
Given right triangle ABC, with AB = 4 , BC = 3 and CA = 5. Circle, $\omega $ passes through $A$ and is tangent to $BC$ at $C$. What is the radius of $\omega $?
Answer
525k+ views
Hint: Here, a right angle triangle $ABC$ is given with $AB = 4$, $BC = 3$ and $CA = 5$. Also, a circle $\omega $ passes through $A$ and a tangent is drawn at $C$, perpendicular to $BC$.
The tangent to a circle is nothing but a line that touches the circle at a single point.
We are asked to calculate the radius of the circle.
First, we need to draw a graph representing the given information.
Formula to be used:
The formula to calculate the distance between two points to determine the radius is as follows.
\[r = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
Where $r$ is the radius of a circle.
The equation of a circle is as follows.
${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
Where $r$ is the radius of a circle and $(h,k)$ is the center of a circle.
Also, ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We shall represent the given information in a diagram as shown.
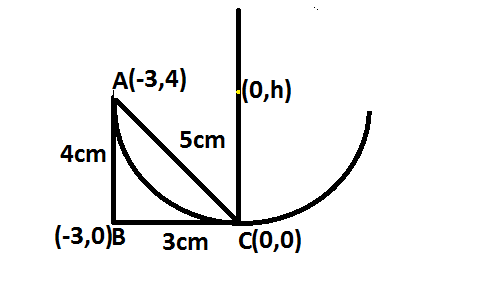
Here, we need to find the coordinates of A and B using the given information.
The distance between the points $\left( {0,0} \right)$ and $\left( {0,h} \right)$ is the radius of the circle.
Now, using the formula \[r = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \], we get,
\[r = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {h - 0} \right)}^2}} \]
\[r = \sqrt {{h^2}} \]
Hence, $r = h$ is the radius of the circle.
Here, $(h,k) = \left( {0,h} \right)$ is the center of the circle.
Now, we need to apply the formula.
The equation of a circle is as follows.
${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
Where $r$ is the radius of a circle and $(h,k)$ is the center of a circle.
Hence, we get,
${\left( {x - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - h} \right)^2} = {h^2}$ ……$\left( 1 \right)$
Here, the equation of a circle passes through a point $A\left( { - 3,4} \right)$.
Hence, the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ becomes,
${\left( { - 3 - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - h} \right)^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9 + {\left( {4 - h} \right)^2} = {h^2}$
Using the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$, we get
$9 + {4^2} - 2 \times 4 \times h + {h^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9 + 16 - 8h + {h^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 8h + {h^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 8h + {h^2} - {h^2} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 8h = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 25 = 8h$
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{25}}{8}$
Therefore, the radius of the circle $\omega $ is $\dfrac{{25}}{8}$.
Note: The tangent to a circle is nothing but a line that touches the circle at a single point and we know that radius is always perpendicular to the tangent at the touching point. We must be clear enough to represent the given information in a diagram so that we can solve the problem easily.
Hence, the radius of the circle $\omega $ is $\dfrac{{25}}{8}$ .
The tangent to a circle is nothing but a line that touches the circle at a single point.
We are asked to calculate the radius of the circle.
First, we need to draw a graph representing the given information.
Formula to be used:
The formula to calculate the distance between two points to determine the radius is as follows.
\[r = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
Where $r$ is the radius of a circle.
The equation of a circle is as follows.
${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
Where $r$ is the radius of a circle and $(h,k)$ is the center of a circle.
Also, ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We shall represent the given information in a diagram as shown.

Here, we need to find the coordinates of A and B using the given information.
The distance between the points $\left( {0,0} \right)$ and $\left( {0,h} \right)$ is the radius of the circle.
Now, using the formula \[r = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \], we get,
\[r = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {h - 0} \right)}^2}} \]
\[r = \sqrt {{h^2}} \]
Hence, $r = h$ is the radius of the circle.
Here, $(h,k) = \left( {0,h} \right)$ is the center of the circle.
Now, we need to apply the formula.
The equation of a circle is as follows.
${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
Where $r$ is the radius of a circle and $(h,k)$ is the center of a circle.
Hence, we get,
${\left( {x - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - h} \right)^2} = {h^2}$ ……$\left( 1 \right)$
Here, the equation of a circle passes through a point $A\left( { - 3,4} \right)$.
Hence, the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ becomes,
${\left( { - 3 - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - h} \right)^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9 + {\left( {4 - h} \right)^2} = {h^2}$
Using the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$, we get
$9 + {4^2} - 2 \times 4 \times h + {h^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9 + 16 - 8h + {h^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 8h + {h^2} = {h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 8h + {h^2} - {h^2} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 8h = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 25 = 8h$
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{25}}{8}$
Therefore, the radius of the circle $\omega $ is $\dfrac{{25}}{8}$.
Note: The tangent to a circle is nothing but a line that touches the circle at a single point and we know that radius is always perpendicular to the tangent at the touching point. We must be clear enough to represent the given information in a diagram so that we can solve the problem easily.
Hence, the radius of the circle $\omega $ is $\dfrac{{25}}{8}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




