
Given figures labelled by A and B represent
A B (1) Isogametes of Rhizopus Heterogametes of Fucus (2) Isogametes of Cladophora Heterogametes of Pinus (3) Isogametes of Rhizopus Heterogametes of angiosperms (4) Isogametes of Chara Heterogametes of Synchytrium
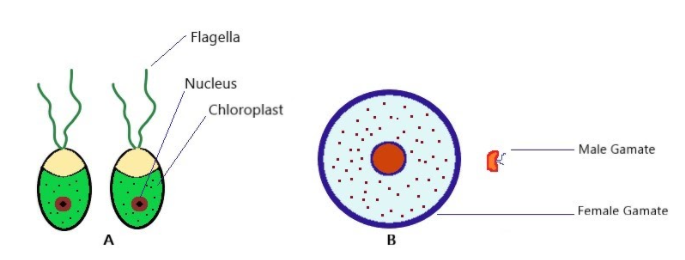
| A | B | |
| (1) | Isogametes of Rhizopus | Heterogametes of Fucus |
| (2) | Isogametes of Cladophora | Heterogametes of Pinus |
| (3) | Isogametes of Rhizopus | Heterogametes of angiosperms |
| (4) | Isogametes of Chara | Heterogametes of Synchytrium |

Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: Iso means similar. Therefore isogametes means gametes that are similar in size and form to the one that unites during the time of fertilization. No difference is seen in terms of size, sex or structure. Heterogametes do differ in size and form. Hence, they are morphologically dissimilar and so the male and female gametes can be distinguished.
Complete answer:
As the hint suggests, the isogametes are the same in appearance. So, the picture on the left is a depiction of isogamy whereas the picture on right is heterogametic.
1) Isogametes of Rhizopus and Heterogametes of Fucus- Rhizopus is a saprophytic fungus which can grow as filamentous branching hyphae. In oomycetes of Fucus, large non-motile female fuses with motile male gametes. This option is the most suitable one in terms of appearance and the definition as well.
2) Cladophora is reticulated filamentous green algae. In this, the sexual reproduction is isogamous. Pinus looks like a cone and they are the largest genus of conifers.
3) Angiosperms make up the majority of all plants on Earth. They are vascular plants. Their seeds can be found in a flower.
4) Chara is a freshwater green algae which can be found in submerged shallow water. Synchytrium is simple parasitic fungi. It is unicellular in nature.
Therefore option 1 is the most appropriate and correct option.
Note: Rhizopus are cosmopolitan in nature which can be commonly found in soil, decaying fruit and vegetables. Rhizopus has many different species. There are some morphological characteristics like the sporangia diameter, length of rhizoids, shape, size and texture which helps to differentiate each of its species.
Complete answer:
As the hint suggests, the isogametes are the same in appearance. So, the picture on the left is a depiction of isogamy whereas the picture on right is heterogametic.
1) Isogametes of Rhizopus and Heterogametes of Fucus- Rhizopus is a saprophytic fungus which can grow as filamentous branching hyphae. In oomycetes of Fucus, large non-motile female fuses with motile male gametes. This option is the most suitable one in terms of appearance and the definition as well.
2) Cladophora is reticulated filamentous green algae. In this, the sexual reproduction is isogamous. Pinus looks like a cone and they are the largest genus of conifers.
3) Angiosperms make up the majority of all plants on Earth. They are vascular plants. Their seeds can be found in a flower.
4) Chara is a freshwater green algae which can be found in submerged shallow water. Synchytrium is simple parasitic fungi. It is unicellular in nature.
Therefore option 1 is the most appropriate and correct option.
Note: Rhizopus are cosmopolitan in nature which can be commonly found in soil, decaying fruit and vegetables. Rhizopus has many different species. There are some morphological characteristics like the sporangia diameter, length of rhizoids, shape, size and texture which helps to differentiate each of its species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




