
Given conversion can be carried out by:
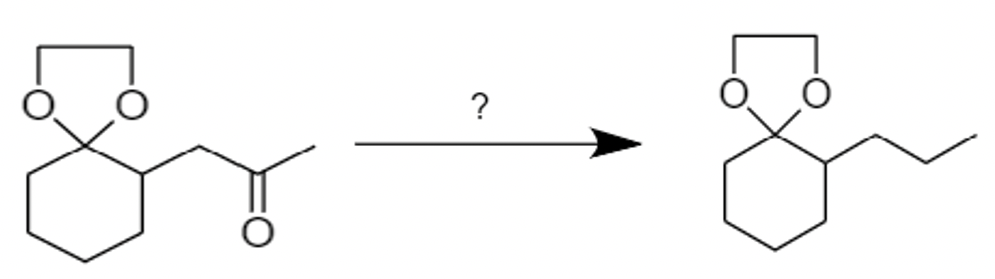
a.) Clemmensen reduction
b.) Wolff-Kishner reduction
c.) \[LiAl{{H}_{4}}\]
d.) \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\]

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Acetal group is acid sensitive group but not a base-sensitive group. For conversion of carbonyl groups into methyl groups and reduction of ketones, Wolff-Kishner reduction method is used.
Complete step by step answer:
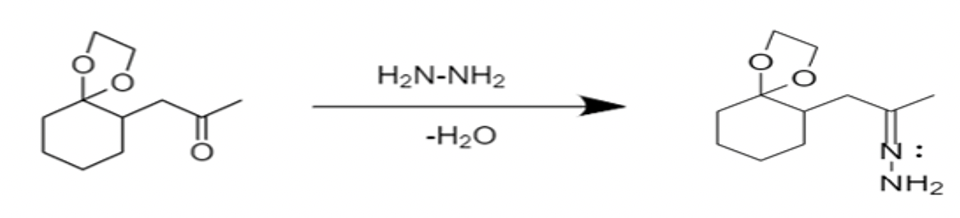
- The Wolff Kishner reduction of ketones utilizes \[N{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}\], known as hydrazine, as a reducing agent. Reaction takes place in the presence of a strong base, \[KOH\].

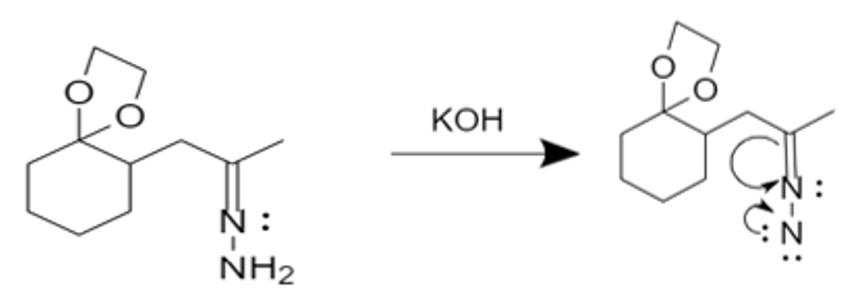
- The first step of mechanism is carried out by deprotonation of hydrazone in presence of strong acid, \[KOH\]. This is a rate limiting step.
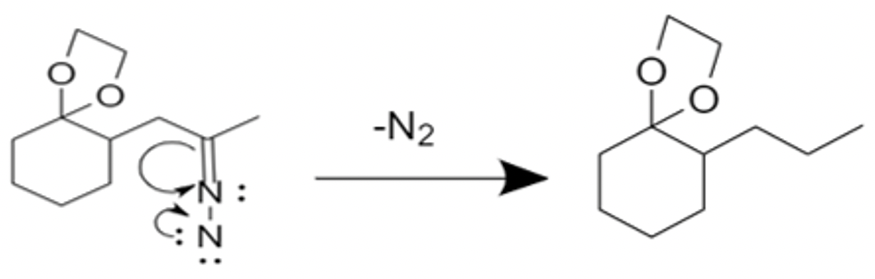
-The second step is the protonation of carbon. This step leaves us with a nitrogen-nitrogen double bond. This double bond is deprotonated by base and decomposes to give a carbanion and nitrogen gas.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional information: The Clemmensen Reduction allows the deoxygenation of aldehydes or ketones, to produce the corresponding hydrocarbon where the substrate must be stable to strong acid. Moreover, the Clemmensen Reduction is complementary to the Wolff-Kishner Reduction. It runs under strongly basic conditions.
Note: Wolff Kishner reduction is a method of reducing aldehydes and ketones to alkanes. Condensation of the carbonyl compound with hydrazine forms the hydrazone, and treatment with base induces the reduction of the carbon coupled with oxidation of the hydrazine to gaseous nitrogen, to yield the corresponding alkane.
Complete step by step answer:
- The Wolff Kishner reduction of ketones utilizes \[N{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}\], known as hydrazine, as a reducing agent. Reaction takes place in the presence of a strong base, \[KOH\].

- The first step of mechanism is carried out by deprotonation of hydrazone in presence of strong acid, \[KOH\]. This is a rate limiting step.

-The second step is the protonation of carbon. This step leaves us with a nitrogen-nitrogen double bond. This double bond is deprotonated by base and decomposes to give a carbanion and nitrogen gas.


So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional information: The Clemmensen Reduction allows the deoxygenation of aldehydes or ketones, to produce the corresponding hydrocarbon where the substrate must be stable to strong acid. Moreover, the Clemmensen Reduction is complementary to the Wolff-Kishner Reduction. It runs under strongly basic conditions.
Note: Wolff Kishner reduction is a method of reducing aldehydes and ketones to alkanes. Condensation of the carbonyl compound with hydrazine forms the hydrazone, and treatment with base induces the reduction of the carbon coupled with oxidation of the hydrazine to gaseous nitrogen, to yield the corresponding alkane.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




