
Given that P is a point on a wheel rolling on a horizontal ground. The radius of the wheel is R. Initially if the point P is in contact with the ground, the wheel rolls through half revolution. What is the displacement of point P?
\[
{\text{A}}{\text{. }}R\sqrt {{\pi ^2} + 1} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. }}R\sqrt {{\pi ^2} + 4} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. }}\pi R \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. 2}}\pi R \\
\]
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: First we need to draw a diagram which shows the wheel before and after the half revolution and the change in the position of point P. After the half revolution, point P will reach the top of the wheel and by analysing the diagram and known values, we can get the required answer.
Complete answer:
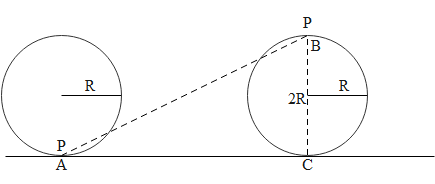
We are given a wheel which is rolling on a horizontal ground as shown in the figure. The radius of the wheel is R. The diagram shows that initially point P is in contact with the ground. Then the wheel rolls through half revolution and the right wheel in the diagram shows the wheel after this half revolution. This means that the wheel covers a distance which is equal to the half of the circumference of the given wheel. So the distance AC can be written as
\[AC = \pi R\]
The length BC is equal to the diameter of the wheel and is given as
$BC = 2R$
The displacement of point P will be equal to the length AB which can be calculated using the Pythagoras theorem in the following way.
$AB = \sqrt {A{C^2} + B{C^2}} $
Now inserting the known values, we get
$AB = \sqrt {{{\left( {\pi R} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2R} \right)}^2}} = R\sqrt {{\pi ^2} + 4} $
This is the required value of the displacement of the point P.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
It should be noted that displacement means the shortest distance between the initial and the final position of point P. If we talk about the distance travelled by point P then we will have to consider the half revolution which took P from A to B. The displacement is simply a straight line drawn between the initial and the final position.
Complete answer:

We are given a wheel which is rolling on a horizontal ground as shown in the figure. The radius of the wheel is R. The diagram shows that initially point P is in contact with the ground. Then the wheel rolls through half revolution and the right wheel in the diagram shows the wheel after this half revolution. This means that the wheel covers a distance which is equal to the half of the circumference of the given wheel. So the distance AC can be written as
\[AC = \pi R\]
The length BC is equal to the diameter of the wheel and is given as
$BC = 2R$
The displacement of point P will be equal to the length AB which can be calculated using the Pythagoras theorem in the following way.
$AB = \sqrt {A{C^2} + B{C^2}} $
Now inserting the known values, we get
$AB = \sqrt {{{\left( {\pi R} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2R} \right)}^2}} = R\sqrt {{\pi ^2} + 4} $
This is the required value of the displacement of the point P.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
It should be noted that displacement means the shortest distance between the initial and the final position of point P. If we talk about the distance travelled by point P then we will have to consider the half revolution which took P from A to B. The displacement is simply a straight line drawn between the initial and the final position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




