}hydrolysis}]{{O{H^ - }}}C{H_3}CON{H_2}\xrightarrow{{B{r_2}/NaOH}}C{H_3}N{H_2}$
So, the correct answer is Option a.
Note: Hofmann bromamide degradation is an important reaction for the preparation of amines. It is also used as a test for amines.
$Y{:^ - } + R - X \to Y - R + :{X^ - }$
Here, R can be an alkyl or an aryl group.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Sodium cyanide is used to substitute cyanide ions into the given which it reacts with. It does a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Bromine in presence of sodium hydroxide is used in bromamide degradation synthesis.
Now, let us solve the given question in a step-wise manner:
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}I\] in the presence of \[NaCN\] would lead to the formation of \[C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\] via nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction would be as follows:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}I\xrightarrow{{NaCN}}C{H_3}C{H_2}CN$
Thus, the product A is \[C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\]
Now, we know that hydrolysis of nitriles lead to the production of amide (ethanamide in the present case) as depicted below:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\xrightarrow[{Partial{\text{ }}hydrolysis}]{{O{H^ - }}}C{H_3}C{H_2}CON{H_2}$
Thus, the product B is $C{H_3}C{H_2}CON{H_2}$
Now, ethanamide in the presence of \[B{r_2}/NaOH\]will lead to the formation of primary amine (with one less carbon atom) via hofmann rearrangement. The reaction is depicted below:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}CON{H_2}\xrightarrow{{B{r_2}/NaOH}}C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}$
The mechanism of this reaction is also demonstrated below:

Therefore the major product C is ethyl amine that is $C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}$
The following reaction sequence would be followed:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}I\xrightarrow{{NaCN}}C{H_3}C{H_2}CN\xrightarrow[{Partial{\text{ }}hydrolysis}]{{O{H^ - }}}C{H_3}CON{H_2}\xrightarrow{{B{r_2}/NaOH}}C{H_3}N{H_2}$
So, the correct answer is Option a.
Note: Hofmann bromamide degradation is an important reaction for the preparation of amines. It is also used as a test for amines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




