
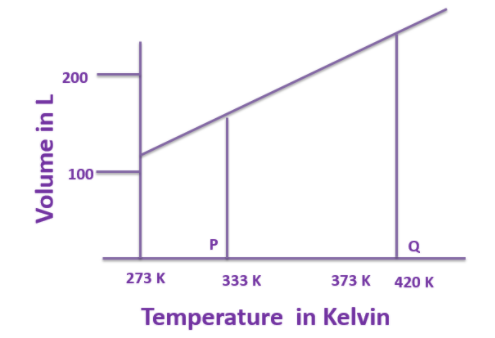
Given below is the part of a graph.
a)Which gas law is related to this graph?
b)Convert the values of temperature at ‘P’ and ‘Q’ given in Kelvin scale (K) to degree Celsius scale (O0C becomes double?

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint:The gases which follow the ideal gas equation, $PV = nRT$ are known as the ideal gases they follow the ideal gas equation at all the conditions of temperature and pressure. The gases which do not follow the ideal gas equation at all ranges of temperature and pressure are known as Real gases.
Complete step by step answer:
Certain laws are given by the different Scientists in order to determine the nature of the gases and the changes they undergo on the change in any one of the physical parameters such as temperature and pressure.
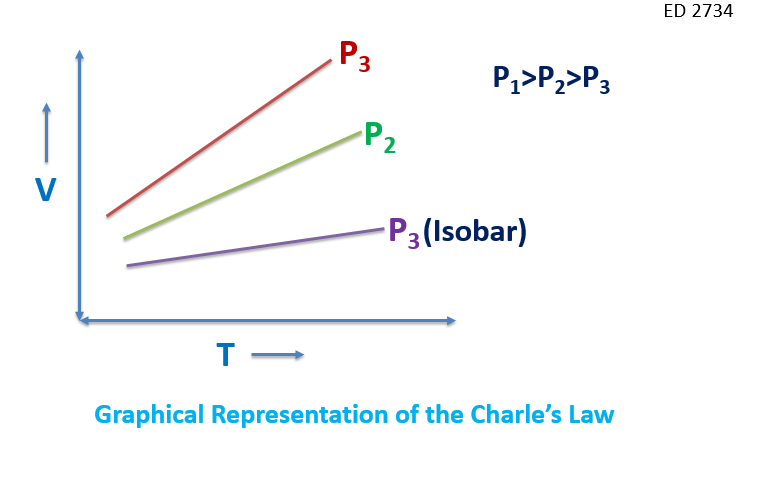
a)The graph given here resembles the graph of Charle's law. Since it is the graph between the Volume and temperature keeping the pressure constant. The Charles law was given in 1780 by Jacques Charles and it states that: “The volume of the gas (ideal gas) is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas, keeping the pressure constant.” The mathematical statement of the law :
b)The temperatures given at point P and Q are 333 K and 420 K , in order to convert the temperature from Kelvin to the Celsius scale the following relationship can be used: $Temperature{(^0}C) = Temperature(K) - 273$
Thus the temperatures can be converted as:
1.At point P: The temperature is 333K
$
Temperature {(^0}C) = Temperature(K) - 273 \\
= 333 - 273 \\
= {60^0}C \\
$
Similarly the temperature at point Q can also be calculated:
2.At point Q: The temperature is 420K
$
Temperature {(^0}C) = Temperature(K) - 273 \\
= 420 - 273 \\
= {47^0}C \\ $
Note:
The Charle’s law has wide applications, some of its applications in the day to day life include in the cold weathers the helium balloons shrink and the capacity of the lungs decreases during winters and thus in turn the jogging becomes difficult in the winters.
Complete step by step answer:
Certain laws are given by the different Scientists in order to determine the nature of the gases and the changes they undergo on the change in any one of the physical parameters such as temperature and pressure.
a)The graph given here resembles the graph of Charle's law. Since it is the graph between the Volume and temperature keeping the pressure constant. The Charles law was given in 1780 by Jacques Charles and it states that: “The volume of the gas (ideal gas) is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas, keeping the pressure constant.” The mathematical statement of the law :
$V\infty T$
Where V= Volume and T is the Temperature.
b)The temperatures given at point P and Q are 333 K and 420 K , in order to convert the temperature from Kelvin to the Celsius scale the following relationship can be used: $Temperature{(^0}C) = Temperature(K) - 273$

Thus the temperatures can be converted as:
1.At point P: The temperature is 333K
$
Temperature {(^0}C) = Temperature(K) - 273 \\
= 333 - 273 \\
= {60^0}C \\
$
Similarly the temperature at point Q can also be calculated:
2.At point Q: The temperature is 420K
$
Temperature {(^0}C) = Temperature(K) - 273 \\
= 420 - 273 \\
= {47^0}C \\ $
Note:
The Charle’s law has wide applications, some of its applications in the day to day life include in the cold weathers the helium balloons shrink and the capacity of the lungs decreases during winters and thus in turn the jogging becomes difficult in the winters.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




